Abstract
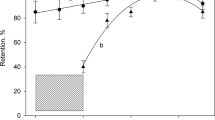
Coprecipitation with terbium hydroxide quantitatively recovered trace amounts of chromium(III), copper(II) and lead(II) at pH 8.4 - 10.8, 8.0 - 11.5 and 8.7 - 11.5, respectively. The precipitate was dissolved in 0.85 mol dm-3 nitric acid, and the analytes were determined by graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS). The presence of terbium (up to 7 g dm-3) did not interfere with the determination. The detection limits were 0.3 μg dnr3 for chromium, 0.4 μg dnr3 for copper and 0.5 μg dnr3 for lead, when the analytes in 200 cm3 of the sample solution were concentrated into 10 cm3. The ions added to river or seawater were quantitatively recovered. Chromium and copper in a contaminated river water were successfully determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mizuike, “Enrichment Techniques for Inorganic Trace Analysis”, 1983, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 56–66.
Yu. A. Zolotov and N. M. Kuz’min, “Preconcentration of Trace Elements”, in “Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry”, ed. G. Svehla, 1990, Vol. 25, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 79–94.
A. Boughriet, L. Deram, and M. Wartel, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1994, 9, 1135.
M. Hiraide, Z. S. Chen, and H. Kawaguchi, Anal. Sci., 1991, 7, 65.
T. Stafilov, G. Pavlovska, and K. Cundeva, Microchem. J., 1998, 60, 32.
K. Cundeva, T. Stafilov, and G. Pavlovska, Microchem. J., 2000, 65, 165.
M. Hiraide, Z. S. Chen, K. Sugimoto, and H. Kawaguchi, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1995, 302, 103.
A. Mizuike, H. Kawaguchi, K. Fukuda, Y. Ochiai, and Y. Nakayama, Microchim. Acta, 1974, 915.
J. Ueda and T. Minami, Chem. Lett., 1997, 681.
T. Minami, K. Atsumi, and J. Ueda, Anal. Sci., 2003, 19, 313.
V. I. Plotnikov, V. L. Kochetkov, and V. P. Chinaeva, kv. Akad. NaukKaz. SSR, Ser. Fiz.-Mat., 1967, 5, 71.
V. I. Plotnikow and E. G. Gibova, Izv. Akad. Nauk Kaz SSR, Ser. Khim., 1968, 18, 9.
K. Himeno, K. Yanagisawa, T. Yuki, and Y. Nakamura, Bunseki Kagaku, 1984, 33, T43.
O. Kujirai, K. Yamada, and R. Hasegawa, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1993, 8, 481.
Y. Toyota, S. Okabe, S. Kanamori, and Y. Kitano, J. Oceanogr. Soc. J., 1982, 38, 357.
S. Saracoglu, M. Soylak, and L. Elci, Talanta, 2003, 59, 287.
W. Feitknecht and P. Schindler, Pure Appl. Chem., 1963, 6, 126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, T., Sohrin, Y. & Ueda, J. Determination of Chromium, Copper and Lead in River Water by Graphite-Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Coprecipitation with Terbium Hydroxide. ANAL. SCI. 21, 1519–1521 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.1519
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.1519