Abstract
Toremifene is a chlorinated triphenylethylene derivative of tamoxifen approved for use in the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Toremifene is well tolerated in patients, and common adverse effects of this drag include vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal discharge. This compound is administered to patients orally at a dose of 60 mg/day, although alternative methods of administration have been investigated.
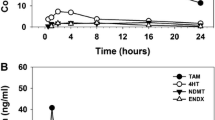
Oral bioavailability is estimated to be approximately 100%. At steady state, toremifene and its metabolites are highly protein bound (>95%). Toremifene is metabolised in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes, and it is eliminated primarily in the faeces following enterohepatic circulation. The half-life of toremifene is approximately 5 days, and steady state is reached by 6 weeks depending on the dose given.
The pharmacokinetics of toremifene have been shown to be altered by certain liver conditions, but age and kidney function do not appear to be as significant.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiseman LR, Goa KL. Toremifene: a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in the management of advanced breast cancer. Drugs 1997 Jul; 54 (1): 141–60.
Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN. Tamoxifen and toremifene in breast cancer: comparison of safety and efficacy. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 348–53.
Gams R. Phase III trials of toremifene vs tamoxifen. Oncology 1997 May; 11 (5 Suppl. 4): 23–8.
Holli K, Joensuu H, Valavaara R, et al., the Finnish Breast Cancer Group, Tampere University Hospital. Interim results of the Finnish toremifene vs. tamoxifen adjuvant trial [abstract no. 332]. 21st Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; 1998 Dec 12–15; San Antonio. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1998; 50 (3): 227–335.
DeGregorio MW, Taras TL. Hormone replacement therapy and breast cancer: revisiting the issues. J Am Pharm Assoc 1998 Nov/Dec; 38 (6): 738–46.
Marttunen MB, Hietanen P, Tiitinen A, et al. Comparison of the effects of tamoxifen and toremifene on bone biochemistry and bone mineral density in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 1158–62.
Saarto T, Blomqvist C, Ehnholm C, et al. Antiatherogenic effects of adjuvant antiestrogens: a randomized trial comparing the effects of tamoxifen and toremifene on plasma lipid levels in postmenopausal women with node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 429–33.
Qu Q, Zheng H, Dahllund J, et al. Selective estrogenic effects of a novel triphenylethylene compound FC 127 la on bone, cholesterol level, and reproductive tissues in intact and ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 2000 Feb; 141 (2): 809–20.
Holli K. Adjuvant trials of toremifene versus tamoxifen: the European experience. Oncology 1998; 12 (3 Suppl. 5): S23–7.
DeGregorio MW, Ford JM, Benz CC, et al. Toremifene: pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic basis of reversing multidrug resistance. J Clin Oncol 1989 Sep; 7 (9): 1359–64.
Soe L, Wurz GT, Maenpaa JU, et al. Tissue distribution of transdermal toremifene. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997; 39: 513–20.
Wurz GT, Maenpaa JU, Hubbard GB, et al. Intratumoral toremifene therapy and tissue distribution in the baboon. Anticancer Drugs 1998; 9: 181–9.
Anttila M, Valavaara R, Kivinen S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of toremifene. J Steroid Biochem 1990; 36 (3): 249–52.
Tominaga T, Abe O, Izuo M, et al. Aphase I study of toremifene. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1990; 16 Suppl.: S27–9.
Wiebe VJ, Benz CC, Shemano I, et al. Pharmacokinetics of toremifene and its metabolites in patients with advanced breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1990; 25: 247–51.
Bishop J, Murray R, Webster L, et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetics study of high-dose toremifene in postmenopausal patients with advanced breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1992; 30 (3): 174–8.
Kivisto KT, Villikka K, Nyman L, et al. Tamoxifen and toremifene concentrations in plasma are greatly decreased by rifampin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1998; 64 (6): 648–54.
Sotaniemi EA, Anttila MI. Influence of age on toremifene pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997; 40: 185–8.
Anttila M, Laakso S, Nylanden P, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the novel antiestrogenic agent toremifene in subjects with altered liver and kidney function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1995; 57 (6): 628–35.
Lonning PE, Lien EA. Pharmacokinetics of anti-endocrine agents. Cancer Surveys 1993; 17: 343–70.
Sipila H, Nanto V, Kangas L, et al. Binding of toremifene to human serum proteins. Pharmacol Toxicol 1988 Jul; 63 (1): 62–4.
Kangas L, Haaparanta M, Paul R, et al. Biodistribution and scintigraphy of 11C-toremifene in rats bearing DMBA-induced mammary carcinoma. Pharmacol Toxicol 1989; 64: 373–7.
Berthou F, Dreano Y, Belloc C, et al. Involvement of cytochrome P450 3A enzyme family in the major metabolic pathways of toremifene in human liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol 1994 May 18; 47 (10): 1883–95.
Kangas L. Biochemical and pharmacological effects of toremifene metabolites. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1990; 27 (1): 8–12.
Wurz GT, Soc L, Emshoff VD, et al. Pharmacokinetic analysis of high-dose toremifene in combination with doxorubicin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1998; 42: 363–6.
Wurz GT, Emshoff VD, DeGregorio MW, et al. Targeting chemosensitizing doses of toremifene based on protein binding. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1993; 31: 412–4.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant 5T32ES07059-NIEHS traineeship, Department of Environmental Toxicology (Tracy L. Taras).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taras, T.L., Wurz, G.T., Linares, G.R. et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Toremifene. Clin Pharmacokinet 39, 327–334 (2000). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200039050-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200039050-00002