Summary
Vigabatrin was designed to increase the levels of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. It does this by replacing GABA as a substrate for the action of the catabolic enzyme GABA-transaminase. As a result of this inhibition, neuronal GABA levels are elevated, resulting in enhanced endogenous GABA transmission.
A number of clinical trials assessing the effect of vigabatrin in epilepsy have been completed. Vigabatrin is of proven benefit in partial seizures and secondarily generalised tonic clonic seizures, and it is licensed for use as adjunctive therapy in these conditions in several European countries. It has been shown to be effective in some epilepsy syndromes in children including West’s syndrome, infantile spasms and cryptogenic partial seizures. Its effect on primary generalised tonic clonic seizures is variable, while there is considerable evidence that it has a deleterious effect on myoclonic and absence seizures. There have been a few reports of the benefits of vigabatrin in other neurological disorders including tardive dyskinesia, degenerative ataxias and GABA metabolism disorders.
The adverse effects associated with vigabatrin are similar to those seen with other anticonvulsants, with a predominance of CNS effects including somnolence, fatigue, irritability, dizziness and headache. Psychiatric symptoms including depression and psychosis are seen in a small number of patients and cause the most problems. These often necessitate discontinuation of vigabatrin, which usually results in resolution of symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleton RE, Montiel-Viesca F.Vigabatrin in infantile spasms —why add on? Lancet 341: 962, 1993
Arezzo JC, Schroeder CE, Litwak MS, et al. Effects of vigabatrin on evoked potentials in dogs. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 53S–60S, 1989
Ben-Menachem E, Persson LI, Schechter PJ, et al. The effect of different treatment regimens of vigabatrin on CSF biochemistry and seizure control in epileptic patients. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 79S–85S, 1989
Betts T, Thomas L. Vigabatrin and behaviour disturbances. Lancet 335: 605–606, 1990
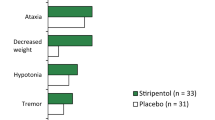
Bonnet AM, Esteguy M, Tell G, et al. A controlled study of oral vigabatrin (GABA) in patients with cerebellar ataxia. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 13: 331–333, 1986
Browne TR, Mattson RH, Penry JK, et al. A multicentre study of vigabatrin for drug resistant epilepsy. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 95S–100S, 1989
Browne TR, Mattson RH, Penry JK, et al. Vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Neurology 37: 184–189, 1987
Cannon DJ, Butler WH, Mumford JP, et al. Neuropathologic findings in patients receiving long-term vigabatrin therapy for chronic intractable epilepsy. Journal of Child Neurology 6 (Suppl. 2): 17–24, 1991
Carella F, Girotti F, Scigliano G, et al. Double blind study of oral gamma-vinyl GABA in the treatment of dystonia. Neurology 36: 98–100, 1986
Chapman AG, De Sarro GB, Premachandra M, et al. Bidirectional effects of carbolines in reflex epilepsy. Brain Research Bulletin 19: 337–346, 1986
Chiron C, Dulac O, Beaumont D, et al. Therapeutic trial of vigabatrin in refractory infantile spasms. Journal of Child Neurology 6 (Suppl. 2): 52–59, 1991
Cocito L, Maffini M, Perfumo P, et al. Vigabatrin in complex partial seizures: a long term study. Epilepsy Research 3: 160–166, 1989
Cosi V, Callieco R, Galimberti CA, et al. Effects of vigabatrin on evoked potentials in epileptic patients. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 61S–68S, 1989
Dam M. Long term evaluation of vigabatrin (γ-vinyl GABA) in epilepsy. Epilepsia 30 (Suppl. 3): S26–S30, 1989
Dam M. Vigabatrin and behaviour disturbances. Lancet 335: 605, 1990
Dulac O, Chiron C, Luna D, et al. Vigabatrin in childhood epilepsy. Journal of Child Neurology 6 (Suppl. 2): 30–37, 1991
Frisk-Holmberg M, Kerth P, Meyer Ph. Effect of food on the absorption of vigabatrin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 23S-25S, 1989
Gibson JP, Yarrinton JT, Loudy DE, et al. Chronic toxicity studies with vigabatrin, a GABA-transaminase inhibitor. Toxicologic Pathology 18: 225–238, 1990
Gibson KM, De Vivo DC, Jakobs C, et al. Vigabatrin therapy in patients with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet 2: 1105–1106, 1989
Graham D. Neuropathology of vigabatrin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 43S–45S, 1989
Gram L, Blatt Lyon B, Dam M. Gamma-vinyl-GABA: a single blind trial in patients with epilepsy. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 68: 34–39, 1983
Gram L, Klosterskov P, Dam M. Gamma-vinyl-GABA: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial in partial epilepsy. Annals of Neurology 17: 262–266, 1985
Gram L, Larsson OM, Johnsen A, et al. Experimental studies of the influence of vigabatrin on the GABA system. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 13S–17S, 1989
Gram L, Sabers A, Dulac O. Treatment of paediatric epilepsies with (vigabatrin). Epilepsia 33 (Suppl. 5): S26–S29, 1992
Grant SM, Heel RC. Vigabatrin. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in epilepsy and disorders of motor control. Drugs 41: 889–926, 1991
Haegele KD, Schechter PJ. Kinetics of the enantiomers of vigabatrin after an oral dose of the racemate or the active S-enantiomer. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 40: 581–586, 1986
Haegele KD, Schoun J, Alken RJ. Determination of the R(−)-and S(+)-enantiomers of γ-vinyl-aminobutyric acid in human body fluids by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography 274: 103–110, 1983
Halonen T, Lehiten M, Pitkänen A, et al. Inhibitory and excitatory amino acids in CSF of patients suffering from complex partial seizures during chronic treatment with vinyl GABA (vigabatrin). Epilepsy Research 2: 246–252, 1988
Jaeken J, Casear P, De Cock P, et al. Vigabatrin in GABA metabolism disorders. Lancet 1: 1074, 1989
Jakobs C, Michael T, Jaeger E, et al. Further evaluation of vigabatrin therapy in 4-hydroxybutyric aciduria. European Journal of Pediatrics 151: 466–468, 1992
Kälviänen R, Äkiä M, Partanen J, et al. Randomized controlled pilot study of vigabatrin versus carbamazepine monotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with epilepsy: an interim report. Journal of Child Neurology 6 (Suppl. 2): 60–69, 1991
Korgaard S, Casey DE, Gerlach J. Effect of gamma-vinyl-GABA in tardive dyskinesia. Psychiatry Research 8: 261–269, 1983
Lippert B, Metcalf BW, Jung MJ, et al. 4-aminohex-5-enoic acid a selective catalytic inhibitor of 4-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase in mammalian brain. European Journal of Biochemistry 74: 4411–4445, 1977
Livingston JH, Beaumont D, Arixmanaglou A, et al. Vigabatrin in the treatment of epilepsy in children. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27 (Suppl. 1): 109S–112S, 1989
Loiseau P, Hardenberg JP, Pestre M, Guyot M, Schechter PJ, et al. Double-blind placebo-controlled study of vigabatrin (γ-vinyl GABA) in drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 27: 115–120, 1986
Luna D, Dulac O, Pajot N, et al. Vigabatrin in the treatment of childhood epilepsies: a single-blind placebo controlled study. Epilepsia 30: 430–437, 1989
McGuire AM, Duncan JS, Trimble MR. Effects of vigabatrin on cognitive function and mood when used as add-on therapy in patients with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 33: 128–134, 1992
Meldrum BS, Murugaiah KM. Anticonvulsant action in mice with sound induced seizures of the optical isomers of gamma-vinyl GABA. European Journal of Pharmacology 89: 149–152, 1983
Michelucci R, Tassinari CA. Response to vigabatrin in relation to seizure type. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 119S-124S, 1989
Mumford JP. A profile of vigabatrin. British Journal of Clinical Practice 42 (Suppl. 6): 7–9, 1988
Pedersen SA, Klosterskov P, Gram L, Dam M. Long-term study of gamma-vinyl GABA in the treatment of epilepsy. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 72: 295–298, 1985
Remy C, Beaumont D. Efficacy and safety of vigabatrin in the long term treatment of refractory epilepsy. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 125S-129S, 1989
Remy C, Favel P, Tell G, et al. Étude en double aveugle cóntre placebo en permutations croisées du vigabatrin dans l’épilepsie de l’adulte résistant à la thérapeutique. Boll. Lega. Ital. Epil. 54/55: 241–243, 1986
Rey E, Pons G, Richard MO, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the individual enantiomers of vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl-GABA) in epileptic children. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 30: 253–257, 1990
Reynolds EH. γ-Vinyl GABA (vigabatrin): clinical experience in adult and adolescent patients with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 33 (Suppl. 5): S30–S35, 1992
Reynolds EH, Ring HA, Fair IN, et al. Open double-blind and long term study of vigabatrin in chronic epilepsy. Epilepsia 32: 530–538, 1991
Rimmer EM, Richens A. A double-blind study of gamma-vinyl GABA in patients with refractory epilepsy. Lancet 1: 189–190, 1984
Rimmer EM, Richens A. Interaction between vigabatrin and phenytoin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27 (Suppl. 1): 27S–34S, 1989
Ring HA, Reynolds EH. Vigabatrin and behaviour disturbance. Lancet 335: 970, 1990
Sander JWAS, Hart YM, Trimble MR, et al. Vigabatrin and psychosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 54: 435–439, 1991
Sander JWAS, Trevisol-Bittencourt PC, Hart YM, et al. Evaluation of vigabatrin as an add-on drug in the management of severe epilepsy. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 53: 1008–1010, 1990
Schechter PJ. Clinical Pharmacology of vigabatrin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 19S-22S, 1989
Schechter PJ, Hanke NF, Grove J, et al. Biochemical and clinical effects of gamma-vinyl-GABA in patients with epilepsy. Neurology 34: 182–186, 1984
Scigliano G, Giovannini P, Girotti F, et al. Gamma-vinyl-GABA treatment of Huntington’s disease. Neurology 34: 94–96, 1984
Sivenius J, Paljärvi, Vapalahti M, et al. Vigabatrin (γ-vinyl-GABA): neuropathologic evaluation in 5 patients. Epilepsia 34: 193–196, 1993
Sivenius J, Ylinen A, Murros K, et al. Vigabatrin in drug resistant partial epilepsy: a 5-year follow-up study. Neurology 41: 562–565, 1991
Stahl SM, Thornton JE, Simpson ML, et al. Gamma-vinyl-GABA treatment of tardive dyskinesia and other movement disorders. Biological Psychiatry 20: 888–893, 1985
Stephenson JBP. Vigabatrin for startle-disease with altered cerebrospinal-fluid free gamma-aminobutyric acid. Lancet 340: 430–431, 1992
Tamminga CA, Thaker GK, Nguyen JA. GABAmimetic treatments for tardive dyskinesia: efficacy and mechanism. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 25: 43–46, 1989
Tartara A, Manni R, Galimberti CA, et al. Vigabatrin in the treatment of epilepsy: a long term follow-up study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 52: 467–471, 1989
Tassinari CA, Michelucci R, Ambrosetto G, Salvi F. Double-blind study of vigabatrin in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy. Archives of Neurology 44: 907–910, 1987
Uldall P, Alving J, Gram L, et al. Vigabatrin in paediatric epilepsy —an open study. Journal of Child Neurology 6 (Suppl. 2): 2S38–2S44, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, J., Richens, A. A Risk-Benefit Assessment of Vigabatrin in the Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Drug-Safety 10, 395–405 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199410050-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199410050-00004