Summary
Joint and muscle pain have been reported with quinolones; however, arthropathies induced by quinolones do not result in erosive changes in humans, although such changes have occurred in animal studies.
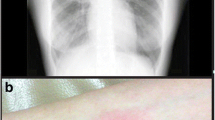
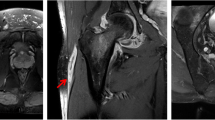
We report an unusual case of destructive polyarthropathy in a 17-year-old boy after treatment with pefloxacin 800 mg/day for 3 months. Pefloxacin may have accentuated the cartilage damage in this case, even if an underlying joint disease could not be excluded.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey RR, Natale R, Linton AL. Nalidixic acid arthralgia. Canadian Medical Association Journal 107: 604, 1972
Boerema JBJ, Pauwels R, Scheeper SJ, Grombach W. Efficacy and safety of pefloxacin in the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 17(B): 103–109, 1986
Cassidy JT. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. In Kelley et al. (Eds) Textbook of Rheumatology, pp. 1289–1311, 3rd edition, Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1989
Chevais M, Reinert P, Rondeau MC, Tobelem R, Albengres E, et al. Critical risk/benefit analysis of pefloxacin use in children under 15 years: the problem of arthralgias. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Therapy and Toxicology 25: 306–309, 1987
Dellamonica P, Bernard E, Etesse M, Garaffo R. The diffusion of pefloxacin into bone and the treatment of osteomyelitis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 17(B): 93–102, 1986
Fast A, Alon M, Weiss S, Zer-Aviv F. Avascular necrosis of bone following short-term dexamethasone therapy for brain oedema. Journal of Neurosurgery 61: 983, 1984
Hooper DC, Wolfson JS. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses and toxicities in humans. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 28: 716–721, 1985
Jorgensen C, Anaya JM, Didry C, Canovas F, Serre I, et al. Arthropathies et tendinopathies achilléennes induites par la péfloxacine. A propos d’une observation. Revue du Rhumatisme et des Maladies Osteo-Articulaires 58: 623–625, 1991
Kato M, Onodeia T. Morphological investigation of osteochondritis induced by ofloxacin in rats. Fundamental and Applied Toxicology 11: 120–131, 1988
Kesseler A, Lacassie A, Hugot JP, Talon Ph, Thomas D, et al. Arthropathies consécutives à l’adminiostration de pefloxacinechez un adolescent atteint de mucoviscidose. Annales de Pediatrie 36: 275–278, 1989
Mc Evans JR, Davey PG. Ciprofloxacin and tenosynovitis. Lancet 2: 900, 1988
Maroteaux P. Epiphyseal dysplasia multiple. In Bergsma D. (Ed.) Birth defects compendium, p. 409, National Foundation, March of Dimes, Alan R. Liss Inc., New York, 1979
Schulter G. Ciprofloxacin: review of potential toxicological effects. American Journal of Medicine 82(Suppl. 4A): 91–93, 1987
Sthalmann R, Merker HJ, Hinz N, Chahoud I, Webb J, et al. Ofloxacin in juvenile non-human primates and rats: arthropathia and drug plasma concentrations. Archives of Toxicology 64: 193–204, 1980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chevalier, X., Albengres, E., Voisin, MC. et al. A Case of Destructive Polyarthropathy in a 17-Year-Old Youth Following Pefloxacin Treatment. Drug-Safety 7, 310–314 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199207040-00007
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199207040-00007