Abstract
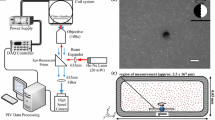
A simultaneous measurement technique for determining the migration velocity of a micrometer-sized particle in a capillary and the adsorption force to the inner surface of the capillary has been proposed. This technique is based on an electromagnetophoretic force being exerted on a micro-particle in an electrolyte solution, which is governed mainly by the electromagnetic buoyancy, when a homogeneous magnetic field is applied at a right angle to the electric current through the medium. By the electromagnetic buoyancy, micro-particles such as polystyrene, carbon and yeast were migrated perpendicular to the direction of the electric current and reached a fused-silica wall. A switching of the current direction could desorb the particle from the wall, and allowed to calculate the detaching force from the desorbing current. The migration velocity normalized to the size in the magnetic field of 10 T was increased in the order of yeast, carbon and polystyrene, while reflecting the decreasing order of the apparent conductivity of the particles. The desorption force could be measured up to 1 nN with a sensitivity of pN. The observed interaction forces of polystyrene and carbon were in the range of 250–600 pN with large deviations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. A. Ducker, T. J. Senden, and R. M. Pashley, Langmuir, 1992, 8, 1831.
D. C. Prieve, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci, 1999, 82, 93.
F. Ming, W. J. D. Whish, J. Hubble, and R. Eisenthal, Enzyme Microb. Technol, 1998, 22, 94.
L. Pla, R. J. Rasia, J. R. Valverde, S. Muller, and J. F. Stolts, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2000, 277, 381.
M. Namba, H. Watarai, and T. Takeuchi, Anal. Sci., 2000, 16, 5.
A. Kolin, Science, 1957, 117, 134.
Y. Iiguni, M. Suwa, and H. Watarai, Anal. Chem., submitted.
J. Zhao and W. Brown, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1996, 179, 255.
K. Svoboda and S. M. Block, Ann. Rev. Biomol. Struct, 1994, 23, 247.
J. N. Israelachvili, “Intermolecular and Surface Forces”, 2nd ed., 1992, Academic Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iiguni, Y., Watarai, H. Simultaneous Measurement of the Migration Velocity and Adsorption Force of Micro-Particles Using an Electromagnetophoretic Force under a High Magnetic Field. ANAL. SCI. 19, 33–37 (2003). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19.33
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19.33