Summary
The impact of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) pandemic has made tuberculosis an increasing worldwide problem, and the effectiveness of modern chemotherapy has been blunted by the high incidence of primary drug resistance, especially in developing countries. The prospect of finding new and highly effective drugs similar to isoniazid or rifampicin is dim, yet the maximum benefits from the existing drugs which are highly effective have not been received.
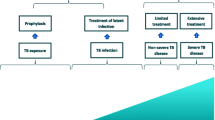
A 6-month regimen of isoniazid plus rifampicin, supplemented by pyrazinamide during the first 2 months, for treatment of uncomplicated tuberculosis is highly effective and the regimen of choice. Ethambutol should be added if the risk of isoniazid resistance is increased. A regimen of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and streptomycin for 4 months provides effective defence against smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis.
Re-treatment of multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis remains a difficult therapeutic problem. At least 3 drugs that the patient has never previously received, and that are effective according to laboratory susceptibility testing, must be used.
Preventive therapy against tuberculosis is accomplished with isoniazid for 6 to 12 months, although rifampicin plus isoniazid for 3 months has been used in the United Kingdom with success. In a mouse model, rifampicin plus pyrazinamide for 2 months is more effective than isoniazid for 6 months as preventive treatment.
Patient noncompliance with medication remains the biggest problem in tuberculosis control, and is a complex issue. It can only be resolved by multiple approaches. Intermittent directly observed short course chemotherapy is a major, but not the only, possible solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acocella G. Human bioavailability studies. Bulletin of the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 64(1): 38, 1989
Acocella G, Conti R. Interaction of rifampin with other drugs. Tubercle 61: 171–177, 1980
Allen BW, Mitchison DA. Amikacin in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle 64: 111–118, 1983
American Hospital Formulary Service. Antituberculosis agents. In McElby (Ed.) Drug Information1990, pp. 335–353, American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Bethesda, 1990
American Thoracic Society and Centers for Diseases Control. Treatment of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in adults and children. American Review of Respiratory Disease 134: 355–363, 1986
American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control. Mycobacteriosis and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. American Review of Respiratory Disease 136: 492–496, 1987
Aviali V, Berti M, Carniti G, Randisi E, Rossi E, et al. Antibacterial activity of DL 473, a new synthetic rifamycin derivative. Journal of Antibiotics 38(8): 1026–1032, 1981
Barnes PF, Bloch AB, Davidson PT, Snider DE. Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. New England Journal of Medicine 364: 1644–1650, 1991
Barry VC, Conalty M. Antituberculosis activity in the phenazine series. American Review of Tuberculosis 78: 62–73, 1958
Broadwell III RO, Broadwell S, Comer PB. Suicide by rifampin overdose. Journal of the American Medical Association 240: 2283–2284, 1978
Canetti G, Kreis B, Thibier R, Grosset J, Gluszy KJ. Donnée actuelle sur la resistance primaire de la tuberculose pulmonaire de l’adulte en France: deuxième enquête du centre d’étude sur la resistance primaire. Années 1965–1967. Revue de la Tuberculose et de Pneumologie 31: 433–474, 1967
Carpenter JL, Covelli HD, Avant ME, McAllister CK, Higbee JW, et al. Drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosisin Korean isolates. American Review of Respiratory Disease 126: 1092–1095, 1982
Casal M, Guitierrez J, Gonzalez J, Ruiz P. In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosisto a new macrolide antibiotic, R 28965. Tubercle 68: 141–143, 1987
Casal M, Rodriguez F, Benavente M, Luna M. In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium fortuitum, and Mycobacterium cheloneito augmentin. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 5: 453–454, 1986
Centers for Disease Control, Tuberculosis and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome New York city. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Report 36(48): 786–795, 1987
Chadwick M, Nicholson G, Gaya H. Brief report: combination chemotherapy with ciprofloxacin for infection with M. tuberculosisin mouse model. American Journal of Medicine 87 (Suppl. 5a): 355–365, 1989
Chaisson RE, Schecter GF, Theuer CP, Rutherford GW, Echenberg DF, et al. Tuberculosis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. American Review of Respiratory Disease 136: 570–574, 1987
Chiu J, Nussbaum J, Bozzette S, Tiles JG, Young LS, et al. Treatment of dissiminated M. aviumcomplex infection in AIDS with amikacin, ethambutol, rifampin and ciprofloxacin. Annals of Internal Medicine 113: 358–361, 1990
Combs DL, O’Brien RJ, Geter LJ. USPHS tuberculosis short course chemotherapy trial 21: effectiveness, toxicity and acceptability. The report of final results. Annals of Internal Medicine 112: 397–406, 1990
Crowle AJ, Sbarbaro JA, Judson FN, May MH. The effect of ethambutol on tubercle bacilli in culture of human macrophages. American Review of Respiratory Disease 132: 742–745, 1985
Crowle AJ, Sbarbaro JA, May MH. Inhibition by pyrazinamide of tubercle bacilli within cultured human macrophages. American Review of Respiratory Disease 134: 1052–1055, 1986
Dautzenberg B, Truffot C, Legris S, Meyohas MC, Berlie HC, et al. Activity of clarithromycin against Mycobacterium aviuminfection in patients with the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. American Review of Respiratory Disease 144: 564–569, 1991
Davidson PT, Goble M, Lester W. The antituberculosis efficacy of rifampin in 136 patients. Chest 61: 574–578, 1972
Dickinson JM, Mitchison DA. In vitro properties of rifapentine (MDL 473) relevant to its use in intermittent chemotherapy of tuberculosis. Tubercle 68: 113–118, 1987
Duncanson FP, Hewlett Jr D, Mayan S, Estepan H, Perla EN, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosisinfection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a review of 14 patients. Tubercle 67: 295–302, 1986
Ellard GA, Ellard DR, Allen BW, Girling DJ, Nunn AJ, et al. The bioavailability of isoniazid, rifamycin, and pyrazinamide in two commercially available combined formulations designed for use in the short course treatment of tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 133: 1076–1080, 1986
Ferguson GC, Nunn AJ, Fox W. A second international cooperative investigation into thiacetazone side effects: rashes on two thiacetazone containing regimens. Tubercle 52: 166, 1971
Forgan-Smith R, Ellard GA, Newton D, Mitchison DA. Pyrazinamide and other drugs in tuberculous meningitis. Lancet 2: 374, 1973
Fox W. Whither short course chemotherapy? British Journal of Diseases of the Chest 75: 331–357, 1981
Fox W. Drug combinations and the bioavailability of rifampicin. Tubercle 71: 241–245, 1990
Gangadharam PRJ. Drug resistance in mycobacteria, p. 149, CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, 1984
Gangadharam PRJ, Pratt PF, Perumal VK, Iseman MD. The effect of exposure time, drug concentration and temperature on the activity of ethambutol versus mycobacterium tuberculosis.American Review of Respiratory Diseases 141: 1478–1482, 1990
Gay DJ, De Young DR, Roberts GD. In vitro activities of nor-floxacin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. aviumcomplex, M. chelonei, M. fortuitumand M. kansasii.Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 21(1): 94–96, 1984
Girling DJ. The hepatic toxicity of antituberculosis regimens containing isoniazid, rifamycin, and pyrazinamide. Tubercle 59: 12–32, 1978
Girling DJ. Hepatitis and other adverse reaction to antituberculosis chemotherapy in perspective. Bulletin of the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 55: 8–12, 1980
Girling DJ. Adverse effects of antituberculosis drugs. Drugs 23: 56–74, 1982
Goodman LS, Gilman A. The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th ed., MacMillan Publishing Co., New York, 1975
Grosset J. Bactériologic basis of short course chemotherapy for tuberculosis. Clinics in Chest Medicine 1: 231–241, 1980
Heifets LB, Iseman MD, Cook JL, Lindholm-Levy PJ, Drupa I. Determination of in vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to cephalosporins by radiometric and conventional methods. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 27: 11–15, 1985
Heifets LB, Lindholm-Levy PJ. Bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal activity of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosisand Mycobacterium aviumcomplex. Tubercle 68: 267–276, 1987
Hong Kong Chest Service/Tuberculosis Research Centre. A controlled trial of 3-month, 4-month and 6-month regimens of chemotherapy for sputum-smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 139: 871–876, 1989
Hong Kong Chest Service/British Medical Research Council. Controlled trial of 2, 4 and 6 months of pyrazinamide in 6-month, three-times weekly regimens for smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis, including an assessment of a combined preparation of isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide. American Review of Respiratory Disease 143: 700–706, 1991
Horsfall PAL, Plummer J, Allan WGL, Girling DJ, Nunn AJ, et al. Double blind controlled comparison of aspirin, allopurinol and placebo in the management of arthralgia during pyrazinamide administration. Tubercle 60: 13–24, 1979
Iseman MD, Madsen L, Goble M, Pomerantz M. Surgical intervention in the treatment of pulmonary disease caused by drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 141: 623–625, 1990
Jack DB, Knepil J, McLay WDS, Fergie R. Fatal rifampicin-ethambutol overdosages. Lancet 2: 1107–1108, 1978
Jindani A, Aber VR, Edwards EA, Mitchison DA. The early bactericidal activity of drugs in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 121: 939–969, 1980
Kasik JE. Mycobacterial betalactamases. In Hamilton-Miller JMT & Smith JT (Eds) Betalactamases, pp. 339–350, Academic Press, London, 1979
Kelly RG, Kaleita E, Eisner HJ. Tissue distribution of [14C]ethambutol in mice. American Review of Respiratory Disease 123: 689–690, 1981
Kucers A, McK Bennett N, et al. The use of antibiotics, pp. 1432–1436, William Heineman Medical Books, London, 1987
Kucks NA, Peets EA, Forbes M. Mode of action of ethambutol on Mycobacterium tuberculosis, strain H37RV. American Review of Respiratory Disease 87: 805–806, 1963
Kushner S, Dalalian H, Sanjurjo JL, Bach FL, Safir SR, et al. Experimental chemotherapy of tuberculosis II: the synthesis of pyrazinamides and related compounds. Journal of the American Chemistry Society 74: 3617, 1952
Lecoeur HF, Truffot-Pernot C, Grosset J. Experimental short course preventive therapy of tuberculosis with rifampin and pyrazinamide. American Review of Respiratory Disease 140: 1189–1193, 1989
Lindholm-Levy PJ, Heifets LB. Clofazimine and other rimino compounds, minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations at different pHs for Mycobacterium aviumcomplex. Tubercle 69: 186, 1988
Liss RH, Letourneau RJ, Schepis JP. Distribution of ethambutol in primate tissues and cells. American Review of Respiratory Disease 123: 529–532, 1981
Leor J, Matetzki S. Ofloxacin and warfarin. Annals of Internal Medicine 109: 761, 1988
Macleod HM, Hay D, Stewart HM. The use of pyrazinamide plus isoniazid in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle 40: 14, 1959
Masud T, Kemp E. Corticosteroids in treatment of disseminated tuberculosis in patients with HIV infestion: short report. British Medical Journal 296: 464–465, 1988
McClatchy JK. Antituberculosis drugs: mechanism of action, drug resistance, susceptibility testing and assay of activities. In Lorian V (Ed.) Antibiotics in laboratory medicine, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1980
McDermot W, Tompset R. Activation of pyrazinamide and nicotinamide in acidic environments in vitro. American Review of Tuberculosis 70: 748, 1954
McNicol MW, Thompson H, Riordan JF, Forde E, Allen CJ. Antituberculous chemoprophylaxis with isoniazid-rifamycin. Abstract. Thorax 39: 223–224, 1984
Miller AB, Fox W, Ruth T. An international cooperative investigation into thiacetazone side effects. Tubercle 47: 33, 1966
Mitchison DA. Mechanisms of drug action in short course chemotherapy. Bulletin of the International Union Against Tuberculosis 60: 34–37, 1985
Mitchison DA, Nunn AJ. Influence of initial drug resistance on the response to short course chemotherapy of pulmonary tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 133: 423–430, 1986
Moulding TM, Redeker AG, Kanel GC. Twenty isoniazid-associated deaths in one state. American Review of Respiratory Disease 140: 700–705, 1989
Nolan CM, Elarth AM, Barr HW. Intentional isoniazid overdosage in young Southeast Asian refugee women. Chest 93: 803–806, 1988
Pilheu JA, Maglio F, Centrangolo R, Pleus AD. Concentration of ethambutol in the cerebrospinal fluid after oral administration. Tubercle 52: 117–122, 1971
Place VA, Thomas JP. Clinical pharmacology of ethambutol. American Review of Respiratory Disease 87: 901–904, 1963
Saslaw S, Klainer AS. Rheumatoid syndrome during isoniazid therapy. American Review of Respiratory Disease 100: 221–223, 1969
Sippel JE, Mikhail IA, Girgis NI. Rifampin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tuberculous meningitis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 109: 579–580, 1974
Slutkin G, Leowski J, Mann J. Les effets de l’épidémie du SIDA sur la situation de la tuberculose et sur les programmes de lutte antituberculeuse. Bulletin de l’Union Interntionale Contre la Tuberculose et les Maladies Respiratoires 63: 22–25, 1988
Snider Jr DR, Layde PM, Johnson MW, Lyle MA. Treatment of tuberculosis during pregnancy. American Review of Respiratory Disease 122: 65–79, 1980
Snider Jr DR, Powel KE. Should women taking antituberculosis drugs breast feed? Archives of Internal Medicine 144: 589–590, 1984
Sorg TB, Cynamon MH. Comparison of four beta-lactamase inhibitors in combination with ampicillin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 19: 59–64, 1987
Steel MA, Burk RF, DesPrez RM. Toxic hepatitis with isoniazid and rifampin, a meta-analysis. Chest 99: 465–471, 1991
Sunderam G, Mangura BT, Lombardo JM, Reichman LB. Failure of optimal four drug short course tuberculosis chemotherapy in a compliant patient with human immunodeficiency virus. American Review of Respiratory Disease 36: 1475–1478, 1987
Theuer CP, Hopewell PC, Elias D, Schecter GF, Rutherford GW, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in tuberculosis patients. Journal of Infectious Disease 162: 8–12, 1990
Truffot-Pernot C, Grosset J, Bismuth R, Lecoeur H. Activité de la rifampicine administrée de manière intermittente et de la cyclopentyl rifamycine (DL 473) sur la tuberculose experimentale de la souris. Revue Française de Maladies Respiratoires 11: 875–882, 1983
Truffot-Pernot C, Ji B, Grosset J. Activities of pefloxacin and ofloxacin against mycobacteria in vitro and mouse experiments. Tubercle 72: 57–64, 1991
Tsukamura M. In vitro antimycobacterial activities of a new antibacterial substance DL-8280: differentiation between some species of mycobacteria and related organisms by the DL-8280 susceptibility test. Microbiology and Immunology 27: 1129–1183, 1983
Tsukamura M, Nakamura E, Yoshi S, Amano H. Therapeutic effect of a new antibacterial substance, ofloxacin (DL 8280) on pulmonary tuberculosis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 131: 352–356, 1985
Uttley AHC, Collins CH. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin in combination with standard antituberculosis drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tubercle 69: 193–195, 1988
Vischer WA. The experimental properties of G 30 320 (B 663), a new antileprotic agent. Leprosy Review 40: 107–110, 1969
Wason S, Lacouture PG, Lovejoy Jr FH. Single high-dose pyridoxine treatment for isoniazid overdose. Journal of the American Medical Association 246: 1102–1104, 1981
Wong P, Bottorff MB, Heritage RW, Piecoro JJ, Rodgers GC, et al. Acute rifampin overdose: a pharmacokinetic study and review of literature. Journal of Pediatrics 104: 781–783, 1984
Woodley C, Kilburn JO. In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium aviumcomplex and Mycobacterium tuberculosisstrains to a spiropiperidyl rifamycin. American Review of Respiratory Disease 126: 586–587, 1982
Young LS, Wiviott L, Kolonoski P, Bolan R, et al. Azrithromycin for treatment of Mycobacterium avium-intracellularecomplex infection in patients with AIDS. Lancet 338: 1107–1109, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davidson, P.T., Le, H.Q. Drug Treatment of Tuberculosis — 1992. Drugs 43, 651–673 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199243050-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199243050-00003