Abstract
Background
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin with complex pathogenesis. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an important regulatory role in the occurrence and progression of many diseases, as well as psoriasis.
Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of the lncRNA, SPRR2C, in M5-induced psoriatic keratinocytes.
Materials & Methods
SPRR2C expression and subcellular localization was detected using FISH and qRT-PCR. Ker-CT and HaCaT cells stimulated by M5 (IL-17A, tumour necrosis factor-α, IL-1α, IL-22, and oncostatin-M) were used to establish a psoriatic cell model. CCK-8 assay, CFSE proliferation assay, flow cytometry, western blotting and ELISA were used to examine the effects of SPRR2C in the keratinocyte model.
Results
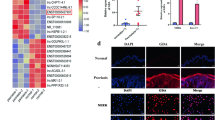
SPRR2C was highly expressed in psoriatic samples and M5-induced psoriatic keratinocytes, and SPRR2C was mainly localised to the cytoplasm. In keratinocytes, SPRR2C regulated proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis, and induced the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, CXCL2 and CCL20. Moreover, SPRR2C cellular effects were shown to be mediated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway, based on experiments with the AKT-specific inhibitor, MK-2206, which was also shown to suppress overexpression of SPRR2C.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that SPRR2C plays a regulatory role and is involved in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in psoriatic keratinocytes, which may provide a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for psoriasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kastelan M, Prpić-Massari L, Brajac I. Apoptosis in psoriasis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 2009; 17: 182–6.
Song JK, Yin S-Y, Li W, et al. An update on the role of long non-coding RNAs in psoriasis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020; 134: 379–89.
Liu Y, Krueger J, Bowcock A. Psoriasis: genetic associations and immune system changes. Genes Immun 2007; 8: 1–12.
Wolf N, Quaranta M, Prescott NJ, et al. Psoriasis is associated with pleiotropic susceptibility loci identified in type II diabetes and Crohn disease. J Med Genet 2008; 45: 114–6.
Harden J, Krueger J, Bowcock A. The immunogenetics of psoriasis: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 2015; 64: 66–73.
Liyanarachchi S, Li W, Yan P, et al. Genome-wide expression screening discloses long noncoding RNAs involved in thyroid carcinogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016; 101: 4005–13.
Ahn R, Gupta R, Lai K, et al. Network analysis of psoriasis reveals biological pathways and roles for coding and long non-coding RNAs. BMC Genomics 2016; 17: 841.
Yi R, Yang L, Zeng S, et al. Different expression profile of mRNA and long noncoding RNA in autoimmune thyroid diseases patients. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 19442–56.
Cai B, Cai J, Yin Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiles in neutrophils revealed potential biomarker for prediction of renal involvement in SLE patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021; 60: 1734–46.
Ahmed Shehata W, Maraee A, El Monem Ellaithy MA, et al. Circulating long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 as a diagnostic marker and indicator of degree of severity in plaque psoriasis. Int J Dermatol 2021; 60: 973–9.
Jia H, Zhang K, Wu W-J, et al. LncRNA MEG3 influences the proliferation and apoptosis of psoriasis epidermal cells by targeting miR-21/caspase-8. BMC Mol Cell Biol 2019; 20: 46.
Qiao M, Li R, Zhao X, et al. Up-regulated lncRNA-MSX2P1 promotes the growth of IL-22-stimulated keratinocytes by inhibiting miR-6731-5p and activating S100A7. Exp Cell Res 2018; 363: 243–54.
Széll M, Danis J, Bata-Csörgő Z, Kemény L. PRINS, a primate-specific long non-coding RNA, plays a role in the keratinocyte stress response and psoriasis pathogenesis. Pflugers Arch 2016; 468: 935–43.
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol 1988; 106: 761–71.
Stahley SN, Saito M, Faundez V, Koval M, Mattheyses AL, Kowalczyk AP. Desmosome assembly and disassembly are membrane raft-dependent. PLoS One 2014; 9: e87809.
Ramirez RD, Herbert B-S, Vaughan MB, et al. Bypass of telomere-dependent replicative senescence (M1) upon overexpression of Cdk4 in normal human epithelial cells. Oncogene 2003; 22: 433–44.
Vaughan MB, Ramirez RD, Brown SA, et al. A reproducible laser-wounded skin equivalent model to study the effects of aging in vitro. Rejuvenation Res 2004; 7: 99–110.
Beckert B, Panico F, Pollman R, Eming R, Banning A, Tikkanen R. Immortalized human hTert/KER-CT keratinocytes a model system for research on desmosomal adhesion and pathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3113.
Hohl D, de Viragh PA, Amiguet-Barras F, Gibbs S, Backendorf C, Huber M. The small proline-rich proteins constitute a multigene family of differentially regulated cornified cell envelope precursor proteins. J Invest Dermatol 1995; 104: 902–9.
Gibbs S, Fijneman R, Wiegant J, van Kessel AG, van De Putte P, Backendorf C. Molecular characterization and evolution of the SPRR family of keratinocyte differentiation markers encoding small proline-rich proteins. Genomics 1993; 16: 630–7.
Carregaro F, Stefanini ACB, Henrique T, Tajara EH. Study of small proline-rich proteins (SPRRs) in health and disease: a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol Res 2013; 305: 857–66.
Tian S, Chen S, Feng Y, Li Y. The interactions of small proline-rich proteins with late cornified envelope proteins are involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2021; 14: 1355–65.
Nomura I, Goleva E, Howell MD, et al. Cytokine milieu of atopic dermatitis, as compared to psoriasis, skin prevents induction of innate immune response genes. J Immunol 2003; 171: 3262–9.
Sugiura H, Ebise H, Tazawa T, et al. Large-scale DNA microarray analysis of atopic skin lesions shows overexpression of an epidermal differentiation gene cluster in the alternative pathway and lack of protective gene expression in the cornified envelope. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: 146–9.
Luo M, Huang P, Pan Y, et al. Weighted gene coexpression network and experimental analyses identify lncRNA SPRR2C as a regulator of the IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cell phenotype through the miR-330/STAT1/S100A7 axis. Cell Death Dis 2021; 12: 86.
Furue M, Furue K, Tsuji G, Nakahara T. Interleukin-17A and keratinocytes in psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 1275.
Tao H, Cheng L, Yang R. Downregulation of miR-34a promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of rat osteoarthritic cartilage cells by activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Clin Interv Aging 2020; 15: 373–85.
Sabnam S, Pal A. Relevance of Erk1/2-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in CEES-induced oxidative stress regulates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol 2019; 35: 541–64.
Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: R17–29.
Gupta R, Ahn R, Lai K, et al. Landscape of long noncoding RNAs in psoriatic and healthy skin. J Invest Dermatol 2016; 136: 603–9.
Zhou Y, Li X, Duan Y, Luo Y, Tang S, Wang J. LncRNA MALAT-1 regulates the growth of interleukin-22-stimulated keratinocytes via the miR-330-5p/S100A7 axis. Autoimmunity 2021; 55: 32–42.
Liu T, Duan X, He J, Yang C. KCNQ1OT1 promotes the proliferation and migration of psoriatic keratinocytes by regulating miR-183-3p/GAB1. Allergol Immunopathol 2021; 49: 125–30.
Wang D, Cheng S, Zou G, Ding X. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and migration of psoriatic keratinocytes via the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-3194-5p/Galectin-7 axis. Anticancer drugs 2021; 33: e423–33.
Bos JD, de Rie MA, Teunissen MBM, Piskin G. Psoriasis: dysregulation of innate immunity. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: 1098–107.
Homey B, Meller S. Chemokines and other mediators as therapeutic targets in psoriasis vulgaris. Clin Dermatol 2008; 26: 539–45.
Griffiths C, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, Barker JNWN. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021; 397: 1301–15.
Wójcik P, Gęgotek A, Žarković N, Skrzydlewska E. Disease-dependent antiapoptotic effects of cannabidiol for keratinocytes observed upon UV irradiation. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 9956.
Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, et al. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell 2017; 170: 605–35.
Gao J, Guo J, Nong Y, et al. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces human HaCaT keratinocytes apoptosis through ROS-mediated PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice. BMC Pharm Toxicol 2020; 21: 41.
Chamcheu J, Adhami VM, Esnault S, et al. Dual inhibition of PI3K/Akt and mTOR by the dietary antioxidant, delphinidin, ameliorates psoriatic features in vitro and in an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like disease in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 2017; 26: 49–69.
Duan Q, Wang G, Wang M, et al. LncRNA RP6-65G23.1 accelerates proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via p-ERK1/2/p-AKT signaling pathway on keratinocytes. J Cell Biochem 2020; 121: 4580–9.
Mercurio L, Albanesi C, Madonna S. Recent updates on the involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR molecular cascade in the pathogenesis of hyperproliferative skin disorders. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021; 8: 665647.
Funding
Financial support: This work was supported by National Major Science and Technology Projects of China (Grant No. 2017YFA0104604) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81773323, 81972937, and 82003344).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Yang, Z., Zhu, M. et al. Role of the long non-coding RNA, SPRR2C, based on an in vitro psoriatic keratinocyte cell model. Eur J Dermatol 32, 171–180 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2022.4247
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2022.4247