Abstract
Danshen, the dried root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Lamiaceae), is one of the traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) most commonly used for the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, little is known about the chemical and metabolic profiles of danshen in vitro or in vivo. In particular, more information is needed in relation to the 50% ethanol extracts usually used in danshen formulations such as Fufang Xueshuantong Capsules and Fufang Danshen tablets. High-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a linear ion trap- Orbitrap mass spectrometer (HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap) provides a sensitive and accurate method for analyzing the composition of samples. This method was used to determine the in vitro and in vivo chemical and metabolic profiles of danshen. Sixty-nine components of danshen extract and 118 components of danshen in rat plasma, urine, feces, and bile were unambiguously or tentatively identified. These results not only revealed the material composition of danshen, but also provided a comprehensive research approach for the identification of multi-constituents in TCMs.
概要
目的
对丹参50%乙醇提取物的体内外物质基础进行系 统全面的分析。
创新点
首次采用高效液相色谱-质谱联用(HPLC-LTQOrbitrap) 方法对丹参50%乙醇提取物的体内外 化学和代谢成分进行全面分析。
方法
建立HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap 方法,对丹参50%乙醇提取物的化学成分以及给药后大鼠血浆、尿液、粪便和胆汁生物样品中的化学和代谢成分进行分析。
结论
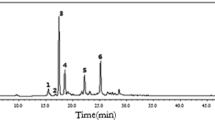
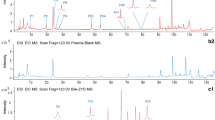
在正负离子模式下,在丹参提取物中鉴定出共69个化合物,包括丹酚酸类化合物23 个,丹参酮类化合物33 个,以及未知化合物13 个;在大鼠灌胃给予丹参提取物后的生物样本中鉴定出共118 个化合物,包括血浆中35 个,尿液中63 个,粪便中62 个,以及胆汁中18 个。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belin DCE, Vessieres E, Guihot AL, et al., 2009. Type 2 diabetes severely impairs structural and functional adaptation of rat resistance arteries to chronic changes in blood flow. Cardiovasc Res, 81(4):788–796. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn334
Cai W, Zhang JY, Dong LY, et al., 2015. Identification of the metabolites of Ixerin Z from Ixeris sonchifolia Hance in rats by HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 107:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.01.004
Duan H, Huang J, Li W, et al., 2013. Protective effects of Fufang Xueshuantong on diabetic retinopathy in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013:408268. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/408268
Gao DY, Han LM, Zhang LH, et al., 2009. Bioavailability of salvianolic acid B and effect on blood viscosities after oral administration of salvianolic acids in beagle dogs. Arch Pharm Res, 32(5):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1517-2
Ji X, Tan BK, Zhu YC, et al., 2003. Comparison of cardioprotective effects using ramipril and DanShen for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sci, 73(11):1413–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00432-6
Kang DG, Oh H, Sohn EJ, et al., 2004. Lithospermic acid B isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorates ischemia/ reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Life Sci, 75(15): 1801–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2004.02.034
Lam BY, Lo AC, Sun X, et al., 2003. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinones in transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Phytomedicine, 10(4):286. https://doi.org/10.1078/094471103322004776
Li X, Yu C, Lu Y, et al., 2007. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of depside salts from Salvia miltiorrhiza in rats. Drug Metab Dispos, 35(2): 234–239. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.106.013045
Liang J, Xu F, Zhang Y, et al., 2013. The profiling and identification of the absorbed constituents and metabolites of Paeoniae Radix Rubra decoction in rat plasma and urine by the HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn technique: a novel strategy for the systematic screening and identification of absorbed constituents and metabolites from traditional Chinese medicines. J Pharmaceut Biomed, 83:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.029
Liu AH, Guo H, Ye M, et al., 2007. Detection, characterization and identification of phenolic acids in Danshen using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A, 1161(1-2):170–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.081
Liu M, Li YG, Zhang F, et al., 2007. Chromatographic fingerprinting analysis of Danshen root (Salvia miltiorrhiza Radix et Rhizoma) and its preparations using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and electrospray mass spectrometry (HPLC-DADESI/ MS). J Sep Sci, 30(14):2256–2267. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200700149
Liu M, Zhao S, Wang Z, et al., 2011. Tentative identification of new metabolites of epimedin C by liquid chromatographymass spectrometry. J Sep Sci, 34(22):3200. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100581
Lv Y, Zhang X, Liang X, et al., 2010. Characterization of the constituents in rat biological fluids after oral administration of Fufang Danshen tablets by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 52(1):155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.12.013
Su CY, Ming QL, Rahman K, et al., 2015. Salvia miltiorrhiza: traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin J Nat Med, 13(3):163–182.
Sun J, Huang SH, Tan BK, et al., 2005. Effects of purified herbal extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza on ischemic rat myocardium after acute myocardial infarction. Life Sci, 76(24):2849–2860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2004.11.016
Sun J, Zhang L, Song J, et al., 2013. Pharmacokinetic study of salvianolic acid A in beagle dog after oral administration by a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method: a study on bioavailability and dose proportionality. J Ethnopharmacol, 148(2):617–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.013
Sun JH, Yang M, Wang XM, et al., 2007. Identification of tanshinones and their metabolites in rat bile after oral administration of TTE-50, a standardized extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza by HPLC-ESI-DAD-MSn. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 44(2):564–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2006.11.003
Wang F, Zhang Q, Lu Z, et al., 2016. Identification of chemical constituents in traditional Chinese medicine formula using HPLC coupled with linear ion trap-Orbitrap MS from high doses of medicinal materials to equivalent doses of formula: study on Xiang-Sha-Liu-Jun-Zi-Jia-Jian granules. J Sep Sci, 39(9):1619–1627. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201501223
Wang YH, Qiu C, Wang DW, et al., 2011. Identification of multiple constituents in the traditional Chinese medicine formula Sheng-Mai San and rat plasma after oral administration by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 54(5):1110–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2010.11.034
Wei Y, Li P, Shu B, et al., 2007. Analysis of chemical and metabolic components in traditional Chinese medicinal combined prescription containing Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza and Radix Panax notoginseng by LC-ESI-MS methods. Biomed Chromatogr, 21(8):797–809. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.775
Wu YT, Chen YF, Hsieh YJ, et al., 2006. Bioavailability of salvianolic acid B in conscious and freely moving rats. Int J Pharm, 326(1-2):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.003
Yang R, Chang L, Guo BY, et al., 2014. Compound danshen dripping pill pretreatment to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2014:256268. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/256268
Zhang J, He Y, Cui M, et al., 2005. Metabolic studies on the total phenolic acids from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza in rats. Biomed Chromatogr, 19(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.415
Zhang J, Cai W, Zhou Y, et al., 2015. Profiling and identification of the metabolites of baicalin and study on their tissue distribution in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci, 985:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.01.018
Zhao X, Yang DH, Xu F, et al., 2015. The in vivo absorbed constituents and metabolites of Danshen decoction in rats identified by HPLC with electrospray ionization tandem ion trap and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr, 29(2):285–304. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2011ZX09201-201-22)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, Hh., Jiang, Mf., Wang, Qh. et al. Metabolic profile of danshen in rats by HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 19, 227–244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700105
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700105