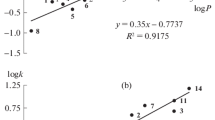
Abstract
Organic solvent-free mobile-phase systems in ion-pair reversed-phase partition high-performance liquid chromatography (IPRP-HPLC) are demonstrated; using urea at 3.0–7.0 molal (mol kg–1) as a modifier in a mobile phase on an octadecylsilanized silica column, four nitrophenolates and metal 4-(2-pyridilazo)resorcinol (PAR) chelates (in PAR chelates system an aqueous mobile phase with 15 wt% methanol was used) were separated rapidly within 6 min at no sacrifice to the separation efficiency. On the addition of urea in the mobile phase, reduced retention times of nitrophenolates and naphthalenesulfonates and also diminution of the height equivalent to a theoretical plate were observed. The addition of urea and guanidium chloride (GuCl) in the mobile phase gave rise to a decrease in the mobile phase volume; in turn, this meant an increased volume of the stationary phase. As the concentration of urea and GuCl in the mobile phase increased, the volume of the mobile phase in the column decreased within about 70% and 40% at 7.0 molal of urea and GuCl, respectively. A decrease in the mobile phase volume suggests an increase in the extent of solvation of the bonded hydrocarbon chain of the stationary phase. The possible explanations for the LC behavior with the urea and GuCl are turned into reduction of hydrophobic interaction in LC processes, solute partitioning and entangling of alkyl chain brushes, with the addition of urea. The water structure breakers, urea and GuCl, most likely affect the solvation states of both solute molecules and the hydrocarboneous stationary phase by changing the nature of the water solvent, which provides a new technique for fine tuning of the LC resolution of the analytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. L. Karger, J. R. Gant, A. Hartkopf, and P. H. Weiner, J. Chromatogr., 1976, 128, 65.
K. A. Dill, J. Phys. Chem., 1987, 91, 1980.
J. A. Dorsey and W. T. Cooper, Anal. Chem., 1994, 66, 857A.
H. Lu and S. C. Rutan, Anal. Chem., 1996, 68, 1387.
W. Kauzmann, Adv. Protein Chem., 1959, 14, 1.
G. Nemethy and H. A. Scheraga, J. Phys. Chem., 1962, 36, 3382.
C. Tanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, 86, 2050.
C. Tanford, “The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Memblanes”, 2nd ed., 1978, Wiley, New York.
N. Muller, Acc. Chem. Res., 1990, 23, 23.
R. Silveston and B. Kronberg, J. Phys. Chem., 1989, 93, 6241.
H. S. Frank and F. Franks, J. Phys. Chem., 1968, 48, 4746.
E. G. Finer, F. Franks, and M. J. Tait, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1972, 94, 4424.
Y. Nozaki and C. Tanford, J. Biol. Chem., 1963, 238, 4074.
E. P. Kirby Hade and C. Tanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1967, 89, 5034.
C. Tanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1966, 88, 2418.
M. Bloemendal and G. Somsen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1985, 107, 3426.
D. B. Wetlaufer, S. K. Malik, L. Stoller, and R. L. Coffin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, 86, 508.
H. S. Frank and M. W. Evans, J. Phys. Chem., 1945, 13, 507.
P. Mukerjee and A. Ray, J. Phys. Chem., 1963, 67, 190.
M. J. Schick, J. Phys. Chem., 1964, 68, 358.
P. Mukerjee and A. K. Ghosh, J. Phys. Chem., 1963, 67, 193
R. M. Kamp, A. Bosserhoff, D. Kamp, and B. Wittmannliebold, J. Chromatogr., 1984, 317, 79.
Y. Esaka, M. Goto, H. Haraguchi, T. Ikeda, and K. Kano, J. Chromatogr. A, 1995, 711, 305.
S. Terabe, Y. Ishihara, H. Nishi, T. Fukuyama, and K. Otsuka, J. Chromatogr., 1991, 545, 359.
E. Kaneko, H. Noda, H. Hoshino, and T. Yotsuyanagi, Chem. Lett., 1996, 1045.
J. Wyman Jr., Chem. Rev., 1936, 19, 213.
P. Jandera, J. Chromatogr. A, 1993, 656, 437.
C. R. Yonker, T. A. Zwier, and M. F. Burke, J. Chromatogr., 1982, 241, 269.
E. H. Slaats, W. Markovski, J. Fekete, and H. Poppe, J. Chromatogr., 1981, 207, 299.
C. R. Yonker, T. A. Zwier, and M. F. Burke, J. Chromatogr., 1982, 241, 257.
V. Gutmann, “The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions”, 1978, Chap. 9, Plenum Press, New York.
R. C. Weast, “CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics”, 68th ed., 1987, CRC Press, Boca Raton, D-266.
M. Abu-Hamiyyah, J. Phys. Chem., 1965, 69, 2720.
R. M. Diamond, J. Phys. Chem., 1963, 67, 2513.
N. Iki, H. Hoshino, and T. Yotsuyanagi, J. Chromatogr. A, 1993, 652, 539.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, T., Hoshino, H. & Yotsuyanagi, T. The Use of Water Structure Breakers, Urea and Guanidium Chloride, New Mobile Phase Modifiers in Reversed-phase Partition High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. ANAL. SCI. 17, 847–851 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.17.847
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.17.847