Abstract
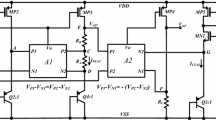
A low temperature drift curvature-compensated complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) bandgap reference is proposed. A dual-differential-pair amplifier was employed to add compensation with a high-order term of TlnT (T is the thermodynamic temperature) to the traditional 1st-order compensated bandgap. To reduce the offset of the amplifier and noise of the bandgap reference, input differential metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) of large size were used in the amplifier and to keep a low quiescent current, these MOSFETs all work in weak inversion. The voltage reference’s temperature curvature has been further corrected by trimming a switched resistor network. The circuit delivers an output voltage of 3 V with a low dropout regulator (LDO). The chip was fabricated in Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC)’s 0.35-μm CMOS process, and the temperature coefficient (TC) was measured to be only 2.1×10−6/°C over the temperature range of −40–125 °C after trimming. The power supply rejection (PSR) was −100 dB @ DC and the noise was 42 μV (rms) from 0.1 to 10 Hz.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan, H., 2006. The Art of Analog Layout (2nd Ed.). Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, China, p.200–212.
Atrash, A.H., Aude, A., 2004. A Bandgap Reference Circuit Utilizing Switching to Reduce Offsets and a Novel Technique for Leakage Current Compensation. 2nd Annual IEEE Northeast Workshop on Circuits and Systems, p.297–300. [doi:10.1109/NEWCAS.2004.1359090]
Behzad, R., 2005. Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China, p.27, 381.
Brito, J.P.M., Bampi, S., Klimach, H., 2007. A 4-bits Trimmed CMOS Bandgap Reference with an Improved Matching Modeling Design. IEEE Int. Symp. on Circuits and Systems, p.1911–1914. [doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2007.378348]
Ekekwe, N., Etienne-Cummings, R., 2008. A 5-bits Precision CMOS Bandgap Reference with On-chip Bi-directional Resistance Trimming. 51st Midwest Symp. on Circuits and Systems, p.257–260. [doi:10.1109/MWSCAS.2008.4616785]
Filanovsky, I.M., Bai, B., Moore, B., 2009. A CMOS Voltage Reference Using Compensation of Mobility and Threshold Voltage Temperature Effects. 52nd IEEE Int. Midwest Symp. on Circuits and Systems, p.29–32. [doi:10.1109/MWSCAS.2009.5236161]
Ge, G., Zhang, C., Hoogzaad, G., Makinwa, K., 2010. A Single-Trim CMOS Bandgap Reference with a 3σ Inaccuracy of ±0.15% from −40 °C to 125 °C. IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits Conf., p.78–79. [doi:10.1109/ISSCC.2010.5434040]
Gray, P.R., Hurst, P.J., Lewis, S.H., Meyer, R.G., 2003. Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits (4th Ed.). Higher Education Press, Beijing, China, p.317–320.
Ivanov, V., Spady, D., 2005. Zero Voltage Class AB Minimal Delay Output Stage and Method. US Patent 0030097.
Ka, N.L., Mok, P.K.T., Chi, Y.L., 2003. A 2-V 23-μA 5.3-ppm/°C curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap voltage reference. IEEE J. Sol.-State Circ., 38(3):561–564. [doi:10.1109/JSSC.2002.808328]
Malcovati, P., Maloberti, F., Fiocchi, C., 2001. Curvaturecompensated BiCMOS bandgap with 1-V supply voltage. IEEE J. Sol.-State Circ., 36(7):1076–1081. [doi:10.1109/4.933463]
Ruzza, S., Dallago, E., Venchi, G., Morini, S., 2008. An Offset Compensation Technique for Bandgap Voltage Reference in CMOS Technology. IEEE Int. Symp. on Circuits and System, p.2226–2229. [doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2008.4541895]
Sanborn, K., Ma, D.S., Ivanov, V., 2007. A sub-1-V low-noise bandgap voltage reference. IEEE J. Sol.-State Circ., 42(11):2466–2481. [doi:10.1109/JSSC.2007.907226]
Spady, D., Ivanov, V., 2005. A CMOS Bandgap Voltage Reference with Absolute Value and Temperature Drift Trims. IEEE Int. Symp. on Circuits and Systems, p.3853–3856. [doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2005.1465471]
Spilka, R., Hirth, M., Hilber, G., Ostermann, T., 2007. On-chip Digitally Trimmable Voltage Reference. Norchip Conf., p.1–4. [doi:10.1109/NORCHP.2007.4481077]
Ueno, K., Hirose, T., Asai, T., Amemiya, Y., 2009. A 300 nW, 15 ppm/°C, 20 ppm/V CMOS voltage reference circuit consisting of subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE J. Sol.-State Circ., 44(7):2047–2053. [doi:10.1109/JSSC.2009.2021922]
Vishal, G., 2007. An Accurate Trimless High PSRR Low-Voltage CMOS Bandgap Reference IC. PhD Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2008ZX01020-001) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, Zh., He, Ln. A low drift curvature-compensated bandgap reference with trimming resistive circuit. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 12, 698–706 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000440
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1000440