Abstract
Objective
Safe and effective anticoagulation is essential for hemodialysis patients who are at high risk of bleeding. The purpose of this trial is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of two-stage regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) combined with sequential anticoagulation and standard calcium-containing dialysate in intermittent hemodialysis (IHD) treatment.
Methods
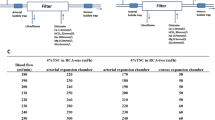
Patients at high risk of bleeding who underwent IHD from September 2019 to May 2021 were prospectively enrolled in 13 blood purification centers of nephrology departments, and were randomly divided into RCA group and saline flushing group. In the RCA group, 0.04 g/mL sodium citrate was infused from the start of the dialysis line during blood draining and at the venous expansion chamber. The sodium citrate was stopped after 3 h of dialysis, which was changed to sequential dialysis without anticoagulant. The hazard ratios for coagulation were according to baseline.
Results
A total of 159 patients and 208 sessions were enrolled, including RCA group (80 patients, 110 sessions) and saline flushing group (79 patients, 98 sessions). The incidence of severe coagulation events of extracorporeal circulation in the RCA group was significantly lower than that in the saline flushing group (3.64% vs. 20.41%, P<0.001). The survival time of the filter pipeline in the RCA group was significantly longer than that in the saline flushing group ((238.34±9.33) min vs. (221.73±34.10) min, P<0.001). The urea clearance index (Kt/V) in the RCA group was similar to that in the saline flushing group with no statistically significant difference (1.12±0.34 vs. 1.08±0.34, P=0.41).
Conclusions
Compared with saline flushing, the two-stage RCA combined with a sequential anticoagulation strategy significantly reduced extracorporeal circulation clotting events and prolonged the dialysis time without serious adverse events.
Abstract
目的
安全有效的抗凝治疗对于高危出血风险的血液透析患者至关重要。本试验的目的是评估应用标准含钙透析液进行双段法局部枸橼酸(RCA)联合序贯抗凝在间歇性血液透析(IHD)治疗中的有效性和安全性。
方法
前瞻性纳入13个肾内科血液净化中心2019年9月至2021年5月行IHD的出血高危患者,随机分为RCA组和生理盐水冲洗组。RCA组使用0.04 g/mL枸橼酸钠分别从透析管路的引血端及静脉壶双段输注,透析3小时后停用枸橼酸钠,并改为无抗凝剂模式序贯透析。根据基线计算凝血风险比。
结果
共纳入159名患者208例次,包括RCA组(80名,110例次)和盐水冲洗组(79名,98例次)。RCA组体外循环管路严重凝血事件的发生率明显低于生理盐水冲洗组(3.64% vs. 20.41%,P<0.001)。RCA组滤器管路的生存时间较生理盐水冲洗组明显延长((238.34±9.33) min和(221.73±34.10) min,P<0.001)。RCA组的尿素清除指数(Kt/V)与生理盐水冲洗组相当,差异无统计学意义(1.12±0.34 vs. 1.08±0.34,P=0.41)。
结论
与生理盐水冲洗相比较,双段法枸橼酸联合序贯抗凝能显著减少体外循环凝血事件,延长透析时间,且未观察到严重不良事件发生。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buturovic J, Gubensek J, Cerne D, et al., 2008. Standard citrate versus sequential citrate/anticoagulant-free anticoagulation during hemodialysis: a randomized trial. Artif Organs, 32(1):77–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2007.00459.x
Buturovic-Ponikvar J, Cerne S, Gubensek J, et al., 2008. Regional citrate anticoagulation for hemodialysis: calcium-free vs. calcium containing dialysate—a randomized trial. Int J Artif Organs, 31(5):418–424. https://doi.org/10.1177/039139880803100507
Buturović-Ponikvar J, Pernat AM, Ponikvar R, 2005. Citrate anticoagulation during plasma exchange in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: short heparin-free hemodialysis helps to attenuate citrate load. Ther Apher Dial, 9(3):258–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1774-9987.2005.00267.x
Daugirdas JT, 1993. Second generation logarithmic estimates of single-pool variable volume Kt/V: an analysis of error. J Am Soc Nephrol, 4(5):1205–1213. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.V451205
European Best Practice Guidelines Expert Group on Hemodialysis, European Renal Association, 2002. V.1 Haemodialysis and prevention of system clotting. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 17(S7):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/17.suppl_7.63
Evenepoel P, Maes B, Vanwalleghem J, et al., 2002. Regional citrate anticoagulation for hemodialysis using a conventional calcium-containing dialysate. Am J Kidney Dis, 39(2): 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.2002.30551
Evenepoel P, Dejagere T, Verhamme P, et al., 2007. Heparincoated polyacrylonitrile membrane versus regional citrate anticoagulation: a prospective randomized study of 2 anticoagulation strategies in patients at risk of bleeding. Am J Kidney Dis, 49(5):642–649. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.02.001
Faguer S, Saint-Cricq M, Nogier MB, et al., 2017. Heparin-free prolonged intermittent hemodialysis using calcium-free citrate dialysate in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med, 45(11):1887–1892. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000002694
Guéry B, Alberti C, Servais A, et al., 2014. Hemodialysis without systemic anticoagulation: a prospective randomized trial to evaluate 3 strategies in patients at risk of bleeding. PLoS ONE, 9(5):e97187. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097187
Khwaja A, 2012. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract, 120(4):c179–c184. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339789
Lin T, Song L, Huang RW, et al., 2019. Modified regional citrate anticoagulation is optimal for hemodialysis in patients at high risk of bleeding: a prospective randomized study of three anticoagulation strategies. BMC Nephrol, 20:472. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1661-y
Morita Y, Johnson RW, Dorn RE, et al., 1961. Regional anticoagulation during hemodialysis using citrate. Am J Med Sci, 242:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000441-196107000-00005
Richtrova P, Rulcova K, Mares J, et al., 2011. Evaluation of three different methods to prevent dialyzer clotting without causing systemic anticoagulation effect. Artif Organs, 35(1):83–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2010.01038.x
Schmitz M, Joannidis M, Czock D, et al., 2018. Regional citrate anticoagulation in renal replacement therapy in the intensive care station: recommendations from the renal section of the DGIIN, ÖGIAIN and DIVI. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed, 113(5):377–383 (in German). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00063-018-0445-7
Swartz RD, Port FK, 1979. Preventing hemorrhage in high-risk hemodialysis: regional versus low-dose heparin. Kidney Int, 16(4):513–518. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1979.157
von Brecht JH, Flanigan MJ, Freeman RM, et al., 1986. Regional anticoagulation: hemodialysis with hypertonic trisodium citrate. Am J Kidney Dis, 8(3):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6386(86)80025-7
Zarbock A, Küllmar M, Kindgen-Milles D, et al., 2020. Effect of regional citrate anticoagulation vs systemic heparin anticoagulation during continuous kidney replacement therapy on dialysis filter life span and mortality among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 324(16):1629–1639. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.18618
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the 1.3.5 Project for Disciplines of Excellence from West China Hospital of Sichuan University (No. ZYGD18027). We thank the assistance of Chengdu Qingshan Likang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author contributions
Ling ZHANG designed the trial and revised the manuscript. Xiaoyan TANG collected and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the conduct of the trial and data collection. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Xiaoyan TANG, Dezheng CHEN, Ling ZHANG, Ping FU, Yanxia CHEN, Zhou XIAO, Xiangcheng XIAO, Weisheng PENG, Li CHENG, Yanmin ZHANG, Hongbo LI, Kehui LI, Bizhen GOU, Xin WU, Qian YU, Lijun JIAN, Zaizhi ZHU, Yu WEN, Cheng LIU, Hen XUE, Hongyu ZHANG, Xin HE, Bin YAN, Liping ZHONG, Bin HUANG, and Mingying MAO declare that they have no conflict of interest.
The ethical approval of this research protocol was obtained from the institutional review boards of the participating hospitals, including West China Hospital of Sichuan University (Project No. 2019 Annual Review (530)), the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University (Project No. 2020 Rapid Approval (035)), Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (Project No. Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Rapid Approval 202008263), Wuhan No. 1 Hospital (Project No. (2020)22), People’s Hospital of Jianyang City (Project No. 2020042), Ziyang People’s Hospital (Project No. 2020-K-2-11), Ya’an People’s Hospital (Project No. 202020), Chengdu Kangfu Kidney Disease Hospital (Project No. 2019530), and the First People’s Hospital of Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture (Project No. 2020068). The trial was registered by the China Clinical Trial Registry with the identification of ChiCTR1900027425. The study has obtained written informed consent from all subjects, and it conforms to the declaration of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki and the code of Good Clinical Practice (GCP).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Chen, D., Zhang, L. et al. Application of regional citrate anticoagulation in patients at high risk of bleeding during intermittent hemodialysis: a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 931–942 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200082
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200082
Key words
- Regional citrate anticoagulation
- Intermittent hemodialysis
- Calcium-containing dialysate
- Saline flushing
- Anticoagulation