Abstract
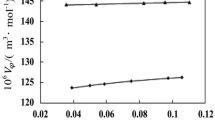
We have found that the enantiomeric isomers of amino acids give different effects on melting of the oxygen adduct of the eutectic compound of sodium chloride and water. The oxygen adduct is formed only in an aqueous sodium chloride solution with concentration below 0.2 mol/1 NaCl. Formation of the adduct is maximal at around 0.1 mol/l NaCl. The latent heat of melting, ΔH, of the oxygen adduct of the eutectic compound under copresence of the L-form enantiomeric isomer of amino acids such as aspartic acid, leucine or threonine is by 5 kJ/ mol NaCl lower than that under copresence of the D-form one. The difference is almost zero with the isomers of serine and phenylalanine. The observed effects suggest that the oxygen adduct of the eutectic compound which is in association with the L-form isomers of aspartic acid, leucine and threonine has thermodynamically higher possibility to get into molten/ liquid state than that with the D-form one. The said phenomena are observed only when the concentration of the solution is in the range of around 0.1 mol/1 NaCl. Furthermore, such a difference does not hold with the enantiomeric isomers of serine or phenylalanine. The specific value of the salt concentration cited above lies in the range almost equal to that of the human blood or that of the physiological saline water for mammals. For the convenience of discussion, it is referred to as the physiological salinity. Thus, it is concluded that the physiological salinity and oxygen will have a basic connection with the biosynthesis and reactions of proteins which are done with identification of the enantiomeric isomers of amino acids. For the interpretation of the observed results which suggest the significance of the specific concentration of 0.1 mol/1 NaCl, the conceptual idea of the “molecular space”, which has been suggested before by one of the present authors (S. F.), will be referred to.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Fujiwara and Y. Nishimoto, Anal. Sci., 6, 771 (1990).
“Gmeiins Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie”, 8, Auf. System Nr. 21, S.332 (1928).
S. Fujiwara and Y. Nishimoto, Anal. Sci., 7, 683 (1991).
S. Fujiwara and Y. Nishimoto, Anal Sci., 6, 907 (1990).
E. Whalley, J. B. R. Heath and D. W. Davidson, J. Chem. Phys., 48, 2362 (1968); cf. “Water”, ed. F. Franks, Vol. 1, p. 117 Prenum Press, New York, 1972.
S. Fujiwara, K. Nagashima, H. Monta and Y. Kanaoka, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 50, 2851 (1977).
W. J. Chazin, J. Kordel, E. Thulin, T. Hofmann, T. Grackenberg and S. Forsen, Biochemistry, 28, 8646 (1989).
E. R. Stadtman, J. Gerontology, 43, B112 (1988).
R. Shapira, G. E. Austin and S. S. Mirra, J. Neurochem., 50, 69 (1988).
R. Shapira, K. D. Wilkinson and G. Shapira, J. Neurochem., 50, 649 (1988).
N. Fujii, S. Muraoka and K. Harada, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 999, 239 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, S., Nishimoto, Y. Effects of Enantiomeric Isomers of Amino Acids on Melting of Oxygen Adduct of Eutectic Compound of Sodium Chloride and Water. ANAL. SCI. 7, 687–690 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.7.687
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.7.687