Abstract
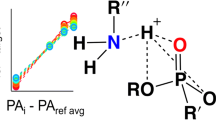
We describe for the first time hydrogen bonded acid (HBA) polymer, poly{methyl[3-(2-hydroxyl, 4,6-bistrifluoromethyl)- phenyl]propylsiloxane}, (DKAP), as stationary phase for gas chromatography (μGC) of organophosphate (OP), chemical warfare agent (CWA) surrogates, dimethylmethylphosphonate (DMMP), diisopropylmethylphosphonate (DIMP), diethylmethylphosphonate (DEMP), and trimethylphosphate (TMP), with high selectivity. Absorption of OPs to DKAP was one-to-several orders of magnitude higher relative to commercial polar, mid-polar, and nonpolar stationary phases. We also present for the first-time thermodynamic studies on the absorption of OP vapors and quantitative binding energy data for interactions with various stationary phases. These data help to identify the best pair of hetero-polar columns for a two-dimensional GC system, employing a nonpolar stationary phase as GC1 and DKAP as the GC2 stationary phase, for selective and rapid field detection of CWAs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wang, T. Satake, and H. Suzuki, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 591.
A. T. Tu, J. Mass Spectrom. Soc. Jpn., 1996, 44, 293.
K. Nakane, S. Shirai, Y. Saito, Y. Moriwake, I. Ueta, M. Inoue, and K. Jinno, Anal. Sci., 2011, 27, 811.
P. R. Lewis, R. P. Manginell, D. R. Adkins, R. J. Kottenstette, D. R. Wheeler, S. S. Sokolowski, D. E. Trudell, J. E. Byrnes, M. Okandan, J. M. Bauer, R. G. Manley, and G. C. Frye-Mason, IEEE Sensors, 2006, 6, 784.
R. P. Manginell, D. R. Adkins, M. W. Moorman, R. Hadizadeh, D. Copic, D. A. Porter, J. M. Anderson, V. M. Hietala, J. R. Bryan, D. R. Wheeler, K. B. Pfeifer, and A. Rumpf, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 2008, 17, 1396.
X. Du, Z. Wang, J. Huang, S. Tao, X. Tang, and Y. Jiang, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44, 5872.
R. P. Manginell, J. M. Bauer, M. W. Moorman, L. J. Sanchez, J. M. Anderson, J. J. Whiting, D. A. Porter, D. Copic, and K. E. Achyuthan, Sensors, 2011, 11, 6517.
R. P. Manginell, C. D. Mowry, A. S. Pimentel, M. A. Mangan, M. W. Moorman, E. S. Sparks, A. Allen, and K. E. Achyuthan, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 1183.
T. Murakami, Y. Iwamuro, S. Chinaka, N. Takayama, and T. Komatsu, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 1325.
Y. Long, X. Du, Y. Wang, J. Zhao, H. Tai, X. Tang, and Y. Jiang, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 59643.
J. W. Grate, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 726.
M. Li, E. B. Myers, H. X. Tang, S. J. Aldridge, H. C. McCaig, J. J. Whiting, R. J. Simonson, N. S. Lewis, and M. L. Roukes, Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 3899.
Y. Wang, X. Du, Y. Long, X. Tang, H. Tai, and Y. Jiang, Anal. Methods, 2014, 6, 1951.
K. Miyabe, Anal. Sci., 2009, 25, 219.
V. R. Reid, J. A. Crank, D. W. Armstrong, and R. E. Synovec, J. Sep. Sci., 2008, 31, 3429.
T. G. Venkatesha, R. Viswanatha, Y. A. Nayaka, and B. K. Chethana, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 198-199, 1.
K. E. Achyuthan and D. G. Whitten, Comb. Chem. HTS, 2007, 10, 399.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by U.S. Defense Threat Reduction Agency under Interagency Order DTRA10027-9009, U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Microsystems Technology Office under Micro Gas Analyzers Program, contract # 017040518, and by Sandia’s LDRD project # 199974. Sandia National Laboratories is a multimission laboratory managed and operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International, Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-NA-0003525. This paper describes objective technical results and analysis. Any subjective views or opinions that might be expressed in the paper do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Energy or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Read, D.H., Achyuthan, K.E., Fix, C.S. et al. Thermodynamic Studies on a Hydrogen Bonded Acidic 3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenol-functionalized Polymer as a Gas Chromatography Stationary Phase for Selectively Speciating Chemical Warfare Agents. ANAL. SCI. 35, 671–677 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P537
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P537