Abstract
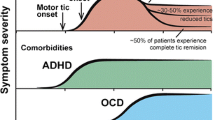
Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome (Tourette’s syndrome; TS) is an inherited tic disorder commonly associated with other neurobehavioural conditions such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). While the clinical presentation of TS and other features of this disorder have been well characterized, the genetic and neurobiological basis of the disease remains incompletely elucidated. The suggestion of a central role of dopamine in the aetiology of TS has been made on the basis of experimental studies, evidence from neuroimaging studies and the therapeutic response patients with TS have to agents that antagonize or interfere with putative dopaminergic pathways. Tetrabenazine is such an agent; it depletes presynaptic dopamine and serotonin stores and blocks postsynaptic dopamine receptors. In clinical studies, tetrabenazine has been found to be effective in a wide range of hyperkinetic movement disorders, including small numbers (<50) of patients with TS in some studies. Results of a retrospective chart review enrolling only patients with TS (n = 77; mean age ≈15 years) showed that 2 years’ treatment with tetrabenazine resulted in an improvement in functioning and TS-related symptoms in over 80% of patients, findings that suggest that treatment with tetrabenazine may have long-term benefits. The authors’ experience with 120 heavily co-medicated patients with TS confirms these findings. Long-term (mean 19 months) tetrabenazine treatment resulted in a Clinical Global Impressions of Change scale rating of ‘improved’ in 76% of patients. Such findings are promising and suggest that tetrabenazine may be suitable as add-on therapy in patients for whom additional suppression of tics is required.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chowdhury U, Heyman I. Tourette’s syndrome in children. BMJ 2004; 329(7479): 1356–7
Muller N. Tourette’s syndrome: clinical features, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2007; 9(2): 161–71
Bruun RD. Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome: an overview of clinical experience. J Am Acad Child Psych 1984; 23(2): 126–33
Apter A, Pauls DL, Bleich A, et al. An epidemiologic study of Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome in Israel. Arch Gen Psych 1993; 50(9): 734–8
Singer HS. Tourette’s syndrome: from behaviour to biology. Lancet Neurology 2005; 4(3): 149–59
Kurlan R, McDermott MP, Deeley C, et al. Prevalence of tics in schoolchildren and association with placement in special education. Neurology 2001; 57(8): 1383–8
Coffey BJ, Park KS. Behavioral and emotional aspects of Tourette syndrome. Neurol Clin 1997; 15(2): 277–89
Swain JE, Scahill L, Lombroso PJ, et al. Tourette syndrome and tic disorders: a decade of progress. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psych 2007; 46(8): 947–68
Robertson MM, Stern JS. Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: symptomatic treatment based on evidence. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000; 9Suppl. 1: 160–75
Robertson MM. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, tics and Tourette’s syndrome: the relationship and treatment implications. A commentary. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2006 Feb; 15(1): 1–11
Como PG, LaMarsh J, O’Brien KA. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in Tourette’s syndrome. Advances Neurol 2005; 96: 249–61
Goodman WK, Storch EA, Geffken GR, et al. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol 2006; 21(8): 704–14
Robertson MM, Banerjee S, Eapen V, et al. Obsessive compulsive behaviour and depressive symptoms in young people with Tourette syndrome: a controlled study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2002; 11(6): 261–5
Robertson MM, Williamson F, Eapen V. Depressive symptomatology in young people with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: a comparison of self-report scales. J Affect Dis 2006; 91(2–3): 265–8
Robertson MM. Tourette syndrome, associated conditions and the complexities of treatment. Brain 2000; 123 (Pt 3): 425–62
Zinner S. Tourette syndrome: more than just tics (part 2). Contemporary Paediatrics 2004; 21(8): 38–49
Coffey B, Frazier J, Chen S. Comorbidity, Tourette syndrome, and anxiety disorders. Adv Neurol 1992; 58: 95–104
Keen-Kim D, Freimer NB. Genetics and epidemiology of Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol 2006; 21(8): 665–71
Pauls DL. Update on the genetics of Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol 2001; 85: 281–93
Leckman JF, Dolnansky ES, Hardin MT, et al. Perinatal factors in the expression of Tourette’s syndrome: an exploratory study. J Am Acad Child Adolescent Psych 1990; 29(2): 220–6
Leckman JF, Price RA, Walkup JT, et al. Nongenetic factors in Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome. Arch Gen Psych 1987; 44(1): 100
Church AJ, Dale RC, Lees AJ, et al. Tourette’s syndrome: a cross sectional study to examine the PANDAS hypothesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 2003; 74(5): 602–7
Mell LK, Davis RL, Owens D. Association between streptococcal infection and obsessive-compulsive disorder, Tourette’s syndrome, and tic disorder. Pediatrics 2005; 116(1): 56–60
Hoekstra PJ, Anderson GM, Limburg PC, et al. Neurobiology and neuroimmunology of Tourette’s syndrome: an update. Cellular Molecular Life sci 2004; 61(7–8): 886–98
Berardelli A, Curra A, Fabbrini G, et al. Pathophysiology of tics and Tourette syndrome. J Neurol 2003; 250(7): 781–7
Singer HS, Minzer K. Neurobiology of Tourette’s syndrome: concepts of neuroanatomic localisation and neurochemical abnormalities. Brain Dev 2003; 25Suppl. 1: S70–84
Frey KA, Albin RL. Neuroimaging of Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol 2006; 21(8): 672–7
Saka E, Graybiel AM. Pathophysiology of Tourette’s syndrome: striatal pathways revisited. Brain Dev 2003; 25Suppl. 1: S15–9
Peterson BS, Skudlarski P, Anderson AW, et al. A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of tic suppression in Tourette syndrome. Arch Gen Psych 1998; 55(4): 326–33
Serrien DJ, Orth M, Evans AH, et al. Motor inhibition in patients with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: functional activation patterns as revealed by EEG coherence. Brain 2005; 128 (Pt 1): 116–25
Francois C, Grabli D, McCairn K, et al. Behavioural disorders induced by external globus pallidus dysfunction in primates: II. Anatomical study. Brain 2004; 127 (Pt 9): 2055–70
Grabli D, McCairn K, Hirsch EC, et al. Behavioural disorders induced by external globus pallidus dysfunction in primates: I. Behavioural study. Brain 2004; 127 (Pt 9): 2039–54
American Psychiatric Association. Task force on DSM-IV. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994; xxvii: 886
Jankovic, J. Diagnosis and classification of tics and Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol 1992; 58: 7–14
Gaze C, Kepley HO, Walkup JT. Co-occurring psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents with Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol 2006; 21(8): 657–64
Robertson MM, Trimble MR, Lees AJ. Self-injurious behaviour and the Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: a clinical study and review of the literature. Psychol Med 1989; 19(3): 611–25
Mathews CA, Waller J, Glidden D, et al. Self injurious behaviour in Tourette syndrome: correlates with impulsivity and impulse control. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004; 75(8): 1149–55
Chatterjee A, Frucht SJ. Tetrabenazine in the treatment of severe pediatric chorea. Mov Disord 2003; 18(6): 703–6
Jain S, Greene PE, Frucht SJ. Tetrabenazine therapy of pediatric hyperkinetic movement disorders. Mov Disord 2006; 21(11): 1966–72
Ondo WG, Hanna PA, Jankovic J. Tetrabenazine treatment for tardive dyskinesia: assessment by randomized videotape protocol. Am J Psychiatry 1999; 156(8): 1279–81
Huntington Study Group. Tetrabenazine as antichorea therapy in Huntington disease: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2006; 66(3): 366–72
Kenney C, Hunter C, Davidson A, et al. Short-term effects of tetrabenazine on chorea associated with Huntington’s disease. Mov Disord 2007; 22(1): 10–3
Sitburana O, Ondo WG. Tetrabenazine for hyperglycemic-in-duced hemichorea-hemiballismus. Mov Disord 2006; 21(11): 2023–5
Vieregge P. Tetrabenazine in the treatment of senile vocal tics. J Neurol 1987; 235(2): 126–7
Jankovic J, Beach J. Long-term effects of tetrabenazine in hyperkinetic movement disorders. Neurology 1997; 48(2): 358–62
Quinn GP, Shore PA, Brodie BB. Biochemical and pharmacological studies of RO 1-9569 (tetrabenazine), a nonindole tranquilizing agent with reserpine-like effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1959; 127: 103–9
Butler PD, Edwards E, Barkai AI. Imipramine and tetrabenazine: effects on monoamine receptor binding sites and phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Eur J Pharmacol 1989; 160(1): 93–100
Tomlinson DR. The mode of action of tetrabenazine on peripheral noradrenergic nerves. Br J Pharmacol 1977; 61(3): 339–44
Login IS, Cronin MJ, Harcus CT, et al. Neuroendocrine evidence that tetrabenazine is a dopamine antagonist. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1983; 172(2): 225–31
Login IS, Cronin MJ, MacLeod RM. Tetrabenazine has properties of a dopamine receptor antagonist. Ann Neurol 1982; 12(3): 257–62
Reches A, Burke RE, Kuhn CM, et al. Tetrabenazine, an amine-depleting drug, also blocks dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1983; 225(3): 515–21
Mehvar R, Jamali F. Concentration-effect relationships of tetrabenazine and dihydrotetrabenazine in the rat. J Pharm sci 1987; 76(6): 461–5
Zheng G, Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA. Vesicular monoamine transporter 2: role as a novel target for drug development. AAPS J 2006 Nov 10; 8(4): E682–92
Pettibone DJ, Totaro JA, Pflueger AB. Tetrabenazine-induced depletion of brain monoamines: characterization and interaction with selected antidepressants. Eur J Pharmacol 1984; 102(3–4): 425–30
Mehvar R, Jamali F, Watson MW, et al. Pharmacokinetics of tetrabenazine and its major metabolite in man and rat: bioavail-ability and dose dependency studies. Drug Metab Dispos 1987; 15(2): 250–5
Roberts MS, McLean S, Millingen KS, et al. The pharmacokinetics of tetrabenazine and its hydroxy metabolite in patients treated for involuntary movement disorders. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 29(6): 703–8
Silay YS, Jankovic J. Emerging drugs in Tourette syndrome. Expert Opinion Emerging Drugs 2005; 10(2): 365–80
Scahill L, Erenberg G, Berlin Jr CM, et al. Contemporary assessment and pharmacotherapy of Tourette syndrome. NeuroRx 2006; 3(2): 192–206
Kenney CJ, Hunter CB, Mejia NI, et al. Tetrabenazine in the treatment of Tourette syndrome. J Ped Neurol 2007; 5(1): 9–13
Bartels M, Zeller E. Tetrabenazine (Nitoman) therapy of chronic spontaneous oral dyskinesia: a video- and EMG-controlled study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol sci 1984; 234(3): 172–4
Hrachovy RA, Frost Jr JD, Glaze DG. Treatment of infantile spasms with tetrabenazine. Epilepsia 1988; 29(5): 561–3
Jankovic J. Treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders with tetrabenazine: a double-blind crossover study. Ann Neurol 1982; 11(1): 41–7
Jankovic J, Glaze DG, Frost Jr JD. Effect of tetrabenazine on tics and sleep of Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome. Neurology 1984; 34(5): 688–92
Jankovic J, Orman J. Tetrabenazine therapy of dystonia, chorea, tics, and other dyskinesias. Neurology 1988; 38(3): 391–4
Kenney C, Jankovic J. Tetrabenazine in the treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders. Expert Rev Neurother 2006; 6(1): 7–17
Paleacu D, Giladi N, Moore O, et al. Tetrabenazine treatment in movement disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol 2004; 27(5): 230–3
Sandyk R, Bamford CR, Iacono RP. Sleep disorders in Tourette’s syndrome. Int J Neurosci 1987 Nov; 37(1–2): 59–65
Kenney C, Hunter C, Jankovic J. Long-term tolerability of tetrabenazine in the treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders. Mov Disord 2007; 22(2): 193–7
Mikkelsen BO. Tolerance of tetrabenazine during long-term treatment. Acta Neurol Scand 1983; 68(1): 57–60
Burke RE, Reches A, Traub MM, et al. Tetrabenazine induces acute dystonic reactions. Ann Neurol 1985; 17(2): 200–2
Ossemann M, Sindic CJ, Laterre C. Tetrabenazine as a cause of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Mov Disord 1996; 11(1): 95
Petzinger GM, Bressman SB. A case of tetrabenazine-induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome after prolonged treatment. Mov Disord 1997; 12(2): 246–8
Stevens E, Roman A, Houa M, et al. Severe hyperthermia during tetrabenazine therapy for tardive dyskinesia. Intensive Care Med 1998; 24(4): 369–71
Kenney C, Hunter C, Mejia N, et al. Is history of depression a contraindication to treatment with tetrabenazine? Clin Neuro-pharmacol 2006; 29(5): 259–64
Fann WE, Lake CR. Amantadine versus trihexyphenidyl in the treatment of neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism. Am J Psychiatry 1976; 133(8): 940–3
Kelly JT, Abuzzahab Sr FS. The antiparkinson properties of amantadine in drug-induced parkinsonism. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs 1971; 11(3): 211–4
Gilbert D. Treatment of children and adolescents with tics and Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol 2006; 21(8): 690–700
Kastrup A, Schlotter W, Plewnia C, et al. Treatment of tics in Tourette syndrome with aripiprazole. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2005; 25(1): 94–6
Kim BN, Lee CB, Hwang JW, et al. Effectiveness and safety of risperidone for children and adolescents with chronic tic or Tourette disorders in Korea. J Child Adolescent Psychopharmacol 2005; 15(2): 318–24
Murphy TK, Bengtson MA, Soto O, et al. Case series on the use of aripiprazole for Tourette syndrome. Intern J Neuropsycho-pharmacol 2005; 8(3): 489–90
Scahill L, Leckman JF, Schultz RT, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of risperidone in Tourette syndrome. Neurology 2003; 60(7): 1130–5
Acknowledgements
Editorial support for this manuscript was provided by the Medical Communications Group, Wolters Kluwer Health, Pharma Solutions Division. Medical writers were involved in the initial literature search and drafting of materials prior to a review and redrafting by Prof. Porta. The medical writing of the review part of this article and not the personal experience section was funded by an educational grant from Chiesi Italia. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porta, M., Sassi, M., Cavallazzi, M. et al. Tourette’s Syndrome and Role of Tetrabenazine. Clin. Drug Investig. 28, 443–459 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200828070-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-200828070-00006