Summary
396 adult and adolescent patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis participated in this randomised double-blind parallel-group study in which the efficacy and tolerability of ebastine 10 or 20mg administered once daily in the morning or evening for 3 weeks were compared with those of placebo. Clinical efficacy was assessed by measuring improvement in rhinitis symptoms (nasal discharge, nasal stuffiness, sneezing, itchy nose and itchy/watery eyes) recorded by patients twice daily on diary cards.
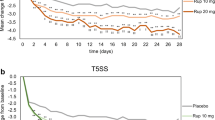
The improvement in individual and total symptom scores at the end of the 3-week treatment period in patients treated with ebastine 10mg in the morning or ebastine 20mg in the morning or evening was significantly greater than the improvement in placebo recipients. The 20mg dose of ebastine administered in the morning was associated with the greatest improvement in symptom scores. There was no significant effect with the 10mg evening dose compared with placebo.
Ebastine was well tolerated by the majority of patients — the incidence of adverse events, including headache, dry mouth, somnolence and asthenia being similar to that reported in placebo recipients. Electrocardiograms showed no evidence of any clinically relevant changes in QTc intervals.
In a subsequent nonblinded 4-month study that included 230 patients from the initial study, global evaluations at monthly intervals showed overall symptom improvement in ≥ 72% of patients who received ebastine 10mg or 20mg once daily. The drug was well tolerated during prolonged therapy, with adverse events being similar in nature and incidence to those reported in the 3-week double-blind study.
In conclusion, ebastine 10mg once daily in the morning is an appropriate starting dose for the treatment of rhinitis, and this can be increased to 20mg as required.
Similar content being viewed by others
Referenc
Philip G, Togias AG. Allergic rhinitis: today’s approach to treatment. J Respir Dis 1995; 16 (4): 367–72.
International consensus report on the diagnosis and management of rhinitis. Allergy 1994; 49 Suppl. 19: 5–34.
Middleton E, Reed CE, Ellis ES, et al. editors. Allergy: principles and practice. 4th ed. St Louis: C.V. Mosby, 1993.
Vallés CP, Garcia AC, Bahima AC, et al. Ebastine in perennial rhinitis. Ann Allergy 1991; 67: 615–8.
Ankier SI, Warrington SJ. A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and tolerability of ebastine against hay fever in general practice patients. J Intern Med 1989; 226: 453–8.
Aaronson DW. Comparative efficacy of H1 antihistamines. Ann Allergy 1991; 67 (5): 541–7.
Meltzer EO. Comparative safety of antihistamines. Ann Allergy 1991; 67 (6): 625–33.
Wiseman LR, Faulds D. Ebastine: a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in the treatment of allergic disorders. Drugs 1996; 51 (2): 260–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storms, W.W. Clinical Studies of the Efficacy and Tolerability of Ebastine 10 or 20mg Once Daily in the Treatment of Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis in the US. Drugs 52 (Suppl 1), 20–25 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199600521-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199600521-00006