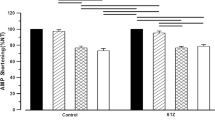
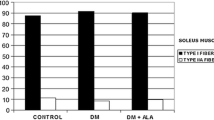
Summary
Slowing of nerve conduction, a hallmark of both experimental and human diabetic neuropathy, is improved or corrected by aldose reductase inhibitors such as sorbinil Animal experiments suggest that a myo-inositol-related defect in nerve sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) is responsible for the acute reversible slowing of nerve conduction in diabetes mellitus. This myo-inositol-related defect is at present viewed as a cyclic metabolic defect. Aldose reductase inhibitors have been shown to restore to normal both the myo-inositol content and the sodium-potassium ATPase activity of nerve. This suggests that the acute effects of aldose-reductase inhibitors on nerve conduction in both diabetic animals and human patients may be modified by the correction of an underlying myo-inositol-related defect of nerve sodium-potassium ATPase. Furthermore, this myoinositol-related defect may contribute to other biochemical, functional and structural abnormalities of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behse F, Buchthal F, Carlsen F. Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 40: 1072, 1977
Boulton AJM, Drury J, Clarke B, Ward JD. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the management of painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 5: 386–390, 1982
Bradbury MWB, Crowder J. Compartments and barriers in the sciatic nerve of rabbits. Brain Research 103: 515–526, 1976
Brismar T, Sima AAF. Changes in nodal function in nerve fibers of the spontaneously diabetic BB-wistar rat. Potential clamp analysis. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 113: 499–506, 1981
Clements RS. Diabetic neuropathy: new concepts of its etiology. Diabetes 28: 604–611, 1979
Das PK, Bray GM, Aguayo AJ, Rasminsky M. Diminished ouabain sensitive sodium potassium ATPase activity in sciatic nerves of rats with streptozotocin induced diabetes. Experimental Neurology 53: 285–288, 1976
Day JF, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW. Non-enzymatically glycosylated albumin. In vitro preparation and isolation from normal human serum. Journal of Biological Chemistry 254: 595–597, 1975
Ellenberg M. Diabetic neuropathy: clinical aspects. Metabolism 25: 1627–1655. 1976
Fagius J, Jameson S. Effects of aldose reductase inhibitor treatment in diabetic polyneuropathy: a clinical and neurophysiological study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 44: 991–1001, 1981
Fraser DM, Campbell IW, Ewing DJ, Murray A, Neilson JMJ, et al. Peripheral and autonomie nerve function in newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 26: 546–550, 1977
Gillon KRW, Hawthorne JN. Sorbitol, inositol and nerve conduction in diabetes. Life Sciences 32: 1943–1947, 1983a
Gillon KRW, Hawthorne JN. Transport of myo-inositol into endoneurial preparations of sciatic nerve from normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Biochemical Journal 210: 775–781, 1983b
Graf RJ, Halter JB, Haler E, Porte Jr D. Nerve conduction abnormalities in untreated maturity-onset diabetes: relation to levels of fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. Annals of Internal Medicine 90: 298–303, 1979
Graf RJ, Halter JB, Pfeifer MZ, Haler E, Brozovich F, et al. Glycemic control and nerve conduction abnormalities in non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Annals of Internal Medicine 94: 307–311, 1981
Greene DA. Metabolic abnormalities in diabetic peripheral nerve: relation to impaired function. Metabolism 32: 118–123, 1983
Greene DA, Lattimer SA. Sodium- and energy-dependent uptake of myo-inositol by rabbit peripheral nerve. Journal of Clinical Investigation 70: 1009–1018, 1982
Greene DA, Lattimer SA. Impaired rat sciatic nerve sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase in acute streptozotocin diabetes and its correction by dietary myo-inositol supplementation. Journal of Clinical Investigation 72: 1058–1063, 1983
Greene DA, Lattimer SA. Impaired energy utilization and Na-K-ATPase in diabetic peripheral nerve. American Journal of Physiology 246: E311–E318, 1984a
Greene DA, Lattimer SA. Action of sorbinil in diabetic peripheral nerve. Relationship of polyol (sorbitol) pathway inhibition to a myo-inositol-mediated defect in sodium-potassium ATPase activity. Diabetes 33: 712–716, 1984b
Greene DA, Winegrad AI. In vitro studies of the substrates for energy production and the effects of insulin on glucose utilization in the neural compartments of peripheral nerve. Diabetes 28: 878–887, 1979
Greene DA, Winegrad AI. Effects of acute experimental diabetes on composite energy metabolism in peripheral nerve axons and Schwann cells. Diabetes 30: 967–974, 1981
Greene DA, DeJesus PV, Winegrad AI. Effects of insulin and dietary myo-inositol on impaired peripheral motor nerve conduction velocity in acute streptozotocin diabetes. Journal of Clinical Investigation 55: 1326–1336, 1975
Greene DA, Brown MJ, Braunstein SN, Schwartz SS, Asbury AK, et al. Comparison of clinical course and sequential electro-physiological tests in diabetics with symptomatic polyneuropathy and its implications for clinical trials. Diabetes 30: 139–147, 1981
Greene DA, Yagihashi S, Lattimer SA, Sima AAF. Nerve Na+-K+-ATPase, conduction and myoinositol in the insulin deficient BB rat. American Journal of Physiology 247: E534–E539, 1984
Greene DA, Lattimer SA, Finefold DN, Tamres LK. Impaired Na-dependent amino acid uptake in diabetic peripheral nerve: correction by aldose reductase inhibition or myo-inositol supplementation. Clinical Research 33: 431A, 1985a
Greene DA, Lattimer SA, Ulbrecht J, Carroll P. Glucose-induced alterations in nerve metabolism: current perspective on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy, and future directions for research and therapy. Diabetes Care 8: 290–299, 1985b
Gregersen G. Variations in motor nerve conduction velocity produced by acute changes in the metabolic state in diabetic patients. Diabetologia 4: 273–277, 1968
Gregersen G, Borstin H, Theil P, Servo C. Myoinositol and function of peripheral nerves in human diabetics. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 58: 241–248, 1978
Gregersen G, Bertelsen B, Harbo H, Larsen E, Andersen JR, et al. Oral supplementation of myo-inositol: effects on peripheral nerve function in human diabetics and on the concentration in plasma, erythrocytes, urine and muscle tissue in human diabetics and normals. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 67: 164–172, 1983
Jacobsen J. Peripheral nerves in early experimental diabetes, expansion of the exoneurial space as a cause of increased water content. Diabetologia 14: 113–119, 1978
Judzewitsch RG, Jaspan JB, Polonsky KS, et al. Aldose reductase inhibition improves nerve conduction velocity in diabetic patients. New England Journal of Medicine 308: 119–125, 1983
Kuwabara T, Kinoshita JH, Cogan DG. Electron microscopic study of galactose-induced cataracts. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 8: 133–149, 1969
Mandersloot JB, Roelofsen B, DeGier J. Phosphatidylinositol as the endogenous activator of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase in microsomes of rabbit kidney. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 508: 478–485, 1972
Mayer JH, Tomlinson DR. The influence of aldose reductase inhibition and nerve myo-inositol on axonal transport and nerve conduction velocity in rats with experimental diabetes. Diabetologia 25: 433–438, 1983
Mayhew JA, Gillon KRW, Hawthorne JN. Free and lipid inositol, sorbitol and sugars obtained post mortem from diabetic and control subjects. Diabetologia 24: 13–15, 1983
McCulloch DK, Campbell IW, Prescott R, Clarke B. Effect of alcohol intake on symptomatic peripheral neuropathy in diabetic men. Diabetes Care 3: 245–247, 1980
Nishizuka Y. Protein kinases in signal transduction. TIBS 9: 163–166, 1984
Pietri A, Ehle AL, Raskin P. Changes in nerve conduction velocity after six weeks of glucose regulation with portable insulin infusion pumps. Diabetes 29: 668–671, 1980
Pirart J. Diabetes mellitus and its degenerative complications. A prospective study of 4400 patients observed between 1947 and 1973. Diabetes Care 1: 168–188, 252–263, 1978
Ritchie JM. The oxygen consumption of mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres at rest and during activity. Journal of Physiology (London) 188: 309–329, 1967
Roelofsen B. The (non) specificity in the lipid requirement of the calcium and (sodium plus potassium) transporting adenosine triphosphatases. Life Sciences 29: 2235–2247, 1981
Salway JG, Finnegan JA, Barnett D, Whitehead L, Karunanayaka A, et al. Effect of myoinositol on peripheral nerve function in diabetes. Lancet 2: 1282–1284, 1978
Service FJ, Rizza RA, Daube JR, Obrien PC, Dyck PJ. Near normoglycemia improved nerve conduction and vibration sensation in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 28: 722–727, 1985
Sima AA, Lattimer SA, Yagihashi S, Greene DA. Axo-glial dysjunction: a novel structural lesion that accounts for poorly reversible slowing of nerve conduction in the spontaneously diabetic bio-breeding rat. Journal of Clinical Investigation 77: 474–484, 1986
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I. Release of Ca++ from a non-mitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate. Nature 306: 67–69, 1983
Thomas PK, Eliasson SG. Diabetic neuropathy. In Dyck PJ, et al. (Eds) Peripheral neuropathy, pp. 956–981, Saunders, Philadelphia, 1975
Thomas PK, Ward JD, Watkins PJ. Diabetic neuropathy. In Keen et al. (Eds) Complications of diabetes, pp. 109–136, Arnold, London, 1982
Tolaymat A, Roque JL, Russo LS. Improvement of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the portable insulin infusion pump. Southern Medical Journal 75: 185–189, 1982
Trachtenberg MC, Packey DJ, Sweeney T. In vivo functioning of the Na++K+- activated ATPase. Current Topics in Cellular Regulation 19: 159–217, 1981
Troni W, Carta Q, Cantello R, Caselle MT, Rainero I. Peripheral nerve function and metabolic control in diabetes mellitus. Annals of Neurology 16: 178–183, 1984
Unakar NJ, Tsui JY, Harding CV. Scanning electron microscopy. Development and reversal of galactose-induced cataracts. Ophthalmology Research 13: 20–35, 1981
Vlassara H, Brownlee M, Cerami A. Non-enzymatic glycosylation of peripheral nerve protein in diabetes mellitus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 78: 5190–5192, 1981
Ward JD, Fisher DJ, Barnes CG, Jessop JD. Improvement in nerve conduction following treatment in newly diagnosed diabetics. Lancet 1: 428–437, 1971
Williams SK, Howarth NL, Devenny JJ, Bitensky MW. Structural and functional consequences of increased tubulin glycosylation in diabetes mellitus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 79: 6546–6550, 1982
Winegrad AI, Greene DA. Diabetic polyneuropathy: the importance of insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia and alterations in myoinositol metabolism in its pathogenesis. New England Journal of Medicine 295: 1416–1420, 1976
Yue DK, Hanwell MA, Satchell FM, Turtle JR. The effect of aldose reductase inhibition on motor nerve conduction velocity in diabetic rat. Diabetes 31: 789–794, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greene, D.A. Sorbitol, Myo-Inositol and Sodium-Potassium ATPase in Diabetic Peripheral Nerve. Drugs 32 (Suppl 2), 6–14 (1986). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198600322-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198600322-00004