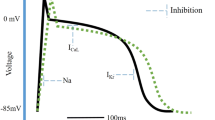
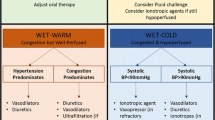
Summary
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common cardiac arrhythmia which is particularly prevalent among the elderly. In patients with AF of recent onset, restoration of sinus rhythm may be feasible and this can be achieved by DC cardioversion, or by the use of one of a number of drugs including amiodarone, flecainide or propafenone. Neither digoxin nor the calcium antagonists facilitate the restoration of sinus rhythm. Recurrence of AF is common after successful cardioversion and, although long term antiarrhythmic drug therapy may help to maintain sinus rhythm, all such drugs are potentially toxic and can have important proarrhythmic actions. In patients with chronic AF, restoration of sinus rhythm is rarely possible and treatment is directed towards control of the ventricular response rate, which may be achieved with digoxin and/or a rate-limiting calcium antagonist such as verapamil or diltiazem; β-blockers may also be used although they appear to impair effort tolerance. In addition, long term anticoagulation may be indicated to reduce the risks of systemic embolisation, even in patients with ‘nonrheumatic’ AF; antiplatelet drugs are of no apparent value in this context. A minority of patients present with AF associated with ventricular pre-excitation; in these individuals both digoxin and the calcium antagonists are contraindicated and the ventricular response rate should be controlled with flecainide, amiodarone or propafenone
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antman EM, Stone PH, Muller JE, Braunwald E. Calcium channel blocking agents in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Annals of Internal Medicine 93: 875–885, 1980
Atwood JE, Sullivan M, Forbes S, Myers J, Pewen W, et al. Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on exercise performance in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiologists 10: 314–320, 1987
Beasley R, Smith DA, McHaffie DJ. Exercise heart rates at different serum digoxin concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation. British Medical Journal 290: 9–11, 1985
Bianconi L, Boccadamo R, Pappalardo A, Gentili C, Pistolese M. Effectiveness of intravenous propafenone for conversion of atrial fibrillationbrillation and flutter of recent onset. American Journal of Cardiology 64: 335–338, 1989
Braunwald E. Mechanism of action of calcium-channel blocking agents. New England Journal of Medicine 307: 1618, 1972
Camm AJ, Evans KE, Ward DE, Martin A. The rhythm of the heart in active elderly subjects. American Heart Journal 99: 598–603,1980
Camm J, Ward D, Spurrell RAJ. The effect of intravenous disopyramide phosphate on recurrent paroxysmal tachycardias. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8: 441–449, 1979
Campbell TJ, Gavaghan TP, Morgan JJ. Intravenous sotalol for the treatment of atrial fibrillationbrillation and flutter after cardiopulmonary bypass. British Heart Journal 54: 86–90, 1985
CAST Investigators Preliminary Report. Effect of encainide and flecainide on mortality in a randomised trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction. New England Journal of Medicine 321: 406–412, 1989
Connolly SJ, Hoffert DL. Usefulness of propafenone for recurrent paroxysmal atrial fibrillationbrillation. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 817–819, 1989
Dethy M, Chassat C, Roy D, Mercier LA. Doppler echocardiographic predictors of recurrence of atrial fibrillationbrillation after cardioversion. American Journal of Cardiology 62: 723–726, 1988
Edmands R, Greenspan K, Fisch C. The role of inotropic variation in ventricular function during atrial fibrillationbrillation. Journal of Clinical Investigation 49: 738–746, 1970
Falk RH. Flecainide-induced ventricular tachycardia and fibrillationbrillation in patients treated for atrial fibrillationbrillation. Annals of Internal Medicine 111: 107–111, 1989
Falk RH, Knowlton AA, Bernard SA, Gotlieb N, Battinelli NJ. Digoxin for converting recent-onset atrial fibrillationbrillation to sinus rhythm. Annals of Internal Medicine 106: 503–506, 1987
Faniel R, Schoenfeld PH. Efficacy of i.v. amiodarone in converting rapid atrial fibrillation and flutter to sinus rhythm in intensive care patients. European Heart Journal 4: 180–185, 1983
Garratt C, Antoniou A, Ward D, Camm AJ. Misuse of verapamil in pre-excited atrial fibrillationbrillation. Lancet 1: 367–369, 1989
Harron DWG, Brogden RN. Propafenone: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in the treatment of arrhythmias. Drugs 34: 617–647, 1987
Heger JJ, Prystowsky E, Miles W, Zipes DP. Clinical experience with amiodarone for treatment of recurrent ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillationbrillation. British Journal of Clinical Practice 40 (Suppl. 44): 16–24, 1986
Holmes B, Heel RC. Flecainide: a preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic effibrillationcacy. Drugs 29: 1–33, 1985
Ito M, Onodera S, Hashimoto J, Noshiro H, Shinoda S, et al. Effect of disopyramide on initiation of atrial fibrillationbrillation and relation to effective refractory period. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 561–566, 1989
Karlson BW, Torstensson I, Abjorn C, Jansson SO, Peterson LE. Disopyramide in the maintenance of sinus rhythm after electroconversion of atrial fibrillationbrillation: a placebo-controlled one-year follow-up study. European Heart Journal 9: 284–290, 1988
Kerr CR, Klein GJ, Axelson JE, Cooper JC. Propafenone for prevention of recurrent atrial fibrillation. American Journal of Cardiology 61: 914–916, 1988
Khalasa A, Olsson SB. Verapamil induced regularity in atrial fibrillationbrillation. Acta Medica Scandinavica 205: 509–515, 1979
Klein HO, Kaplinsky E. Digitalis and verapamil in atrial fibrillationbrillation and flutter. Drugs 31: 185–197, 1986
Kulbertus HE, Leval-Rutten F, Bartsch P, Petit J. Atrial fibrillationbrillation in elderly ambulatory patients. In Kulbertus, Olsson & Schlepper (Eds) Atrial fibrillationbrillation, pp. 148–155, A.B. Hassle, Molndal, Sweden, 1984
Lang R, Klein HO, Di Segni E, Gefen J, Sareli P, et al. Verapamil improves exercise capacity in chronic atrial fibrillationbrillation: double-blind crossover study. American Heart Journal 105: 820–825, 1983a
Lang R, Klein HO, Weiss E, et al. Superiority of oral verapamil therapy to digoxin in the treatment of chronic atrial fibrillationbrillation. Chest 83: 491–498, 1983b
Lewis R, Lakhani M, Moreland TA, McDevitt DG. A comparison of verapamil and digoxin in the treatment of atrial fibrillationbrillation. European Heart Journal 8: 148–153, 1987
Lewis RV, Irvine NI, McDevitt DG. Relationships between heart rate, exercise tolerance and cardiac output in atrial fibrillationbrillation: the effects of treatment with digoxin, verapamil and diltiazem. European Heart Journal 9: 777–781, 1988a
Lewis RV, Laing E, Moreland T, Service E, McDevitt DG. A comparison of digoxin, diltiazem and their combination in the treatment of atrial fibrillationbrillation. European Heart Journal 9: 279, 1988b
Lewis RV, McDevitt DG. Adverse reactions and interactions with beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. Medical Toxicology 1: 343–361, 1986
Lewis RV, McDevitt DG. The relative effects of digoxin and diltiazem upon ventricular ectopic activity in patients with chronic atrial fibrillationbrillation. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26: 327–329, 1988
Lipkin DP, Frenneaux M, Stewart R, Joshi J, Lowe T, et al. Delayed improvement in exercise capacity after cardioversion of atrial fibrillationbrillation to sinus rhythm. British Heart Journal 59: 572–577, 1988
Manolis AS, Salem DN, Mark Estes NA. Electrophysiologic effects, effibrillationcacy and tolerance of class lc antiarrhythmic agents in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 746–750, 1989
Meijler FL. Atrial fibrillationbrillation: symptoms and haemodynamics (discussion). In Kulbertus, Olsson & Schlepper (Eds), pp. 122–133, A.B. Hassle, Molndal, Sweden, 1984
Myers J, Atwood JE, Sullivan M, Forbes S, Friis R, et al. Perceived exertion and gas exchange after calcium and β-blockade in atrial fibrillationbrillation. Journal of Applied Physiology 63: 97–104, 1987
Naito M, Dreifus LS, Mardelli TJ, Chien CC, David D, et al. Echocardiographic features of atrioventricular and ventriculoatrial conduction. American Journal of Cardiology 46: 625–633, 1980
Petch MC. Lessons from ambulatory electrocardiography. British Medical Journal 291: 617–618, 1985
Petersen P, Boysen G, Godtfredsed J, Andersen ED, Andersen B. Placebo-controlled, randomised trial of warfarin and aspirin for prevention of thromboembolic complications in chronic atrial fibrillationbrillation. Lancet 1: 175–178, 1989
Pitcher DW, Papouchada M, James MA, Rees JR. 24-Hour ambulatory electrocardiography in patients with chronic atrial fibrillationbrillation. British Medical Journal 292: 594, 1986
Redfors A. The effect of different digoxin doses on subjective symptom and physical working capacity in patients with atrial fibrillationbrillation. Acta Medica Scandinavica 190: 307–320, 1971
Rowlands DJ. Understanding the electrocardiogram. Section 3: Rhythm abnormalities, Imperial Chemical Industries, PLC, 1987
Salerno DM, Dias VC, Kleiger RE, Tschida VN, Sung RJ, et al. Effibrillationcacy and safety of intravenous diltiazem for treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 1046–1351, 1989
Samet P, Bernstein WN, Nathan D. Atrial contribution to cardiac output in complete heart block. American Journal of Cardiology 16: 1–10, 1965
Sandercock P, Warlow C, Bamford J, Peto R, Starkey I. Is a controlled trial of long-term oral anticoagulants in patients with stroke and non-rheumatic atrial fibrillationbrillation worthwhile? Lancet 1: 788–792, 1986
Schamroth L, Krikler DM, Garret C. Immediate effects of intravenous verapamil in cardiac arrhythmias. British Medical Journal 1: 660–662, 1972
Schutzenberger W, Leisch F, Gmeiner R. Enhanced accessory pathway conduction following intravenous amiodarone in atrial fibrillationbrillation. International Journal of Cardiology 16: 93–95, 1987
Shenasa M, Kus T, Fromer M, LeBlanc RA, Dubuc M, et al. Effect of intravenous and oral calcium antagonists (diltiazem and verapamil) on sustenance of atrial fibrillationbrillation. American Journal of Cardiology 62: 403–407, 1988
Singh BN, Deedwania P, Nademanee K, Ward A, Sorkin EM. Sotalol: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use. Drugs 34: 311–349, 1987
Sonnhag C, Kallryd A, Nylander E, Ryden L. Long-term efficacy of flecainide in paroxysmal atrial fibrillationbrillation. Acta Medica Scandinavica 224: 563–569, 1988
Strasberg B, Arditti A, Sclarovsky S, Lewin R, Buimovici B, et al. Efficacy of intravenous amiodarone in the management of paroxysmal or new atrial fibrillationbrillation with fast ventricular response. International Journal of Cardiology 7: 47–55, 1985
Suttorp MJ, Kingma JH, Lie-A-Huen L, Mast EG. Intravenous flecainide versus verapamil for conversion of paroxysmal atrial fibrillationbrillation or flutter to sinus rhythm. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 693–696, 1989
Tucker AR, Ng KI. Digoxin related impairment of learning and memory in cardiac patients; Psychopharmacology 81: 86–88, 19
Van Gelder IC, Crijns H, Van Gilst WH, De Langen C, Van Wijk L, et al. Effects of flecainide on the atrial defibrillationbrillation threshold. American Journal of Cardiology 63: 112–114, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, R.V. Atrial Fibrillation. Drugs 40, 841–853 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199040060-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199040060-00006