Summary
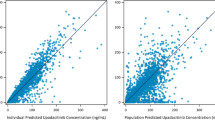
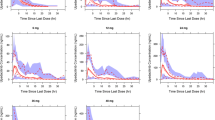
By what mechanism do nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) move from plasma into synovial fluid and back, and how does binding to plasma albumin in vitro relate to articular transport in vivo? To evaluate these issues, concurrent plasma and synovial fluid data of 8 different NSAIDs from 10 single-dose trials were analysed by a simple compartmental model incorporating intra-articular volume, synovial plasma flow rates and protein transport. All pharmacological and physiological data were taken from published studies of chronic knee effusions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The analysis shows that these protein-bound NSAIDs readily leave the vasculature and enter synovial fluid during each transit of synovial microvessels. The mean rate of transport, 0.23 min−1, is consistent with passive diffusion at rates far in excess of those attributable to movement of albumin-bound drug or of the small, free-drug fraction found by equilibrium dialysis. These findings are explained by association and dissociation of NSAIDs and albumin that occur far more rapidly than vascular transit. Ongoing dissociation makes bound drug available for transvascular exchange and thereby diminishes the pharmacokinetic significance of binding data obtained in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson SB, Weissmann G. The mechanisms of action of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Arthritis and Rheumatism 32: 1–9, 1989
Ahern M, Booth J, Loxton A, McCarthy P, Meffin P, et al. Methotrexate kinetics in rheumatoid arthritis: is there an interaction with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs? Journal of Rheumatology 15: 1356–1360, 1988
Altman PL, Dittmer DS (Eds). Blood and other body fluids. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda, Maryland, 1961
AMA drug evaluations, 5th ed., American Medical Association, Chicago, 1983
Barnhart ER (Ed.) Physician’s desk reference, 45th ed., Medical Economics Data, Oradell, 1991
Berman M, Weiss M. SAAM Manual, DHEW Publication No. 78–180, Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1978
Berman M, Weiss M, Shahn E. Some formal approaches to the analysis of kinetic data in terms of linear compartmental systems. Biophysical Journal 2: 289–315, 1962
Bird HA, Allen JG, Dixon JS, Wright V. A pharmacokinetic comparison of tenoxicam in plasma and synovial fluid. British Journal of Rheumatology 24: 351–356, 1985
Branemark PI, Lindstrom J, Jonsson I, Laine V, Vainio K. Capillary structure and function in rheumatoid arthritis. A vital microscopic study of conjunctival and surgically exposed joint tissues. Acta Rheumatologica Scandinavica 9: 284–292, 1963
Chalmers TM, Glass RC, Risdall PC. Concentrations of flurbiprofen in serum and synovial fluid from patients with active rheumatoid disease: some preliminary observations. Current Medical Research and Opinion 5: 17–20, 1977
Daymond TJ, Rowell FJ. Reduction of prostaglandin E2 concentrations in synovial fluid of patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis following tiaprofenic acid or indomethacin treatment. Drugs 35 (Suppl.): 4–8, 1988
Dougados M, Coste PH, Stalla-Bourdillon A, Amor B. Influence de la nature de l’eparchement articulaire sur la diffusion des anti-inflammatoires non steroidiens a travers la membrane synoviale: a propos du Naproxene sodique 550 mg au cours de la polyarthrite rheumatoide et la gonarthrose. Revue Internationale Rheumatologie 16: 105–109, 1987
Emori HW, Champion GD, Bluestone R, Paulus HE. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics of indomethacin in serum and synovial fluid. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 32: 433–435, 1973
Foster DM, Aamodt RL, Henkin RI, Berman M. Zinc metabolism in humans: a kinetic model. American Journal of Physiology 237: R340–R349, 1979
Franchimont P, Hauwaert Ch, Mailleux E. Concentrations of Tolmetin in plasma and synovial fluid after a single intake in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation 4: 387–391, 1981
Furst DE. Synovial fluid kinetics of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In Brooks & Day (Eds) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: basis for variability in response, pp. 65–78, Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, 1985
Gibaldi M. Biopharmaceutics and clinical pharmacokinetics, pp. 1–9, Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1991
Graham GG. Kinetics of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in synovial fluid. Agents and Actions 24 (Suppl.) 66–75, 1988
Katona G, Burgos R, Ortega E. Pharmacokinetics of a single dose of naproxen in plasma and synovial fluid in Naproxen. Proceedings of the IXth European Congress of Rheumatology, pp. 41–45, Wiesbaden, 1979
Kean WF, Lock CJL, Howard-Lock HE. Chirality in antirheumatic drugs. Lancet 338: 1565–1568, 1991
Koch-Weser J, Sellers EM. Binding of drugs to serum albumin. New England Journal of Medicine 294: 311–316, 1976
Levick JR. Blood flow and mass transport in synovial joints. In Renkin et al. (Eds) Handbook of physiology, Vol. IV, Microcirculation Part 2, pp. 917–947, American Physiological Society, Bethesda, 1984
Lin JH, Cocchetto DM, Duggan DE. Protein binding as a primary determinant of the clinical pharmacokinetic properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 12: 402–432, 1987
McCrea JD, Telford AM, Kaye CM, Boyd MWJ. A comparison of plasma and synovial fluid profiles of standard and controlled-release formulations of ketoprofen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 10: 73–81, 1986
Netter P, Bannwarth B, Royer-Morrot MJ. Recent findings on the pharmacokinetics of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in synovial fluid. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 17: 145–162, 1989
Rowland M. Protein binding and drug clearance. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 9 (Suppl. 1): 10–17, 1984
Scheife RT. Protein binding: what does it mean? DICP: Annals of Pharmacotherapy 23: S27, 1989
Simkin PA. The pathogenesis of podagra. Annals of Internal Medicine 86: 230–233, 1977
Simkin PA, Nilson KL. Trans-synovial exchange of large and small molecules. Clinics in Rheumatic Diseases 7: 99–129, 1981
Simkin PA, Pizzorno JR. Transynovial exchange of small molecules in normal human subjects. Journal of Applied Physiology 36: 581–587, 1974
Skeith KJ, Russell AS, Jamali F, Coates J, Friedman H. Lack of significant interaction between low dose methotrexate and ibuprofen or flurbiprofen in patients with arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 17: 1008–1010, 1990
Thomas GM, Rees P, Dippy JE, Maddock J. Simultaneous pharmacokinetics of alclofenac in plasma and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 3: 264–267, 1975
Verbeeck RK. Pathophysiologic factors affecting the pharmacokinetics of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Journal of Rheumatology 15 (Suppl. 7): 44–57, 1983
Wallis WJ, Simkin PA. Antirheumatic drug levels in human synovial fluid and synovial tissue: observations on extravascular pharmacokinetics. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 8: 496–522, 1983
Wallis WJ, Simkin PA, Nelp WB. Low synovial clearance of iodide provides evidence of hypoperfusion in chronic rheumatoid synovitis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 28: 1096–1104, 1985a
Wallis WJ, Simkin PA, Nelp WB. Protein traffic in human synovial effusions. Arthritis and Rheumatism 30: 57–63, 1987
Wallis WJ, Simkin PA, Nelp WB, Foster DM. Intra-articular volume and clearance in human synovial effusions. Arthritis and Rheumatism 28: 441–449, 1985b
Wanwimolruk S, Brooks PM, Birkett DJ. Protein binding of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in plasma and synovial fluid of arthritic patients. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 15: 91–94, 1983
Wilkinson GR. Plasma and tissue binding considerations in drug disposition. Drug Metabolism Reviews 14: 427–465, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simkin, P.A., Wu, M.P. & Foster, D.M. Articular Pharmacokinetics of Protein-Bound Antirheumatic Agents. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 25, 342–350 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325040-00007
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325040-00007