Summary
10 psychiatric inpatients with a diagnosis of depression were entered into a prospective study to investigate the repeated one-point method as a method of predicting steady-state concentrations for nortriptyline. Four males and 4 females completed all requirements of the protocol.
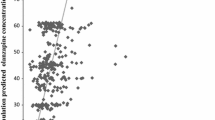
Single plasma concentrations obtained after the first and second daily doses were found to be accurate predictors of the steady-state minimum plasma concentrations. The difference between the measured and the predicted steady-state minimum values ranged from 2.10 to 32.7 μg/L with a standard deviation 10.4 and a mean of 10.5 μg/L, assuming a normal distribution. The correlation coefficient of predicted versus measured concentrations was 0.946 with 90% confidence limits, ranging from 0.800 to 0.990.
The repeated one-point method was found to be an accurate predictor of steady-state minimum plasma concentrations in patients receiving nortriptyline. This method should allow for individual adjustment of dose while minimising the time required to achieve therapeutic, non-toxic plasma concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexanderson, B.: Pharmacokinetics of nortriptyline in man after singl, and multiple oral doses: The predictability of steady-state plasma concentrations from single-dose plasma-level data. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 4: 82–91 (1972).
Alexanderson, B.: Prediction of steady-state plasma levels of nortriptyline from single oral dose kinetics: A study in twins. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 6: 44–53 (1973).
Åsberg, M.; Crönholm, B.; Sjöqvist, F. and Tuck, D.: Correlation of subjective side effects with plasma concentrations of nortriptyline. British Medical Journal 4: 18–21 (1970).
Åsberg, M.; Crönholm, B.; Sjöqvist, F. and Tuck, D.: Relationship between plasma leve, and therapeutic effect of nortriptyline. British Medical Journal 3: 331–334 (1971).
Cooper, T.B. and Simpson, G.M.: Prediction of individual dosage of nortriptyline. American Journal of Psychiatry 135: 333–335 (1978).
Kragh-Sørensen, P.; Åsberg, M. and Eggert-Hansen, C.: Plasma nortriptyline levels in endogenous depression. Lancet 1: 113–115 (1973).
Kragh-Sørensen, P.; Hansen, C.E.; Baastrup, P.C. and Hvidberg, E.F.: Self-inhibiting action of nortriptyline’s antidepressant effect at high plasma levels: A randomized double blind study controlled by plasma concentrations in patients with endogenous depression. Psychopharmacologia 45: 305–312 (1976).
Montgomery, S.A.; Braithwaite, R.E. and Cramer, J.L.: Routine nortriptyline levels in treatment of depression. British Medical Journal 2: 166–167 (1977).
Montgomery, S.A.; Braithwaite, R.A.; Dawling, S. and McCauley, R.: High plasma nortriptyline levels in the treatment of depression. Clinical Pharmacolog, and Therapeutics 23: 309–314 (1978).
Montgomery, S.A.; McCauley, R.; Montgomery, D.B.; Braithwaite, R.A. and Dawling, S.: Dosage adjustment from simple nortriptyline spot level predictor tests in depressed patients. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 4: 129–136 (1979).
Ritschel, W.A. and Thompson, G.A.: The one-point method in predicting dosage regimen in case of hepatic and/or renal failure in presence or absence of change in volume of distribution. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 19: 350–356 (1979).
Sjöqvist, F.; Alexanderson, B.; Åsberg, M.; Bertilsson, L.; Borgå, O.; Hamberger, B. and Tuck, D.: Pharmacokinetic, and biological effects of nortriptyline in man. Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica Suppl. 3: 255–280 (1971).
Sørensen, B.; Kragh-Sørensen, P.; Laresen, N.E. and Hvidberg, E.F.: The practical significance of nortriptyline plasma level control. A prospective evaluation under routine conditions in endogenous depression. Psychopharmacology 59: 35–39 (1978).
Waters Associate, Inc.: Publication J45, January, 1979 [Reference: Kuss, H.J. vo, and Nathmann, M.: Quantitative Bestimmung trizyklischer Antidepressiva mit der Hochdruckflüssigkeitschromatographie. Arzneimittel-Forschung 28: 1301 (1978)].
Ziegler, V.E.; Clayton, P.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Co, B.T. and Biggs, J.T.: Nortriptyline plasma level, and therapeutic response. Clinical Pharmacolog, and Therapeutics 20: 458–463 (1976).
Ziegler, V.E.; Co, B.T. and Biggs, J.T.: Plasma nortriptyline level, and ECG findings. American Journal of Psychiatry 134: 441–443 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fant, W.K., Ritschel, W.A., Alwis, S.K. et al. Prediction of Steady-State Nortriptyline Plasma Levels by the Repeated One-Point Method. Clin Pharmacokinet 9, 450–456 (1984). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198409050-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198409050-00004