Summary
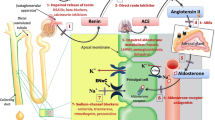
A number of drugs can affect potassium levels by a variety of different mechanisms. Diuretics remain the most important cause of drug-induced alterations. ACE inhibitors may produce hyperkalaemia, particularly in patients with autonomic neuropathy, adrenal insufficiency, renal impairment and when used in combination with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Cathartic and/or diuretic abuse should be suspected when hypokalaemia occurs in young patients suspected of having an eating disorder. NSAIDs may occasionally produce hyperkalaemia, particularly in patients with renal impairment or when used with ACE inhibitors.
Sympathomimetics and theophylline derivatives may lower serum potassium levels, but this is usually only of clinical significance when overdosage occurs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isaac G, Holland OB. Drug-induced hypokalaemia. A cause for concern. Drugs Aging 1992 Jan–Feb; 2(1): 35–41
Routine use of potassium-sparing diuretics. Drug Ther Bull 1991 Oct 28; 29(22): 85–7
Schlueter W, Keilani T, Batlle DC. Tissue renin angiotensin systems: theoretical implications for the development of hyperkalemia using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. A J Med Sci 1994 Feb; 307 Suppl. 1: S81–6
Rigolin VH, Chap L. Extreme hyperkalemia induced by drugs. Postgrad Med 1991 Oct; 90(5): 129–31
Masud T, Winocour P, Clarke F. Reversible hyporeninaemic hypoaldosteronism and life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias: the interaction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and autonomic dysfunction [letter]. Postgrad Med J 1993 Jul: 69(813): 593–4
Whelton A, Hamilton CW. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: effects on kidney function. J Clin Pharmacol 1991 Jul; 31(7): 588–98
Muller-Lissner SA. Adverse effects of laxatives: fact and fiction. Pharmacology 1993 Oct; 47 Suppl. 1: 138–45
Haffner CA, Kendall MJ. Metabolic effects of beta 2-agonists. J Clin Pharm Ther 1992 Jun; 17(3): 155–64
Lipworth BJ, McDevitt DG, Struthers AD. Prior treatment with diuretic augments the hypokalemic and electrocardiographic effects of inhaled albuterol. Am J Med 1989 Jun; 86 (6 Pt 1): 653–7
Struthers AD, Reid JL. The role of adrenal medullary catecholamines in potassium homeostasis. Clin Sci 1984 Apr; 66(4): 377–82
Nasar MA, Lyle EM. Hypokalaemia in the elderly: is it always diuretic-induced? Br J Clin Pract 1994 Jan–Feb; 48(1): 19–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howes, L.G. Which Drugs Affect Potassium?. Drug-Safety 12, 240–244 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199512040-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199512040-00003