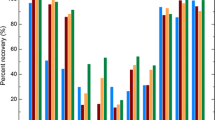
Abstact
Water-soluble carbon nanodots (CND) were synthesized under microwave irradiation from glutamic acid or glutamic acid-boric acid mixture. The CNDs were collected in an aqueous solution through size fractionation by centrifugal filtration. The CNDs thus prepared were subjected to characterization by capillary electrophoresis (CE). A peak signal of anionic substance was detected in the electropherogram, and it was found to be a major component of the CNDs. The effective electrophoretic mobility of the major component was almost identical over the pH range between 6.7 and 11.6, suggesting that the functional group of amine or boric acid moiety was not included in the CNDs. The effective electrophoretic mobility decreased at an acidic pH of less than 5, and it was suggested that carboxylate moiety was included in the CNDs. A signal of less-charged CNDs was also detected in the electropherogram, and the CNDs were characterized by a CE format of micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Two or four peaks were detected just after the electroosmotic flow; the less-charged CNDs were thus hydrophilic. The affinity interaction was also examined between the major anionic CNDs and a hydrophobic pairing cation. The peak signal of the major anionic CNDs broadened, and its theoretical number of plates decreased in the presence of tetrabutylammonium ion in the separation buffer. A small portion of the anionic CNDs were a little hydrophobic at different degrees, and their effective electrophoretic mobility decreased by the hydrophobic interaction, resulting in peak broadening of the anionic CNDs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Xu, R. Ray, Y. Gu, H. J. Ploehn, L. Gearheart, K. Raker, and W. A. Scrivens, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 12736.
Y.-P. Sun, B. Zhou, Y. Lin, W. Wang, K. A. Shiral Fernando, P. Pathak, M. J. Meziani, B. A. Harruff, X. Wang, H. Wang, P. G. Luo, H. Yang, M. E. Kose, B. Chen, L. Monica Veca, and S.-Y. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 7756.
S. N. Baker and G. A. Baker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 6726.
Q.-L. Zhao, Z.-L. Zhang, B.-H. Huang, J. Peng, M. Zhang, and D.-W. Pang, Chem. Commun., 2008, 5116.
H. Zhu, X. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Wang, F. Yang, and X. Yang, Chem. Commun., 2009, 5118.
K. Morita, A. Kobayashi, H. Nagatani, and H. Imura, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 481.
K. Morita, S. Kurusu, H. Kodama, and N. Hirayama, Anal. Sci., 2017, 33, 1461.
Y. Sun, Q. Bi, X. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Zhang, S. Dong, and L. Zhao, Anal. Biochem., 2016, 500, 38.
Q. Hu, X. Gong, L. Liu, and M. M. F. Choi, J. Nanomater., 2017, 1804178.
J. C. Vinci and L. A. Colon, Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 1178.
J. C. Vinci and L. A. Colón, Microchem. J., 2013, 110, 660.
E. Duffy, D. P. Mitev, P. N. Nesterenko, A. A. Kazarian, and B. Paull, Electrophoresis, 2014, 35, 1864.
Z. Markova, A. B. Bourlinos, K. Safarova, K. Polakova, J. Tucek, I. Medrik, K. Siskova, J. Petr, M. Krysmann, E. P. Giannelis, and R. Zboril, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 16219.
Q. Hu, M. C. Paau, Y. Zhang, W. Chan, X. Gong, L. Zhang, and M. M. F. Choi, J. Chromatogr. A, 2013, 1304, 234.
Y. Wu and V. T. Remcho, Talanta, 2016, 161, 854.
H. K. Sadhanala and K. K. Nanda, Carbon, 2016, 96, 166.
M. B. Müller, J. P. Quirino, P. N. Nesterenko, P. R. Haddad, S. Gambhir, D. Li, and G. G. Wallace, J. Chromatogr. A, 2010, 1217, 7593.
T. Takayanagi, M. Morimoto, and T. Yabutani, Anal. Sci., 2013, 29, 769.
T. Takayanagi, Y. Becchaku, Y. Tomiyama, M. Kurashina, and H. Mizuguchi, Anal. Sci., 2019, 35, 307.
T. Takayanagi, M. Amiya, N. Shimakami, and T. Yabutani, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 1193.
The R Project for Statistical Computing, http://www.r-project.org/.
S. Terabe, K. Otsuka, K. Ichikawa, A. Tsuchiya, and A. Ando, Anal. Chem., 1984, 56, 111.
S. Terabe, TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem., 1989, 8, 129.
R. Ciriello, P. T. Iallorenzi, A. Laurita, and A. Guerrieri, Electrophoresis, 2017, 38, 922.
T. Takayanagi, E. Wada, and S. Motomizu, Analyst [London], 1997, 122, 57.
Understanding your ChemStation, https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/usermanuals/Public/G2070-91126_Understanding.pdf, 240.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI [grant number 17K05903 and 18K05184].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takayanagi, T., Iwasaki, S., Becchaku, Y. et al. Capillary Electrophoretic Characterization of Water-soluble Carbon Nanodots Formed from Glutamic Acid and Boric Acid under Microwave Irradiation. ANAL. SCI. 36, 941–946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19P484
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19P484