Summary
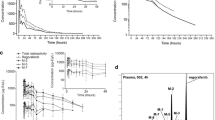
The pharmacokinetics of omeprazole and its metabolites following single doses were studied in 8 patients with liver cirrhosis. Each patient participated in 2 experiments in which [14C]omeprazole was administered either intravenously (20mg) or in an oral solution (40mg) in a randomised crossover design. Plasma concentrations of omeprazole and 2 of its identified metabolites, as well as total radioactivity were followed for 24h; urinary excretion was followed for 96h.
The mean elimination half-life of omeprazole in the patients with cirrhosis was 2.8h and the mean total plasma clearance was 67 ml/min (4.02 L/h); corresponding values from separate studies in young healthy volunteers were 0.7h and 594 ml/min (35.64 L/h). The mean systemic availability was nearly 100% in the patients with cirrhosis whereas the previously reported value in young volunteers was only 56%. Almost 80% of a given dose was excreted as urinary metabolites in both patients and young volunteers. It is concluded that, as the hepatic clearance of omeprazole was substantially reduced in these patients, the dose of omeprazole needed for a certain degree of acid suppression is lower in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson T. Pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in man: with special reference to single and repeated administration, drug interactions, and polymorphic metabolism, Thesis, University of Göteborg, Sweden, 1991
Andersson T, Cederberg C, Regårdh CG, Skånberg I. Pharmacokinetics of various single intravenous and oral doses of omeprazole. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 39: 195–197, 1990a
Andersson T, Regårdh CG, Dahl-Puustinen ML, Bertilsson L. Slow omeprazole metabolizers are also poor S-mephenytoin hydroxylators. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 12: 415–416, 1990b
Arns PA, Wilkinson GR, Branch RA. The stereoselective disposition of mephenytoin provides a probe of hepatic function and development of portasystemic shunts in liver disease. Hepatology 8: 1277, 1988
Bardhan KD, Bianchi Porro G, Bose K, Daly M, Hinchliffe RFC, et al. A comparison of two different doses of omeprazole versus ranitidine in treatment of duodenal ulcers. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 8: 408–413, 1986
Brändström A, Lindberg P, Bergman NÅ, Alminger T, Ankner K, et al. Chemical reactions of omeprazole and omeprazole analogues. Acta Chemica Scandinavica 43: 536–611, 1989
Caulin C, Gouérou H, Bretagne JF, Ebrard F. Tolérance de l’oméprazole chez l’insuffisant hépatique — étude ouverte chez 24 cirrhotiques. Abstract. Gastroentérologie Biologique et Clinique 11: 42A, 1987
Fellenius E, Berglindh T, Sachs G, Olbe L, Elander B, et al. Substituted benzimidazoles inhibit gastric acid secretion by blocking (H+,K+)ATPase. Nature 290: 159–161, 1981
Grundevik I, Jerndal G, Balmér K, Persson BA. Fully automated gradient elution liquid chromatographic assay of omeprazole and 2 metabolites. Journal of Pharmacology and Biomedical Analysis 4: 389–398, 1986
Hetzel DJ, Dent J, Reed WD, Narielvala FM, Mackinnon M, et al. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology 95: 903–912, 1988
Klinkenberg-Knol EC, Jansen JMBJ, Festen HPM, Meuwissen SGM, Lamers CBHW. Double-blind multicentre comparison of omeprazole and ranitidine in the treatment of reflux oesophagitis. Lancet 1: 349–351, 1987
Klotz U. Influence of liver disease on the elimination of drugs. European Journal of Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 1: 129–140, 1976
Landahl S, Andersson T, Larsson HE, Lernfeldt B, Lundborg P, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of omeprazole in elderly healthy volunteers. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 23: 469–476, 1992
Lind T, Andersson T, Skånberg I, Olbe L. Biliary excretion of intravenous [14C]omeprazole in humans. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 42: 504–508, 1987
Lind T, Cederberg C, Ekenved G, Haglund U, Olbe L. Effect of omeprazole — a gastric proton pump inhibitor — on pentagastrin stimulated acid secretion in man. Gut 24: 270–276, 1983
Lorentzon P, Eklundh B, Brändström A, Wallmark B. The mechanism for inhibition of gastric (H++K+)-ATPase by omeprazole. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 817: 25–32, 1985
Regårdh CG, Andersson T, Lagerström PO, Lundborg P, Skånberg I. The pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in humans — a study of single intravenous and oral doses. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 12: 163–172, 1990
Walan A, Bader JP, Classen M, Lamers CBHW, Piper DW, et al. Effect of omeprazole and ranitidine on ulcer healing and relapse rates in patients with benign gastric ulcer. New England Journal of Medicine 320: 69–75, 1989
Wallmark B, Lorentzon P, Larsson H. The mechanism of action of omeprazole: a survey of its inhibitory actions in vitro. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 20 (Suppl. 108): 37–51, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersson, T., Olsson, R., Regårdh, CG. et al. Pharmacokinetics of [14C]Omeprazole in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Clin-Pharmacokinet 24, 71–78 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199324010-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199324010-00006