Abstract
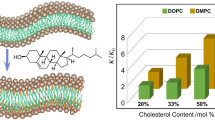
Although the mechanical properties and compositions of lipid bilayer membranes can change upon deformation, the fundamental relations between the composition, membrane tension and fluidity of membranes with little curvature have not yet been studied. In the current study, the membrane tension and the diffusion coefficients of free-standing black lipid membranes (BLMs), based on 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC), were observed by systematic control of the cholesterol concentration and the osmotic pressure with the laser-induced surface deformation (LISD) and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) techniques. When the osmotic pressure was raised and, therefore, the curvature became larger, both the membrane tension and the diffusion coefficients increased as well. On the other hand, when the cholesterol concentration was raised, the membrane tension increased whereas the diffusion coefficient decreased. The importance of the present results goes beyond this quantitative evaluation of the relation between the membrane tension and the fluidity, as it clarifies the changes in the fundamental properties of lipid bilayers upon natural fluctuations and perturbative deformation that were hitherto unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Sprong, P. van der Sluijs, and G. van Meer, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2001, 2, 504.
D. M. Engelman, Nature, 2005, 438, 578.
O. S. Andersen, I. Roger, and E. Koeppe, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 2007, 36, 107.
P. A. Janmey and P. K. J. Kinnunen, Trends Cell Biol., 2006, 16, 538.
B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, D. Morgan, M. Raff, K. Roberts, and P. Walter, “Molecular Biology of the Cell”, 2014, Garland Science.
R. Phillips, J. Kondev, J. Theriot, H. G. Garcia, and N. Orme, “Physical Biology of the Cell”, 2nd ed., 2013, Chap. 11, Garland Science.
T. Harayama and H. Riezman, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2018, 19, 281.
E. Perozo, A. Kloda, D. M. Cortes, and B. Martinac, Nat. Struct. Biol., 2002, 9, 696.
S. Sukharev and D. P. Corey, Sci. STKE, 2004, 2004, re4.
P. Wiggins and R. Phillips, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 101, 4071.
E. A. Evans, Biophys. J., 1973, 13, 941.
E. Evans and A. Yeung, Biophys. J., 1989, 56, 151.
R. M. Hochmuth, J. Biomech., 2000, 33, 15.
S. U. Alam Shibly, C. Ghatak, M. A. Sayem Karal, M. Moniruzzaman, and M. Yamazaki, Biophys. J., 2016, 111, 2190.
T. Takei, T. Yaguchi, T. Fujii, T. Nomoto, T. Toyota, and M. Fujinami, Soft Matter, 2015, 11, 8641.
M. Montal and P. Mueller, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1972, 69, 3561.
A. Hirano-Iwata, M. Niwano, and M. Sugawara, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2008, 27, 512.
A. Hirano-Iwata, K. Aoto, A. Oshima, T. Taira, R.-t. Yamaguchi, Y. Kimura, and M. Niwano, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 1949.
A. Hirano-Iwata, T. Nasu, A. Oshima, Y. Kimura, and M. Niwano, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101, 023702.
A. Hirano-Iwata, A. Oshima, H. Mozumi, Y. Kimura, and M. Niwano, Anal. Sci., 2012, 28, 1049.
M. Zagnoni, Lab Chip, 2012, 12, 1026.
S. Mitani and K. Sakai, Phys. Rev. E, 2002, 66, 031604.
T. Morisaku, M. Ishihara, and H. Yui, Anal. Sci., 2018, 8, 979.
T. Morisaku and H. Yui, Analyst, 2018, 143, 2397.
D. Axelrod, D. E. Koppel, J. Schlessinger, E. Elson, and W. W. Webb, Biophys. J., 1976, 16, 1055.
D. M. Soumpasis, Biophys. J., 1983, 41, 95.
J. Korlach, P. Schwille, W. W. Webb, and G. W. Feigenson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1999, 96, 8461.
H. Basit, V. Gaul, S. Maher, R. J. Forster, and T. E. Keyes, Analyst, 2015, 140, 3012.
Y.-L. Zhang, J. A. Frangos, and M. Chachisvilis, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2006, 347, 838.
A. S. Reddy, D. T. Warshaviak, and M. Chachisvilis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2012, 1818, 2271.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by JSPS (Japan Society for the Promotion of Science) KAKENHI Grant No. 15H03824.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomoto, T., Takahashi, M., Fujii, T. et al. Effects of Cholesterol Concentration and Osmolarity on the Fluidity and Membrane Tension of Free-standing Black Lipid Membranes. ANAL. SCI. 34, 1237–1242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P200
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P200