Abstract
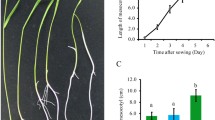
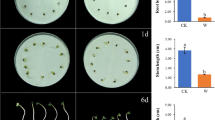
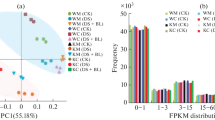
Mesocotyl elongation is a key trait influencing seedling emergence and establishment in direct-seeding rice cultivation. The phytohormone gibberellin (GA) has positive effects on mesocotyl elongation in rice. However, the physiological and molecular basis underlying the regulation of mesocotyl elongation mediated by GA priming under deep-sowing conditions remains largely unclear. In the present study, we performed a physiological and comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of the function of GA priming in mesocotyl elongation and seedling emergence using a direct-seeding japonica rice cultivar ZH10 at a 5-cm sowing depth. Physiological experiments indicated that GA priming significantly improved rice seedling emergence by increasing the activity of starch-metabolizing enzymes and compatible solute content to supply the energy essential for subsequent development. Transcriptomic analysis revealed 7074 differentially expressed genes (false discovery rate of <0.05, |log2(fold change)| of ⩾1) after GA priming. Furthermore, gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses revealed that genes associated with transcriptional regulation, plant hormone biosynthesis or signaling, and starch and sucrose metabolism were critical for GA-mediated promotion of rice mesocotyl elongation. Further analyses showed that the expression of the transcription factor (TF) genes (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (MYB) alternative splicing 1 (MYBAS1), phytochrome-interacting factors 1 (PIF1), Oryza sativa teosinte branched 1/cycloidea/proliferating cell factor 5 (OsTCP5), slender 1 (SLN1), and mini zinc finger 1 (MIF1)), plant hormone biosynthesis or signaling genes (brassinazole-resistant 1 (BZR1), ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase-like (KAO), GRETCHEN HAGEN 3.2 (GH3.2), and small auxin up RNA 36 (SAUR36)), and starch and sucrose metabolism genes (α-amylases (AMY2A and AMY1.4)) was highly correlated with the mesocotyl elongation and deep-sowing tolerance response. These results enhance our understanding of how nutrient metabolism-related substances and genes regulate rice mesocotyl elongation. This may facilitate future studies on related genes and the development of novel rice varieties tolerant to deep sowing.
概要
目的
了解深播条件下赤霉素引发处理调控直播稻中胚轴伸长的生理及分子机制, 以期为水稻中胚轴伸长及耐深播相关候选基因挖掘奠定基础.
创新点
深播条件下, 赤霉素引发处理通过激活淀粉和蔗糖代谢相关基因表达进而增加淀粉酶活性和可溶性糖含量为直播稻中胚轴伸长及深播出苗提供能量; 转录因子基因 (MYBAS1、 PIF1、 OsTCP5、 SLN1、 MIF1)、 植物激素合成和信号转导相关基因 (BZR1、 KAO、 GH3.2、 SAUR36) 及淀粉和蔗糖代谢的相关基因 (AMY2A 和 AMY1.4) 与直播稻深播耐受性高度相关.
方法
设置一系列不同赤霉素浓度的种子引发试验, 在播种后不同时期测定5cm播深条件下直播稻郑旱10号的出苗率、 中胚轴长、 α-淀粉酶和β-淀粉酶活性及可溶性糖等生理指标并进行统计分析; 通过转录组测序及生物信息学的方法研究赤霉素引发处理对深播条件下直播稻中胚轴基因表达的影响; 通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应 (qRT-PCR)方法对筛选出的相关基因进行基因表达分析.
结论
深播条件下, 中胚轴伸长是直播稻出苗的主要动力源, 赤霉素引发处理能够通过增加淀粉酶活性和可溶性糖含量为直播稻中胚轴伸长及深播出苗提供能量; 参与转录调控、 植物激素合成和信号转导、 淀粉和蔗糖代谢的相关基因在由赤霉素介导的水稻中胚轴伸长过程中发挥关键作用; MYBAS1、 PIF1、 BZR1、 KAO、 GH3.2、 AMY2A、 AMY1.4 等正调控因子和 OsTCP5、 SLN1、 SAUR36、 MIF1 等负调控因子与直播稻深播耐受性高度相关.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibu S, Saito Y, Shiwachi H, et al., 2012. Genotypic variation in coleoptile or mesocotyl lengths of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) and seedling emergence in deep sowing. Afr J Agric Res, 7(47):6239–6248. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR12.022
Bai MY, Shang JX, Oh E, et al., 2012. Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol, 14(8): 810–817. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2546
Cai H, Morishima H, 2002. QTL clusters reflect character associations in wild and cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet, 104(8):1217–1228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-001-0819-7
Caño-Delgado A, Yin YH, Yu C, et al., 2004. BRL1 and BRL3 are novel brassinosteroid receptors that function in vascular differentiation in Arabidopsis. Development, 131(21):5341–5351. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01403
Cao LY, Yuan SJ, Zhou HP, et al., 2005. Effect of different hormones on mesocotyl length in Oryza sativa L. Acta Agron Sin, 31(8): 1098–1100 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2005.08.024
Carciofi M, Blennow A, Jensen SL, et al., 2012. Concerted suppression of all starch branching enzyme genes in barley produces amylose-only starch granules. BMC Plant Biol, 12:223. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-223
Claeys H, de Bodt S, Inzé D, 2014. Gibberellins and DELLAs: central nodes in growth regulatory networks. Trends Plant Sci, 19(4):231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.10.001
Dilday RH, Mgonja MA, Amonsilpa SA, et al., 1990. Plant height vs. mesocotyl and celeoptile elongation in rice: linkage or pleitropism? Crop Sci, 30(4):815–818. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1990.0011183X003000040010x
Ding G, Che P, Ilarslan H, et al., 2012. Genetic dissection of methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase indicates a complex role for mitochondrial leucine catabolism during seed development and germination. Plant J, 70(4):562–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04893.x
Feng FJ, Mei HW, Fan PQ, et al., 2017. Dynamic transcriptome and phytohormone profiling along the time of light exposure in the mesocotyl of rice seedling. Sci Rep, 7: 11961. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12326-2
Frigerio M, Alabadí D, Pérez-Gómez J, et al., 2006. Transcriptional regulation of gibberellin metabolism genes by auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 142(2): 553–563. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.084871
He YQ, Cheng JP, He Y, et al., 2019. Influence of isopropylmalate synthase OsIPMS1 on seed vigour associated with amino acid and energy metabolism in rice. Plant Biotechnol J, 17(2):322–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12979
Hirano K, Kouketu E, Katoh H, et al., 2012. The suppressive function of the rice DELLA protein SLR1 is dependent on its transcriptional activation activity. Plant J, 71(3): 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05000.x
Hu W, Ma H, 2006. Characterization of a novel putative zinc finger gene MIF1: involvement in multiple hormonal regulation of Arabidopsis development. Plant J, 45(3): 399–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02626.x
Hu ZY, Yamauchi T, Yang JH, et al., 2014. Strigolactone and cytokinin act antagonistically in regulating rice mesocotyl elongation in darkness. Plant Cell Physiol, 55(1):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct150
Huang C, Jiang SK, Feng LL, et al., 2010. Analysis of QTLs for mesocotyl length in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin, 36(7):1108–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-2780(09)60060-2
Huang YT, Wu W, Zou WX, et al., 2020. Drying temperature affects rice seed vigor via gibberellin, abscisic acid, and antioxidant enzyme metabolism. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(10):796–810. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000297
Hussain S, Zheng MM, Khan F, et al., 2015. Benefits of rice seed priming are offset permanently by prolonged storage and the storage conditions. Sci Rep, 5:8101. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08101
Ikeda M, Fujiwara S, Mitsuda N, et al., 2012. A triantagonistic basic helix-loop-helix system regulates cell elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 24(11):4483–4497. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.105023
Jiang HK, Shui ZW, Xu L, et al., 2020. Gibberellins modulate shade-induced soybean hypocotyl elongation downstream of the mutual promotion of auxin and brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol Biochem, 150:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.042
Jiang HY, 2018. Function Analysis of Maize ZmMYB59 Gene and Its Homologous Gene OsMYBS1 in Rice. MS Thesis, Zhejiang Agriculture & Forestry University, Hangzhou, China (in Chinese).
Jiang SY, Chi YH, Wang JZ, et al., 2015. Sucrose metabolism gene families and their biological functions. Sci Rep, 5: 17583. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17583
Kaneko M, Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, et al., 2002. The α-amylase induction in endosperm during rice seed germination is caused by gibberellin synthesized in epithelium. Plant Physiol, 128(4):1264–1270. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010785
Kato-Noguchi H, Macías FA, 2005. Effects of 6-methoxy-2-benzoxazolinone on the germination and α-amylase activity in lettuce seeds. J Plant Physiol, 162(12): 1304–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2005.03.013
Kwon Y, Kim JH, Nguyen HN, et al., 2013. A novel Arabidopsis MYB-like transcription factor, MYBH, regulates hypocotyl elongation by enhancing auxin accumulation. J Exp Bot, 64(12):3911–3922. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert223
Lee HS, Sasaki K, Higashitani A, et al., 2012. Mapping and characterization of quantitative trait loci for mesocotyl elongation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-5-13
Lee HS, Sasaki K, Kang JW, et al., 2017. Mesocotyl elongation is essential for seedling emergence under deep-seeding condition in rice. Rice, 10:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-017-0173-2
Li KL, Yu RB, Fan LM, et al., 2016. DELLA-mediated PIF degradation contributes to coordination of light and gibberellin signalling in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun, 7:11868. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11868
Li QF, He JX, 2013. Mechanisms of signaling crosstalk between brassinosteroids and gibberellins. Plant Signal Behav, 8(7):e24686. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.24686
Liang Q, Wang C, Ma DR, et al., 2016. Cortical microtubule disorganized related to an endogenous gibberellin increase plays an important role in rice mesocotyl elongation. Plant Biotechnol, 33(2):59–69. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.16.0205a
Lu Q, Zhang MC, Niu XJ, et al., 2016. Uncovering novel loci for mesocotyl elongation and shoot length in indica rice through genome-wide association mapping. Planta, 243(3): 645–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2434-x
Lv YS, Shao GN, Jiao GA, et al., 2021. Targeted mutagenesis of POLYAMINE OXIDASE 5 that negatively regulates mesocotyl elongation enables the generation of direct-seeding rice with improved grain yield. Mol Plant, 14(2): 344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.11.007
Ma DR, Kong DX, Liu XL, et al., 2014. Mesocotyl elongation of weedy rice and its relationship with grain amylase activities and soluble sugar contents. Chin J Rice Sci, 28(1): 97–102 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2014.01.014
Ma WW, Wu FQ, Sheng PK, et al., 2017. The LBD12-1 transcription factor suppresses apical meristem size by repressing argonaute 10 expression. Plant Physiol, 173(1): 801–811. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01699
Mo WP, Tang WJ, Du YX, et al., 2020. PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR-LIKE 14 and SLENDER RICE1 interaction controls seedling growth under salt stress. Plant Physiol, 184(1):506–517. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00024
Oh E, Zhu JY, Wang ZY, 2012. Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses. Nat Cell Biol, 14(8):802–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2545
Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Wei N, et al., 2000. Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature, 405(6785):462–466. https://doi.org/10.1038/35013076
Paik I, Kathare PK, Kim JI, et al., 2017. Expanding roles of PIFs in signal integration from multiple processes. Mol Plant, 10(8):1035–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.07.002
Paparella S, Araújo SS, Rossi G, et al., 2015. Seed priming: state of the art and new perspectives. Plant Cell Rep, 34(8): 1281–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1784-y
Park M, Yim HK, Park HG, et al., 2010. Interference with oxidative phosphorylation enhances anoxic expression of rice α-amylase genes through abolishing sugar regulation. J Exp Bot, 61(12):3235–3244. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq145
Redoña ED, Mackill DJ, 1996. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci in japonica rice. Genome, 39(2):395–403. https://doi.org/10.1139/g96-050
Sakamoto T, Miura K, Itoh H, et al., 2004. An overview of gibberellin metabolism enzyme genes and their related mutants in rice. Plant Physiol, 134(4):1642–1653. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.033696
Salah SM, Guan YJ, Cao DD, et al., 2015. Seed priming with polyethylene glycol regulating the physiological and molecular mechanism in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under nano-ZnO stress. Sci Rep, 5:14278. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14278
Soy J, Leivar P, Monte E, 2014. PIF1 promotes phytochrome-regulated growth under photoperiodic conditions in Arabidopsis together with PIF3, PIF4, and PIF5. J Exp Bot, 65(11):2925–2936. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert465
Stamm P, Kumar PP, 2013. Auxin and gibberellin responsive Arabidopsis SMALL AUXIN UP RNA36 regulates hypocotyl elongation in the light. Plant Cell Rep, 32(6):759–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1406-5
Staswick PE, Serban B, Rowe M, et al., 2005. Characterization of an Arabidopsis enzyme family that conjugates amino acids to indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Cell, 17(2): 616–627. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.026690
Stewart JL, Maloof JN, Nemhauser JL, 2011. PIF genes mediate the effect of sucrose on seedling growth dynamics. PLoS ONE, 6(5):e19894. https://doi.org/10.1371/j.jurnal.pone.0019894
Sun SY, Wang T, Wang LL, et al., 2018. Natural selection of a GSK3 determines rice mesocotyl domestication by coordinating strigolactone and brassinosteroid signaling. Nat Commun, 9:2523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04952-9
Tong HN, Xiao YH, Liu DP, et al., 2014. Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell, 26(11):4376–4393. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.132092
Wang Y, Zhang XB, Lu SJ, et al., 2012. Inhibition of a basal transcription factor 3-like gene Osj10gBTF3 in rice results in significant plant miniaturization and typical pollen abortion. Plant Cell Physiol, 53(12):2073–2089. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs146
Watanabe H, Takahashi K, Saigusa M, 2001. Morphological and anatomical effects of abscisic acid (ABA) and fluridone (FLU) on the growth of rice mesocotyls. Plant Growth Regul, 34(3):273–275. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013333718573
Wu JH, Feng FJ, Lian XM, et al., 2015. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) of mesocotyl elongation based on re-sequencing approach in rice. BMC Plant Biol, 15:218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0608-0
Xiong Q, Ma B, Lu X, et al., 2017. Ethylene-inhibited jasmonic acid biosynthesis promotes mesocotyl/coleoptile elongation of etiolated rice seedlings. Plant Cell, 29(5):1053–1072. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00981
Yang B, Cheng JP, Wang JK, et al., 2019. Physiological characteristics of cold stratification on seed dormancy release in rice. Plant Growth Regul, 89(2):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00516-z
Yang GY, Gao XQ, Ma KH, et al., 2018. The walnut transcription factor JrGRAS2 contributes to high temperature stress tolerance involving in Dof transcriptional regulation and HSP protein expression. BMC Plant Biol, 18:367. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1568-y
Yang L, He ZJ, Zhao WJ, et al., 2017. Growth, physiological, and biochemical responses of Rhodiola kirilowii seedlings to water and shading. Acta Ecol Sin, 37(14): 4706–4714 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201604070639
Zhan JH, Lu X, Liu HY, et al., 2020. Mesocotyl elongation, an essential trait for dry-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.): a review of physiological and genetic basis. Planta, 251:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03322-z
Zhang GF, Zhao HT, Zhang CG, et al., 2019. TCP7 functions redundantly with several Class I TCPs and regulates endoreplication in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol, 61(11): 1151–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12749
Zhang GH, Lin JR, Wu MG, et al., 2005. Analysis on germinating dynamic source of rice (Oryza sativa). Chin J Rice Sci, 19(1):59–62 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.2005.01.011
Zhang YQ, He JX, 2015. Sugar-induced plant growth is dependent on brassinosteroids. Plant Signal Behav, 10(12): e1082700. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1082700
Zhang YQ, Liu ZJ, Wang LG, et al., 2010. Sucrose-induced hypocotyl elongation of Arabidopsis seedlings in darkness depends on the presence of gibberellins. J Plant Physiol, 167(14):1130–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.03.007
Zhao Y, Zhao WP, Jiang CH, et al., 2018. Genetic architecture and candidate genes for deep-sowing tolerance in rice revealed by non-syn GWAS. Front Plant Sci, 9:332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00332
Zheng JS, Hong K, Zeng LJ, et al., 2020. Karrikin signaling acts parallel to and additively with strigolactone signaling to regulate rice mesocotyl elongation in darkness. Plant Cell, 32(9):2780–2805. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00123
Zheng YY, Gao ZP, Zhu ZQ, 2016. DELLA—PIF modules: old dogs learn new tricks. Trends Plant Sci, 21(10):813–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.08.006
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFD0100101-19), the Rice Industry Technology System of Henan Province (No. S2012-04), and the Independent Innovation Fund Program of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (No. 2020ZC07). We thank Dr. Yufeng YANG (Cereal Crops Research Institute, Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Zhengzhou, China) for his helpful suggestions in discussion, as well as Editage (https://www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ya WANG contributed to data analysis and writing of the manuscript. Yuetao WANG, Ruifang YANG, Fuhua WANG, Jing FU, Wenbo YANG, Tao BAI, and Shengxuan WANG performed the experimental research and data analysis. Haiqing YIN contributed to the study design, and writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ya WANG, Yuetao WANG, Ruifang YANG, Fuhua WANG, Jing FU, Wenbo YANG, Tao BAI, Shengxuan WANG, and Haiqing YIN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Supplementary information
Tables S1–S6; Figs. S1–S4
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Yang, R. et al. Effects of gibberellin priming on seedling emergence and transcripts involved in mesocotyl elongation in rice under deep direct-seeding conditions. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22, 1002–1021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100174