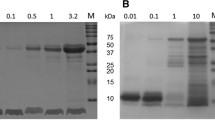
Abstract
Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) is an effective orally administered antibody used to protect against various intestinal pathogens, but which cannot tolerate the acidic gastric environment. In this study, IgY was microencapsulated by alginate (ALG) and coated with chitooligosaccharide (COS). A response surface methodology was used to optimize the formulation, and a simulated gastrointestinal (GI) digestion (SGID) system to evaluate the controlled release of microencapsulated IgY. The microcapsule formulation was optimized as an ALG concentration of 1.56% (15.6 g/L), COS level of 0.61% (6.1 g/L), and IgY/ALG ratio of 62.44% (mass ratio). The microcapsules prepared following this formulation had an encapsulation efficiency of 65.19%, a loading capacity of 33.75%, and an average particle size of 588.75 µm. Under this optimum formulation, the coating of COS provided a less porous and more continuous microstructure by filling the cracks on the surface, and thus the GI release rate of encapsulated IgY was significantly reduced. The release of encapsulated IgY during simulated gastric and intestinal digestion well fitted the zero-order and first-order kinetics functions, respectively. The microcapsule also allowed the IgY to retain 84.37% immune-activity after 4 h simulated GI digestion, significantly higher than that for unprotected IgY (5.33%). This approach could provide an efficient way to preserve IgY and improve its performance in the GI tract.
摘 要
目 的
制备、 优化、 表征和体外评价包埋免疫球蛋白 Y (IgY) 的壳寡糖-海藻酸盐微胶囊, 以实现 IgY 的胃肠道控释, 提高 IgY 胃肠道消化过程中的活性保持率.
创新点
以壳寡糖为涂层, 采用两步法制备包埋 IgY 的微胶囊; 采用响应面法全面优化了微胶囊的配方工艺; 对 IgY 的体外控释进行了系统的评价.
方 法
通过两步离子凝胶法制备包埋 IgY 的微胶囊, 采用响应面法优化微胶囊配方工艺, 通过包埋率、 负载率、 平均粒径、 微观形貌、 色度和球形度等指标表征微胶囊, 采用模拟胃肠道消化体系体外评价 IgY 的释放动力学和免疫活性保持率.
结 论
采用响应面法优化的微胶囊配方工艺为海藻酸钠浓度1.56%(15.6 g/L)、 壳寡糖浓度 0.61%(6.1 g/L) 和 IgY/海藻酸钠比率 62.44% (质量比), 由此制备的微胶囊包埋率达 65.19%, 负载率达 33.75%, 平均粒径为 588.75 μm. 壳寡糖涂层通过填充效应和静电相互作用使微胶囊表面更加光滑和连续, 从而显著降低了模拟胃肠道消化过程中 IgY 的释放速率. 微胶囊中 IgY 的模拟胃部控释和模拟肠道控释分别符合零级动力学方程和一级动力学方程 (R2 > 0.99). 微胶囊在模拟胃肠道消化 4 h 后的 IgY 免疫活性保持率达 84.37%, 远高于未进行微胶囊化保护的 IgY (5.33%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anal AK, Bhopatkar D, Tokura S, et al., 2003. Chitosanalginate multilayer beads for gastric passage and controlled intestinal release of protein. Drug Dev Ind Pharm, 29(6):713–724. https://doi.org/10.1081/DDC-120021320
Bakhshi M, Ebrahimi F, Nazarian S, et al., 2017. Nanoencapsulation of chicken immunoglobulin (IgY) in sodium alginate nanoparticles: in vitro characterization. Biologicals, 49:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biologicals.2017.06.002
Cai YC, Guo J, Chen SH, et al., 2012. Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY) for detecting circulating antigens of Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitol Int, 61(3):385–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2012.01.008
Carlander D, Kollberg H, Wejåker PE, et al., 2000. Peroral immunotheraphy with yolk antibodies for the prevention and treatment of enteric infections. Immunol Res, 21(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1385/ir:21:1:1
Chandika P, Ko SC, Oh GW, et al., 2015. Fish collagen/alginate/chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application. Int J Biol Macromol, 81: 504–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.038
Dávalos-Pantoja L, Ortega-Vinuesa JL, Bastos-González D, et al., 2000. A comparative study between the adsorption of IgY and IgG on latex particles. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed, 11(6):657–673. https://doi.org/10.1163/156856200743931
Eltayeb M, Stride E, Edirisinghe M, 2015. Preparation, characterization and release kinetics of ethylcellulose nanoparticles encapsulating ethylvanillin as a model functional component. J Funct Foods, 14:726–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.02.036
Gandomi H, Abbaszadeh S, Misaghi A, et al., 2016. Effect of chitosan-alginate encapsulation with inulin on survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG during apple juice storage and under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. LWT-Food Sci Technol, 69:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.01.064
Gåserød O, Smidsrød O, Skjåk-Bræk G, 1998. Microcapsules of alginate-chitosan-I: a quantitative study of the interaction between alginate and chitosan. Biomaterials, 19(20): 1815–1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00073-8
Ha HK, Kim JW, Lee MR, et al., 2013. Formation and characterization of quercetin-loaded chitosan oligosaccharide/β-lactoglobulin nanoparticle. Food Res Int, 52(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.02.021
He SD, Zhang Y, Sun HJ, et al., 2019. Antioxidative peptides from proteolytic hydrolysates of false abalone (Volutharpa ampullacea perryi): characterization, identification, and molecular docking. Mar Drugs, 17(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020116
Higuchi T, 1963. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci, 52(12):1145–1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600521210
Igathinathane C, Ulusoy U, 2016. Machine vision methods based particle size distribution of ball- and gyro-milled lignite and hard coal. Powder Technol, 297:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2016.03.032
Jain S, Anal AK, 2016. Optimization of extraction of functional protein hydrolysates from chicken egg shell membrane (ESM) by ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) and enzymatic hydrolysis. LWT-Food Sci Technol, 69:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt2016.0L057
Jeong C, Kim S, Lee C, et al., 2020. Changes in the physical properties of calcium alginate gel beads under a wide range of gelation temperature conditions. Foods, 9(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020180
Kovacs-Nolan J, Mine Y, 2012. Egg yolk antibodies for passive immunity. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol, 3:163–182. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-022811-101137
Kumar Giri T, Thakur D, Alexander A, et al., 2012. Alginate based hydrogel as a potential biopolymeric carrier for drug delivery and cell delivery systems: present status and applications. Curr Drug Deliv, 9(6):539–555. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720112803529800
Lee J, Kang HE, Woo HJ, 2012. Stability of orally administered immunoglobulin in the gastrointestinal tract. J Immunol Methods, 384(1–2):143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2012.06.001
Li XY, Wu MB, Xiao M, et al., 2019. Microencapsulated β-carotene preparation using different drying treatments. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 20(11):901–909. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900157
Lian ZR, Pan R, Wang JT, 2016. Microencapsulation of norfloxacin in chitosan/chitosan oligosaccharides and its application in shrimp culture. Int J Biol Macromol, 92:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.074
Liu CZ, Liu ZZ, Sun X, et al., 2018. Fabrication and characterization of β-lactoglobulin-based nanocomplexes composed of chitosan oligosaccharides as vehicles for delivery of astaxanthin. J Agric Food Chem, 66(26):6717–6726. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00834
Lu CH, Engelmann NJ, Lila MA, et al., 2008. Optimization of lycopene extraction from tomato cell suspension culture by response surface methodology. J Agric Food Chem, 56(17):7710–7714. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf801029k
Mahasukhonthachat K, Sopade PA, Gidley MJ, 2010. Kinetics of starch digestion in sorghum as affected by particle size. J Food Eng, 96(1):18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.06.051
Marcet I, Salvadores M, Rendueles M, et al., 2018. The effect of ultrasound on the alkali extraction of proteins from eggshell membranes. J Sci Food Agric, 98(5):1765–1772. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8651
Mohammadi R, Mohammadifar MA, Mortazavian AM, et al., 2016. Extraction optimization of pepsin-soluble collagen from eggshell membrane by response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chem, 190:186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.073
Otsuka M, Matsuda Y, 1996. Comparative evaluation of mean particle size of bulk drug powder in pharmaceutical preparations by fourier-transformed powder diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy and dissolution kinetics. J Pharm Sci, 85(1):112–116. https://doi.org/10.1021/js9500520
Pauly D, Chacana PA, Calzado EG, et al., 2011. IgY technology: extraction of chicken antibodies from egg yolk by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation. J Vis Exp, (51): e3084. https://doi.org/10.3791/3084
Pereira EPV, van Tilburg MF, Florean EOPT, et al., 2019. Egg yolk antibodies (IgY) and their applications in human and veterinary health: a review. Int Immunopharmacol, 73: 293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.015
Rahman S, van Nguyen S, Icatlo FC Jr., et al., 2013. Oral passive IgY-based immunotherapeutics: a novel solution for prevention and treatment of alimentary tract diseases. Hum Vacc Immunother, 9(5):1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.23383
Ren ZY, Zhang XR, Guo Y, et al., 2017. Preparation and in vitro delivery performance of chitosan-alginate microcapsule for IgG. Food Agric Immunol, 28(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2016.1202206
Ritger PL, Peppas NA, 1987. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J Controlled Release, 5(1):23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-3659(87)90034-4
Rosa-Sibakov N, Sibakov J, Lahtinen P, et al., 2015. Wet grinding and microfluidization of wheat bran preparations: improvement of dispersion stability by structural disintegration. J Cereal Sci, 64:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2015.04.002
Scheraiber M, Grzeskowiak L, Zentek J, et al., 2019. Inclusion of IgY in a dog’s diet has moderate impact on the intestinal microbial fermentation. J Appl Microbiol, 127(4):996–1003. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14378
Vueba ML, Batista de Carvalho LAE, Veiga F, et al., 2004. Influence of cellulose ether polymers on ketoprofen release from hydrophilic matrix tablets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 58(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2004.03.006
Wang T, He N, 2010. Preparation, characterization and applications of low-molecular-weight alginate-oligochitosan nanocapsules. Nanoscale, 2(2):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1039/B9NR00125E
Wang YL, Khan A, Liu YX, et al., 2019. Chitosan oligosaccharide-based dual pH responsive nano-micelles for targeted delivery of hydrophobic drugs. Carbohydr Polym, 223: 115061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115061
Wei TT, Hishikawa A, Shimizu Y, et al., 2014. Particulate characterization of bovine bone granules pulverized with a high-speed blade mill. Powder Technol, 261:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.04.020
Xing PP, Shi YN, Dong CC, et al., 2017. Colon-targeted delivery of IgY against Clostridium difficile toxin A and B by encapsulation in chitosan-Ca pectinate microbeads. AAPS PharmSciTech, 18(4):1095–1103. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-016-0656-2
Xu YF, Lin H, Sui JX, et al., 2012. Effects of specific egg yolk antibody (IgY) on the quality and shelf life of refrigerated Paralichthys olivaceus. J Sci Food Agric, 92(6):1267–1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4693
Zhang J, Yin T, Xiong SB, et al., 2016. Thermal treatments affect breakage kinetics and calcium release of fish bone particles during high-energy wet ball milling. J Food Eng, 183:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.03.027
Zhang J, He SX, Kong FB, et al., 2017. Size reduction and calcium release of fish bone particles during nanomilling as affected by bone structure. Food Bioprocess Technol, 10(12):2176–2187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1987-z
Zhang J, Du HY, Zhang GN, et al., 2020. Identification and characterization of novel antioxidant peptides from crucian carp (Carassius auratus) cooking juice released in simulated gastrointestinal digestion by UPLC-MS/MS and in silico analysis. J Chromatogr B, 1136:121893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121893
Zhang YL, Wei W, Lv PP, et al., 2011. Preparation and evaluation of alginate-chitosan microspheres for oral delivery of insulin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 77(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.09.016
Zimet P, Mombrú ÁW, Faccio R, et al., 2018. Optimization and characterization of nisin-loaded alginate-chitosan nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity in lean beef. LWT, 91:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.01.015
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Chun-jiao SONG and Mrs. Zhenfeng LIAO (Electronic Imaging Laboratory, Public Experimental Platform, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China) for their advice and support on the surface morphology observation of microcapsules.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jin ZHANG performed the experimental research and data analysis, wrote and edited the manuscript. Huan-huan LI, Yi-fan CHEN, Yun-xin YAO, and Xu-ming LIU performed the data analysis. Qian LAN and Xiao-fan YU collected and analyzed the data. Li-hong CHEN and Hong-gang TANG contributed to the study design and data analysis. Fan-bin KONG contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Jin ZHANG, Huan-huan LI, Yi-fan CHEN, Li-hong CHEN, Hong-gang TANG, Fan-bin KONG, Yun-xin YAO, Xu-ming LIU, Qian LAN, and Xiao-fan YU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
No studies using human or animal subjects were performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFD0400305), the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China (No. CARS-40-K26), and the “One Belt and One Road” International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of Zhejiang, China (No. 2019C04022)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, Hh., Chen, Yf. et al. Microencapsulation of immunoglobulin Y: optimization with response surface morphology and controlled release during simulated gastrointestinal digestion. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 611–627 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000172
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000172
Key words
- Immunoglobulin Y (IgY)
- Microencapsulation
- Chitooligosaccharide (COS)
- Response surface methodology (RSM)
- Controlled release
- Simulated gastrointestinal digestion (SGID)