Abstract
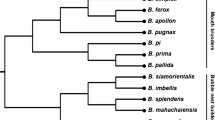
The worldwide chicken gene pool encompasses a remarkable, but shrinking, number of divergently selected breeds of diverse origin. This study was a large-scale genome-wide analysis of the landscape of the complex molecular architecture, genetic variability, and detailed structure among 49 populations. These populations represent a significant sample of the world’s chicken breeds from Europe (Russia, Czech Republic, France, Spain, UK, etc.), Asia (China), North America (USA), and Oceania (Australia). Based on the results of breed genotyping using the Illumina 60K single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chip, a bioinformatic analysis was carried out. This included the calculation of heterozygosity/homozygosity statistics, inbreeding coefficients, and effective population size. It also included assessment of linkage disequilibrium and construction of phylogenetic trees. Using multidimensional scaling, principal component analysis, and ADMIXTURE-assisted global ancestry analysis, we explored the genetic structure of populations and subpopulations in each breed. An overall 49-population phylogeny analysis was also performed, and a refined evolutionary model of chicken breed formation was proposed, which included egg, meat, dual-purpose types, and ambiguous breeds. Such a large-scale survey of genetic resources in poultry farming using modern genomic methods is of great interest both from the viewpoint of a general understanding of the genetics of the domestic chicken and for the further development of genomic technologies and approaches in poultry breeding. In general, whole genome SNP genotyping of promising chicken breeds from the worldwide gene pool will promote the further development of modern genomic science as applied to poultry.
摘要
全球范围内的鸡品种基因库中涵盖了数量庞大且多样化起源的多种品系,不过这个数量正逐渐减少。本研究采用了大规模的全基因组分析,探究了49个种群的复杂分子结构、遗传变异性以及详细结构组成。这些种群来自于欧洲(如俄罗斯、捷克共和国、法国、西班牙、英国等)、亚洲(如中国)、北美(如美国)和大洋洲(如澳大利亚),代表了世界各地的鸡品种。我们使用Illumina 60K单核苷酸多态性(SNP)芯片对品种进行了基因型分析,然后进行了生物信息学分析。这一分析包括了杂合子/纯合子统计、近交系数和有效种群大小的计算,以及连锁不平衡的评估和系统发生树的构建。通过多维缩放、主成分分析和ADMIXTURE辅助全球祖先分析,我们探索了每个品种种群和亚群的遗传结构。此外,还进行了总体的49个种群的系统发生分析,并提出了一种精细化的鸡品种形成演化模型,其中包括蛋、肉、兼用型和混合的品种。利用现代基因组方法对家禽养殖中的遗传资源进行如此大规模的调查,不仅对于普遍了解家鸡遗传学的角度具有重要意义,而且对于进一步发展家禽育种中的基因组技术和方法也是至关重要的。总而言之,对来自全球基因库的有发展潜力的鸡品种进行全基因组SNP基因分型,将促进现代基因组学在家禽育种中的进一步发展。
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The proprietary SNP genotyping data produced and analyzed in this study were generated using the 60K chicken SNP chip produced by Illumina Inc. for the GWMAS Consortium represented by Cobb-Vantress Inc. (Siloam Springs, AR, USA) and Hendrix Genetics B. V. (Boxmeer, The Netherlands). As such, the datasets generated using this chip are confidential and protected as intellectual property or as trade secrets. As a consequence, the SNP genotyping information used in this study was not made public but rather is kept in a secure database at the RRIFAGB. However, the data can be provided upon reasonable request and can be shared with the third parties upon approval with the GWMAS Consortium. The authors affirm that all data necessary for confirming the conclusions of the article are present within the article, figures, and tables.
References
Abdelmanova AS, Dotsev AV, Romanov MN, et al., 2021. Unveiling comparative genomic trajectories of selection and key candidate genes in egg-type Russian White and meat-type White Cornish chickens. Biology, 10(9):876. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090876
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K, 2009. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res, 19(9):1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.094052.109
Andersson L, 2001. Genetic dissection of phenotypic diversity in farm animals. Nat Rev Genet, 2(2):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/35052563
Barbato M, Orozco-terWengel P, Tapio M, et al., 2015. SNeP: a tool to estimate trends in recent effective population size trajectories using genome-wide SNP data. Front Genet, 6:109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00109
Baumung R, Wieczorek M, 2015. Status and trends of animal genetic resources. In: Scherf BD, Pilling D (Eds.), The Second Report on the State of the World’s Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Assessments, Rome, Italy, p.25–42.
Beissinger TM, Gholami M, Erbe M, et al., 2016. Using the variability of linkage disequilibrium between subpopulations to infer sweeps and epistatic selection in a diverse panel of chickens. Heredity, 116(2): 158–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2015.81
Biscarini F, Cozzi P, Gaspa G, et al., 2019. detectRUNS: detect runs of homozygosity and runs of heterozygosity in diploid genomes. Version 0.9.6. The Comprehensive R Archive Network.
Bondarenko Y, Khvostik V, 2020. Improving the productivity of domestic meat and egg chickens. Bull Sumy Natl Agrar Univ Ser Livest, 2(41):29–32. https://doi.org/10.32845/bsnau.lvst.2020.2.5
Bondarenko YV, Kutnyuk PI, 1995. Some results of genetic monitoring of embryonic defects in poultry populations. In: Gene Pool of Animal Breeds and Methods of its Use: Materials of the International Scientific and Practical Conference Dedicated to the 110th Anniversary of the Birth of Academician N. D. Potemkin. Kharkov, Ukraine, 5–6 December 1995. Ministry of Agriculture and Food of Ukraine, Kharkov Zooveterinary Institute, RIO KhZVI, Kharkov, Ukraine, p.63–64 (in Russian).
Bondarenko YV, Podstreshny AP, 1996. Genetic monitoring of chicken populations. In: Abstracts of the 2nd International Conference on Molecular Genetic Markers of Animals (Kiev, Ukraine, 15–17 May 1996). Agrarna Nauka, Kiev, Ukraine, p.47–48 (in Russian).
Bondarenko YV, Zharkova IP, Romanov MN, 1986. Study of down colour genotype in the collection flock geese at the All-Union Poultry Research and Technological Institute. Naučno-tehničeskij BûLleten’ — Ukrainskij Naučnoissledovatel’skijInstitutPticevodstva, 21:3–7 (in Russian).
Christensen OF, Lund MS, 2010. Genomic prediction when some animals are not genotyped. Genet Sel Evol, 42:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9686-42-2
Corti E, Moiseyeva IG, Romanov MN, 2010. Five-toed chickens: their origin, genetics, geographical spreading and history. Izv Timiryazev S-Kh Akad, (7): 156–170.
Dementeva NV, Romanov MN, Kudinov AA, et al., 2017. Studying the structure of a gene pool population of the Russian White chicken breed by genome-wide SNP scan. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biol, 52(6): 1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.15389/agrobiology.2017.6.1166eng
Dementeva NV, Kudinov AA, Mitrofanova OV, et al., 2018. Genome-wide association study of reproductive traits in a gene pool breed of the Russian White chickens. Reprod Domest Anim, 53(Suppl 2):123–124.
Dementieva NV, Fedorova ES, Krutikova AA, et al., 2020a. Genetic variability of indels in the prolactin and dopamine receptor D2 genes and their association with the yield of allanto-amniotic fluid in Russian White laying hens. Tarım Bilim Derg — J Agric Sci, 26(3):373–379. https://doi.org/10.15832/ankutbd.483561
Dementieva NV, Kudinov AA, Larkina TA, et al., 2020b. Genetic variability in local and imported germplasm chicken populations as revealed by analyzing runs of homozygosity. Animals, 10(10):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10101887
Dementieva NV, Shcherbakov YS, Mitrofanova OV, et al., 2022a. Analysis of the accumulation of homozygosity regions in chickens of the Pushkin breed using data from whole genome genotyping. Ecol Genet, 20(1):31–39. https://doi.org/10.17816/ecogen105942
Dementieva NV, Shcherbakov YS, Tyshchenko VI, et al., 2022b. Comparative analysis of molecular RFLP and SNP markers in assessing and understanding the genetic diversity of various chicken breeds. Genes, 13(10):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101876
Fedorova ES, Dementieva NV, Shcherbakov YS, et al., 2022. Identification of key candidate genes in runs of homozygosity of the genome of two chicken breeds, associated with cold adaptation. Biology, 11(4):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040547
Felício AM, Boschiero C, Balieiro JCC, et al., 2013. Identification and association of polymorphisms in CAPN1 and CAPN3 candidate genes related to performance and meat quality traits in chickens. Genet Mol Res, 12(1):472–482. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.February.8.12
Felsenstein J, 1989. PHYLIP—Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics, 5:164–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-0031.1989.tb00562.x
Felsenstein J, 2005. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.6. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, USA.
Gao CQ, Wang KJ, Hu XY, et al., 2023. Conservation priority and run of homozygosity pattern assessment of global chicken genetic resources. Poult Sci, 102(11):103030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2023.103030
Groenen MAM, Megens HJ, Zare Y, et al., 2011. The development and characterization of a 60K SNP chip for chicken. BMC Genomics, 12:274. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-274
Guo Y, Ou JH, Zan YJ, et al., 2022. Researching on the fine structure and admixture of the worldwide chicken population reveal connections between populations and important events in breeding history. Evol Appl, 15(4):553–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.13241
Jensen J, Mantysaari EA, Madsen P, et al., 1997. Residual maximum likelihood estimation of (co)variance components in multivariate mixed linear models using average information. J Ind Soc Agric Stat, 49:215–236.
Kudinov AA, Dementieva NV, Mitrofanova OV, et al., 2019. Genome-wide association studies targeting the yield of extraembryonic fluid and production traits in Russian White chickens. BMC Genomics, 20:270. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5605-5
Kulibaba R, Tereshchenko A, 2015. Transforming growth factor β1, pituitary-specific transcriptional factor 1 and insulinlike growth factor I gene polymorphisms in the population of the Poltava clay chicken breed: association with productive traits. Agric Sci Pract, 2(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.15407/agrisp2.01.067
Larkina TA, Barkova OY, Peglivanyan GK, et al., 2021. Evolutionary subdivision of domestic chickens: implications for local breeds as assessed by phenotype and genotype in comparison to commercial and fancy breeds. Agriculture, 11(10):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11100914
Letunic I, Bork P, 2019. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res, 47(W1):W256–W259. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz239
Li DY, Li Y, Li M, et al., 2019. Population genomics identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection in chicken. BMC Genomics, 20:263. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5622-4
Mastrangelo S, Ben-Jemaa S, Perini F, et al., 2023. Genome-wide mapping of signatures of selection using a high-density array identified candidate genes for growth traits and local adaptation in chickens. Genet Sel Evol, 55:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-023-00790-6
Mohammadabadi MR, Nikbakhti M, Mirzaee HR, et al., 2010. Genetic variability in three native Iranian chicken populations of the Khorasan province based on microsatellite markers. Genetika, 46(4):572–576.
Moiseeva I, 1995. Fowl genetic resources in Russia. Ptitsevodstvo, 5:12–15 (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, 1996. The state of poultry genetic resources in Russia. Anim Genet Resour, 17:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1014233900000596
Moiseyeva IG, Bannikova LV, Altukhov YP, 1993. State of poultry breeding in Russia: genetic monitoring. Mezhdunar S-Kh Zh, 5–6:66–69.
Moiseyeva IG, Romanov MN, Nikiforov AA, et al., 2003. Evolutionary relationships of Red Jungle Fowl and chicken breeds. Genet Sel Evol, 35(5):403. https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9686-35-5-403
Moiseyeva IG, Kovalenko AT, Mosyakina TV, et al., 2006. Origin, history, genetics and economic traits of the Poltava chicken breed. Elektronnyi Zhurnal [Electronic J], Issue 4. https://web.archive.org/web/20120205195904/http://www.lab-cga.ru/articles/Jornal04/Statia2.htm [Accessed on Sept. 29, 2023] (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, Nikiforov AA, Romanov MN, et al., 2007a. Origin, history, genetics and economic traits of the Yurlov Crower chicken breed. Elektronnyi Zhurnal [Electronic J]. https://web.archive.org/web/20120210170800/http://www.lab-cga.ru/articles/Yurlovskaya/Yurlovskaya.htm [Accessed on Sept. 29, 2023] (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, Romanov MN, Kovalenko AT, et al., 2007b. The Poltava chicken breed of Ukraine: its history, characterization and conservation. Anim Genet Resour, 40: 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1014233900002212
Moiseyeva IG, Corti E, Romanov MN, 2009a. Polydactyly in chickens. In: Fisinin VI (Ed.), Advances in Modern Poultry Science. Proceedings of the 16th International Conference (Sergiyev Posad, Russia, 19–21 May 2009). WPSA, RAAS, Poultry Science and Technology Institute, Sergiyev Posad, Russia, p.51–53 (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, Romanov MN, Alexandrov AV, et al., 2009b. Evolution and genetic diversity of old domestic hen’s breed–Yurlovskaya golosistaya: system analysis of variability forms. Izv Timiryazev S-Kh Akad, (3): 132–147 (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, Sevastyanova AA, Alexandrov AV, et al., 2011. Singing breeds of hens. Priroda, 4:10–18 (in Russian).
Moiseyeva IG, Sevastyanova AA, Alexandrov AV, et al., 2016. Orloff chicken breed: history, current status and studies. Izv Timiryazev S-Kh Akad, (1):78–96 (in Russian).
Oyun NY, Moiseyeva IG, Sevastianova AA, et al., 2015a. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in different populations of Spangled Orloff chickens. Genetika, 51(9):1057–1065 (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.7868/S001667581509009X
Oyun NY, Moiseyeva IG, Sevastianova AA, et al., 2015b. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in different populations of Orloff Spangled chicken breed. Russ J Genet, 51(9): 908–915. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415090094
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D, 2006. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet, 2(12):e190. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0020190
Perini F, Cendron F, Wu Z, et al., 2023. Genomics of dwarfism in Italian local chicken breeds. Genes, 14(3):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030633
Plemyashov KV, Smaragdov MG, Romanov MN, 2021a. Genomic assessment of breeding bulls. In: Pozyabin SV, Kochish II, Romanov MN (Eds.), Materials of the 3rd International Scientific and Practical Conference on Molecular Genetic Technologies for Analysis of Gene Expression Related to Animal Productivity and Disease Resistance. Moscow, Russia, 30 September 2021. Sel’skokhozyaistvennye Tekhnologii, Moscow, Russia, p.363–367 (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.18720/SPBPU/2/z21-43
Plemyashov KV, Smaragdov MG, Romanov MN, 2021b. Molecular genetic polymorphism in animal populations and its application in intensive breeding of dairy cattle—a review. In: Pozyabin SV, Kochish II, Romanov MN (Eds.), Materials of the 3rd International Scientific and Practical Conference on Molecular Genetic Technologies for Analysis of Gene Expression Related to Animal Productivity and Disease Resistance. Moscow, Russia, 30 September 2021. Sel’skokhozyaistvennye Tekhnologii, Moscow, Russia, p.368–378 (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.18720/SPBPU/2/z21-43
Pocrnic I, Obšteter J, Gaynor RC, et al., 2023. Assessment of long-term trends in genetic mean and variance after the introduction of genomic selection in layers: a simulation study. Front Genet, 14:1168212. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1168212
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, et al., 2007. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet, 81(3):559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Qanbari S, Seidel M, Strom TM, et al., 2015. Parallel selection revealed by population sequencing in chicken. Genome Biol Evol, 7(12):3299–3306. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evv222
Ren XF, Guan Z, Zhao XR, et al., 2023. Systematic selection signature analysis of Chinese gamecocks based on genomic and transcriptomic data. Int J Mol Sci, 24(6):5868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065868
Romanov MN, Bondarenko YV, 1994. Introducing the Ukrainian indigenous poultry - the Poltava chickens. Fancy Fowl, 14(2):8–9.
Romanov MN, Weigend S, 1999. Genetic diversity in chicken populations based on microsatellite markers. In: Dekkers JCM, Lamont SJ, Rothschild MF (Eds.), Proceedings of the Conference “From Jay Lush to Genomics: Visions for Animal Breeding and Genetics”. Iowa State University, Department of Animal Science, Ames, IA, USA, p.174.
Romanov MN, Sazanov AA, Moiseyeva IG, et al., 2009. Poultry. In: Cockett NE, Kole C (Eds.), Genome Mapping and Genomics in Animals. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, p.75–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73835-0_5
Romanov MN, Abdelmanova AS, Fisinin VI, et al., 2023. Selective footprints and genes relevant to cold adaptation and other phenotypic traits are unscrambled in the genomes of divergently selected chicken breeds. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 14:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-022-00813-0
Romé H, Varenne A, Hérault F, et al., 2015. GWAS analyses reveal QTL in egg layers that differ in response to diet differences. Genet Sel Evol, 47:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-015-0160-2
Ryabokon YO, Pabat VO, Mykytyuk DM, et al., 2005. Catalog of Poultry Breeding Resources of Ukraine. Poultry Research Institute, Kharkiv, Ukraine (in Ukrainian).
Saitou N, Nei M, 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol, 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sallam M, Wilson PW, Andersson B, et al., 2023. Genetic markers associated with bone composition in Rhode Island Red laying hens. Genet Sel Evol, 55:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-023-00818-x
Sulimova GE, Stolpovsky YA, Kashtanov SN, et al., 2005. Methods of managing the genetic resources of domesticated animals. In: Rysin LP (Ed.), Fundamentals of Biological Resource Management: Collection of Scientific Articles. Partnership of Scientific Publications KMK LLC, Moscow, Russia, p.331–342 (in Russian).
Tagirov MT, Tereshchenko LV, Tereshchenko AV, 2006. Substantiation of the possibility of using primary germ cells as material for the preservation of poultry genetic resources. Ptakhivnytstvo, 58:464–473 (in Russian).
Tan XD, Liu RR, Li W, et al., 2022. Assessment the effect of genomic selection and detection of selective signature in broilers. Poult Sci, 101(6):101856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2022.101856
Tereshchenko OV, Pankova SM, Katerynych OO, 2015. Directions of development of poultry industry. Vìsnik Agrar Nauk, 93:27–30.
Tixier-Boichard M, Coquerelle G, Vilela-Lamego C, et al., 1999. Contribution of data on history, management and phenotype to the description of the diversity between chicken populations sampled within the AVIANDIV project. In: Preisinger R (Ed.), Proceedings of the Poultry Genetics Symposium. Working Group 3 of WPSA, Lohmann Tierzucht, Cuxhaven, Germany, p.15–21.
Vakhrameev AB, Narushin VG, Larkina TA, et al., 2023. Disentangling clustering configuration intricacies for divergently selected chicken breeds. Sci Rep, 13:3319. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-28651-8
VanRaden PM, 2008. Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci, 91(11):4414–4423. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0980
Wang MS, Zhang JJ, Guo X, et al., 2021. Large-scale genomic analysis reveals the genetic cost of chicken domestication. BMC Biol, 19:118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-021-01052-x
Weigend S, Romanov MN, Rath D, 2004a. Methodologies to identify, evaluate and conserve poultry genetic resources. In: XXII World’s Poultry Congress & Exhibition, Book of Abstracts. WPSA - Turkish Branch, Istanbul, Turkey, p.84.
Weigend S, Romanov MN, Ben-Ari G, et al., 2004b. Overview on the use of molecular markers to characterize genetic diversity in chickens. In: XXII World’s Poultry Congress & Exhibition, Book of Abstracts. WPSA–Turkish Branch, Istanbul, Turkey, p.192.
Weir BS, Cockerham CC, 1984. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution, 38(6): 1358–1370. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408641
Wickham H, 2009. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer, New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-98141-3
Wragg D, Mwacharo JM, Alcalde JA, et al., 2012. Analysis of genome-wide structure, diversity and fine mapping of Mendelian traits in traditional and village chickens. Heredity, 109:6–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2012.9
Zakharov-Gesekhus IA, Stolpovsky YA, Ukhanov SV, et al., 2007. Monitoring the gene pools of animal populations in connection with selection tasks and the study of phylogeny. In: Farm Animals. Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia, p.122–124 (in Russian).
Zhang GX, Zhao XH, Wang JY, et al., 2012. Effect of an exon 1 mutation in the myostatin gene on the growth traits of the Bian chicken. Anim Genet, 43(4):458–459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2011.02274.x
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (No. 075-15-2021-1037, Internal No. 15. BRK. 21.0001). We thank the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Chicken GWMAS Consortium, Cobb-Vantress Inc., and Hendrix Genetics B.V. for access to the developed 60K chicken SNP chip produced by Illumina Inc. for the GWMAS Consortium. The skilled technical assistance of Olga M. ROMANOVA in preparing Fig. 4 is kindly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Natalia V. DEMENTIEVA: conceptualization, methodology, software application, investigation, writing - original draft, project administration, and funding acquisition. Michael N. ROMANOV: conceptualization, methodology, software application, investigation, writing - original draft, visualization, project administration, and writing - review & editing. Olga A. NIKOLAEVA, Anna E. RYABOVA, and Artem P. DYSIN: validation. Yuri S. SHCHERBAKOV and Tatiana A. LARKINA: formal analysis. Olga I. STANISHEVSKAYA, Olga V. MITROFANOVA, and Anastasiia I. AZOVTSEVA: resources. Anatoly B. VAKHRAMEEV and Grigoriy K. PEGLIVANYAN: data curation. Darren K. GRIFFIN: writing - review & editing and supervision. Natalia R. REINBACH: visualization. All authors have read and approved the content of the manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Natalia V. DEMENTIEVA, Yuri S. SHCHERBAKOV, Olga I. STANISHEVSKAYA, Anatoly B. VAKHRAMEEV, Tatiana A. LARKINA, Artem P. DYSIN, Olga A. NIKOLAEVA, Anna E. RYABOVA, Anastasiia I. AZOVTSEVA, Olga V. MITROFANOVA, Grigoriy K. PEGLIVANYAN, Natalia R. REINBACH, Darren K. GRIFFIN, and Michael N. ROMANOV declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The experiments on chickens were carried out following the ethical approval by the institutional review board of the RRIFAGB, Branch of the L. K. Ernst Federal Research Center for Animal Husbandry (Protocol No. 2020–4 dated 3 March 2020).
Additional information
Supplementary information
Tables S1–S3; Fig. S1; Data S1 and S2
Electronic supplementary material
11585_2024_443_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds
11585_2024_443_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds
11585_2024_443_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds
11585_2024_443_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds
11585_2024_443_MOESM5_ESM.pdf
Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dementieva, N.V., Shcherbakov, Y.S., Stanishevskaya, O.I. et al. Large-scale genome-wide SNP analysis reveals the rugged (and ragged) landscape of global ancestry, phylogeny, and demographic history in chicken breeds. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 25, 324–340 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300443
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300443
Key words
- Chicken genome diversity
- Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis
- Gene pool
- Global ancestry
- Phylogeny
- Demographic history