Summary
Ebastine is a new second generation histamine H1 receptor antagonist that has shown clinical efficacy in the treatment of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria after once-daily administration. This double-blind multi-centre randomised placebo-controlled study has investigated the long term efficacy of ebastine 10mg once daily in the treatment of chronic urticaria compared with that of terfenadine 60mg twice daily.
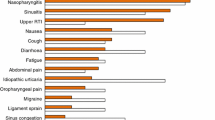
At the end of a 3-month treatment period, ebastine was significantly superior to placebo in improving symptoms of chronic urticaria (including severity of itching, number of wheals per day), and its efficacy was similar to that of terfenadine. In a global assessment of efficacy, investigators considered chronic urticaria to have improved in 73% of ebastine recipients compared with 68% and 52% of patients treated with terfenadine or placebo, respectively. The patients’ assessments of efficacy were similar to those of the investigators.
Ebastine was well tolerated, the incidence and nature of adverse events with this agent being similar to those reported in patients treated with terfenadine or placebo. The most common adverse events were headache and dry mouth.
Thus, these results, which show ebastine to be an effective and well tolerated agent, indicate that the drug should be considered for the first-line therapy of chronic urticaria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Referenc
Wiseman LR, Faulds D. Ebastine: a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in the treatment of allergic disorders. Drugs 1996; 51 (2): 260–77.
Peyri J, Vidal J, Marrón J, et al. Ebastine in chronic urticaria: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Dermatol Treat 1991; 2: 51–3.
Kukita A, Harada S, Yoshida H, et al. Early phase II study of LAS-90 on chronic urticaria [in Japanesel. Rinsho Iyaku 1994; 10 Suppl. 1: 43–53.
Kukita A, Harada S, Yoshida H, et al. Late phase II study of LAS-90 on chronic urticaria: optimal dose finding study by double-blind technique [in Japanese]. Rinsho Iyaku 1994; 10 Suppl. 1: 55–72.
Kukita A, Harada S, Yoshida H, et al. Phase III study of LAS-90 on chronic urticaria: double blind comparative study with ketotifen fumarate [in Japanese]. Rinsho Iyaku 1994; 10 (4): 895–912.
Haria M, Fitton A, Peters DH. Loratadine: a reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in allergic disorders. Drugs 1994; 48 (4): 617–37.
Spencer CM, Faulds D, Peters DH. Cetirizine: a reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in selected allergic disorders. Drugs 1993; 46 (6): 1055–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalis, B. Double-Blind Multicentre Comparative Study of Ebastine, Terfenadine and Placebo in the Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria in Adults. Drugs 52 (Suppl 1), 30–34 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199600521-00008
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199600521-00008