Abstract
Background
The efficacy and safety of secukinumab, an interleukin-17 inhibitor, as systemic treatment for patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis have been demonstrated, but real-world data pertaining to this is limited in China.
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of secukinumab in clinical practice in Chinese psoriasis patients with or without psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and identify potential baseline factors that affect the response of patients to secukinumab treatment.
Materials & Methods
Data from 81 patients treated with secukinumab for at least 16 weeks were analysed in a retrospective observational study.
Results
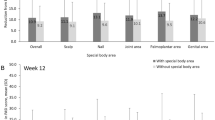
After 16 weeks of treatment with secukinumab, 91.1%, 73%, and 38.3% of patients achieved a PASI 75 (75% improvement based on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index), PASI 90, and PASI 100, respectively. A significant improvement in the quality of life of patients was also observed. Notably, baseline factors, such as young age, lower BMI, no scalp involvement and absence of concomitant PsA, were associated with better clinical response to secukinumab. Approximately 42% of patients (34/81) experienced adverse events, of which the most common was pruritus.
Conclusion
The results demonstrated that secukinumab appears to be an effective treatment alternative for the majority of Chinese plaque psoriasis patients. Baseline factors, including age, BMI, scalp involvement and concomitant presence of PsA, were associated with response to secukinumab.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimball AB, Jacobson C, Weiss S, Vreeland MG, Wu Y. The psychosocial burden of psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol 2005; 6: 383–92.
Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007; 370: 263–71.
Choudhary S, Pradhan D, Pandey A, et al. The association of metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational study. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2020; 20: 703–17.
Lubrano E, Perrotta FM. The role of IL-17 in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017; 13: 815–21.
Alunno A, Carubbi F, Cafaro G, et al. Targeting the IL-23/IL-17 axis for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2015; 15: 1727–37.
Brembilla NC, Senra L, Boehncke WH. The IL-17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: IL-17A and beyond. Front Immunol 2018; 9: 1682.
Blauvelt A, Prinz JC, Gottlieb AB, et al. Secukinumab administration by pre-filled syringe: efficacy, safety and usability results from a randomized controlled trial in psoriasis (FEATURE). Br J Dermatol 2015; 172: 484–93.
Blauvelt A, Reich K, Tsai TF, et al. Secukinumab is superior to ustekinumab in clearing skin of subjects with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis up to 1 year: results from the CLEAR study. JAm Acad Dermatol 2017; 76: 60–9.
Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis-results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 326–38.
Paul C, Lacour JP, Tedremets L, et al. Efficacy, safety and usability of secukinumab administration by autoinjector/pen in psoriasis: a randomized, controlled trial (JUNCTURE). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015; 29: 1082–90.
Zhang J, Gu H, Gu J, et al. Secukinumab 300 mg showed faster and higher efficacy in Chinese moderate to severe plaque psoriasis patients. American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Annual Meeting, 2019. March 1st 2019; Washington, DC.
Mangoni AA, Jackson SH. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2004; 57: 6–14.
Herron MD, Hinckley M, Hoffman MS, et al. Impact of obesity and smoking on psoriasis presentation and management. Arch Dermatol 2005; 141: 1527–34.
Shumack S, Szepietowski J, Rich P, Loffler J, Papavassilis C, Fox T. Secukinumab 300mg shows superior efftcacy across subject body weight groups: Pooled analysis of phase 3 ERASURE and FIXTURE trials. 24th Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology, 2015. Copenhagen, Denmark.
Notario J, Deza G, Vilarrasa E, et al. Treatment of patients with plaque psoriasis with secukinumab in a real-life setting: a 52-week, multicenter, retrospective study in Spain. J Dermatolog Treat 2019; 30: 424–9.
Rompoti N, Katsimbri P, Kokkalis G, et al. Real world data from the use of secukinumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis, including scalp and palmoplantar psoriasis: a 104-week clinical study. Dermatol Ther 2019; 32: e13006.
van den Reek J, van Vugt LJ, van Doorn MBA, et al. Initial results of secukinumab drug survival in patients with psoriasis: a multicentre daily practice cohort study. Acta Derm Venereol 2018; 98: 648–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclosure
Financial support: this study was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81872527, 81130031, 81803117) and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (grant number 1808085QH284). Conflicts of interest: none.
Supplementary material
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Cai, ML., Hong, XJ. et al. Real-world data on the use of secukinumab as treatment for moderate-to-severe psoriasis in Chinese patients. Eur J Dermatol 30, 554–560 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2020.3878
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2020.3878