Abstract
Standard treatment options for breast cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies, such as adjuvant hormonal therapy and monoclonal antibodies. Recently, the recognition that chronic inflammation in the tumor microenvironment promotes tumor growth and survival during different stages of breast cancer development has led to the development of novel immunotherapies. Several immunotherapeutic strategies have been studied both preclinically and clinically and already have been shown to enhance the efficacy of conventional treatment modalities. Therefore, therapies targeting the immune system may represent a promising next-generation approach for the treatment of breast cancers. This review will discuss recent findings that elucidate the roles of suppressive immune cells and proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the tumor-promoting microenvironment, and the most current immunotherapeutic strategies in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Breast cancer continues to be the most common cancer in women and represents a major issue of public health (Basu et al., 2013) with 1.38 million new cases and 458 000 deaths yearly world-wide (Bray et al., 2012). Although the incidence and mortality rates of breast cancer in western countries have decreased or at least been stable over the last few decades, both rates are increasing in many developing countries (Jemal et al., 2010). In China, breast cancers are often found at more advanced stages, likely because of the incomplete nationwide screening program. These cancers require more effective treatment combinations (Li et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2013). The majority of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer patients develop resistance to adjuvant hormonal therapy (Osborne and Schiff, 2011), and triple negative breast cancers (TNBCs) (i.e., ER−, progesterone receptor negative (PR−), and HER2/neu negative) also lack effective targeted treatments (Stagg and Allard, 2013). Therefore, novel therapeutic targets are urgently needed to improve the efficacy of conventional treatments.
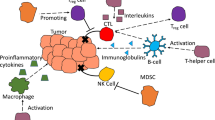
It has long been recognized that the immune system plays a role in the development of tumors. Immune cells can suppress tumor development by killing tumor cells or inhibiting their growth. Conversely, they can also promote tumor progression by selecting tumor cells that are fit to grow in an immune competent host or by establishing an immunosuppressive microenvironment. The interplay between the tumor and the immune system during tumor progression is called immunoediting and comprises three phases: elimination, equilibrium, and escape (Schreiber et al., 2011; Vesely et al., 2011). In the elimination and equilibrium phases, tumors can be completely eliminated or kept in a dormant state by tumor-inhibiting inflammation, characterized by the production of tumor-inhibiting cytokines and the infiltration of cells of both the innate immune system, such as dendritic cells (DCs) and natural killer (NK) cells, and the adaptive immune system, such as Th1 CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (Schreiber et al., 2011; Vesely et al., 2011; Jiang and Shapiro, 2014). On the other hand, in the escape phase, breast tumors often develop multiple mechanisms to evade immunosurveillance. These include the creation of cell autonomous modifications which allow cancer cells to evade antitumor cell-mediated destruction (Shin et al., 2001; Jiang et al., 2006; 2007; 2008; Ryan et al., 2006), and the induction of an immunosuppressive microenvironment by tumor and/or stromal cells, which diminishes the function of effector cells and directly promotes cancer cell proliferation and migration (Jiang and Shapiro, 2014). Chronic inflammation in the tumor microenvironment and the resulting tumor evasion of the immune system have recently been recognized as another hallmark of cancer (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). Although preexisting inflammation and infection are not considered a risk factor for breast cancer development, it is generally accepted that infiltration of immunosuppressive leukocytes and accompanying chronic inflammation during tumor progression promote breast cancer growth (DeNardo and Coussens, 2007; Coussens and Pollard, 2011; Coussens et al., 2013). This review will focus on the protumorigenic immune cell subsets and proinflammatory mediators that form suppressive tumor microenvironments and the most recent findings in human breast cancer immunotherapeutics.
2 Protumorigenic immune cells
2.1 Macrophages
Macrophages are the most plastic cells of the hematopoietic system and have diverse gene-expression profiles and functions (Murray and Wynn, 2011; Gautier et al., 2012; Wynn et al., 2013). Although macrophages were originally thought to be antitumorigenic, compelling preclinical and clinical studies suggest that in most cases macrophages promote tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis (Qian and Pollard, 2010). Increasing macrophage infiltration in the tumor is associated with a worse prognosis for both relapse-free and overall survival of breast cancer patients (Leek et al., 1996; Tsutsui et al., 2005; Mahmoud et al., 2012). Profiling of stromal gene expression in human breast cancers showed that the expression of macrophage-associated genes predicted poorer outcomes (Finak et al., 2008). Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) also inversely correlate with the expression of hormone receptors (i.e., ER, PR, HER2/neu), which are considered favorable prognostic factors (Campbell et al., 2011). As the key element of cancer-related inflammation, macrophages are often classified into either Th1-activated M1 or Th2-activated M2 subtypes. Macrophages within tumor sites are usually of the M2 subtype (Mantovani et al., 2008; Biswas and Mantovani, 2010; Ruffell et al., 2012). Suppressing the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway by hydrazinocurcumin converts the TAM phenotype from M2 to M1 and inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis (Zhang X. et al., 2013). Inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 or enhanced expression of microRNA miR-19a-3p also suppresses breast cancer metastasis by preventing M2 phenotype polarization (Na et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2013a). Anti-angiogenic treatment has also been shown to reprogram TAMs from the M2 to the M1 phenotype and enhance immunotherapy (Huang et al., 2012). This suggests that the M2 subtype promotes tumor progression and metastasis, and that reprogramming macrophages from the M2 to the M1 sub-type can be utilized as a therapeutic strategy. Blockade of macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) or its receptor (CSF1R) rapidly decreases macrophage infiltration, promotes Th1 responses in late-stage breast cancer, and prolongs survival (DeNardo et al., 2011). This suggests that macrophage depletion can be another effective therapeutic strategy.
A huge body of research has demonstrated that, through various mechanisms, TAMs promote tumor angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation, migration and metastasis, and contribute to the creation of a proinflammatory and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (Laoui et al., 2011; Obeid et al., 2013; Tang, 2013). TAMs produced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other proangiogenic factors, such as interleukin (IL)-1, IL-8, and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2, which have all been shown to promote breast cancer angiogenesis (Leek et al., 2000; Lewis et al., 2000; Dirkx et al., 2006). TAMs are also known to directly stimulate breast cancer cell proliferation by producing a wide range of growth factors, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), FGF-2, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) (O’Sullivan et al., 1993; Ribatti et al., 2007). TAMs also promote breast cancer cell survival through α4-integrin-dependent binding of macrophage to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)- expressing tumor cells, which favors breast cancer cell metastatic colonization (Chen et al., 2011). Wolford et al. (2013) showed that induction of the expression of ATF3 and its downstream gene matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in macrophages leads to enhanced breast cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Ishihara et al. (2013) revealed that Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp)-mediated EGF shedding by TAMs was required to enhance breast cancer motility, intravasation, and metastasis. These studies suggest that TAMs promote breast tumor metastasis through enhancing breast cancer cell proliferation and migration.
Breast cancer stem cells (CSCs) represent a population of cells associated with treatment resistance and relapse following therapy (Kakarala and Wicha, 2008; Korkaya et al., 2011). Yang et al. (2013b) showed that TAMs induce a CSC phenotype in breast tumor cells through EGF-activated EGFR/STAT3/SOX2 signaling, suggesting a novel pathway through which TAMs promote breast cancer growth, metastasis, and resistance to chemotherapy. TAMs may also promote the development of a CSC phenotype through fusion with breast cancer cells (Ding et al., 2012). Macrophage- produced IL-6 has also been shown to promote breast CSC self-renewal (Iliopoulos et al., 2009) (Fig. 1). Together, these studies suggest that TAMs play a profound role in many different stages of breast cancer development and may represent a promising therapeutic target (de Palma and Lewis, 2013).
M2-polarized TAM promotes breast cancer progression, metastasis, treatment resistance and recurrence
COX-2 or STAT3 activation polarizes TAM to the M2 phenotype. Expression of microRNA miR-19a-3p in TAM or low dose anti-VEGFR2 treatment polarizes TAM to the M1 phenotype. TAM promotes angiogenesis by producing VEGF, FGF-2, IL-1, and IL-8. TAM also promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by producing EGF, FGF-2, IL-6, TGF-ß, and PDGF. In addition, TAM promotes the breast cancer stem cell phenotype by producing EGF, IL-6, and IL-8 or by fusing with breast cancer cells. Lastly, TAM promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness by producing MMPs and EGF. Abbreviations: TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; BCC, breast cancer cell; BCSC, breast cancer stem cell
2.2 T regulatory (Treg) cells
Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3)-expressing Treg cells are a potent mediator of peripheral immune tolerance and suppress a wide range of immune cells, including CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, NK cells, NKT cells, B cells, and antigen presenting cells, through suppression of target cell activation, proliferation, and effector functions (Shevach, 2009; Sakaguchi et al., 2010; Jiang and Shapiro, 2014). Infiltration of Treg cells into breast cancers has been observed in numerous studies, and the number of Treg cells in the tumor site has been shown to be associated with a worse prognosis (Bates et al., 2006; Bohling and Allison, 2008; Ohara et al., 2009). Circulating Treg cells can be recruited to a breast cancer site through multiple signaling axes, including PGE2/EP2 (EP4), CCL22/CCR4, SDF1/ CXCR4, and CCL5/CCR1 (Gobert et al., 2009; Tan et al., 2011; Yan et al., 2011; Karavitis et al., 2012). Interestingly, the tumor environment may play an active role in promoting Treg cell differentiation and expansion. Tumor cell activated regulatory B cells can directly convert CD4+ T cells into Treg cells in a TGF-β-dependent manner (Olkhanud et al., 2011). Also, impaired production of interferon-α (IFN-α) by plasmacytoid DCs favors expansion of Treg cells infiltrating breast tumor sites (Sisirak et al., 2012). Enhanced TGF-β signaling stimulates tumor infiltrating DCs to produce CCL22, thus promoting Treg cell recruitment and activation (Hanks et al., 2013). CD8+ T cell-derived CCL22 also appears to recruit CCR4+ Treg cells which contribute to forming an immune intrinsic negative feedback loop in the tumor microenvironment (Spranger et al., 2013). This suggests that the tumor-inhibiting immune response may initiate Treg cell recruitment and proliferation in the tumor microenvironment. It was recently shown that Treg cells produce large amounts of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (RANK) ligand (RANKL), which in turn acts on RANK-expressing breast cancer cells and promotes lung metastasis (Tan et al., 2011). This suggests that Tregs can also promote tumor metastasis by directly acting on breast cancer cells in a paracrine fashion. Tamoxifen was shown in an ex vivo study to induce FOXP3 expression in tumor- infiltrating lymphocytes, which may represent a mechanism for hormonal therapy resistance through Treg-mediated immunosuppression (Joffroy et al., 2010). Inhibition of galectin-1 expressed in breast cancer cells is associated with decreased Treg cell accumulation within the tumor and significantly decreases tumor growth and lung metastasis (Dalotto- Moreno et al., 2013). This suggests direct crosstalk between the tumor cells and Treg cells. Consistent with the large body of studies showing that Treg cells are strong promoters of breast cancer progression and metastasis, anti-CD25 antibody-mediated Treg blockade or depletion leads to a stronger antitumor immune response and better clinical outcomes (Rech et al., 2012; Weiss et al., 2012). Together, these studies suggest that the Treg cell is a potent negative regulator of antitumor immune responses and represents an attractive therapeutic target in breast cancer.
2.3 Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs)
MDSCs comprise a heterogeneous population of cells of myeloid origin that expand during pathological conditions such as cancer, inflammation, and infection (Gabrilovich and Nagaraj, 2009; Gabrilovich et al., 2012). Two main populations of MDSCs have been characterized: monocytic MDSC (M-MDSC) and polymorphonuclear MDSC (PMN-MDSC), the latter of which is the prevalent population in tumor-bearing mice (Gabrilovich et al., 2012). The MDSC is another major immunosuppressive cell type found in breast tumors (Markowitz et al., 2013). Circulating levels of MDSCs were shown to correlate with clinical stages of breast cancer, with the highest levels found in patients with extensive metastatic tumor burden (Diaz-Montero et al., 2009). Circulating levels of MDSCs, both before and after chemotherapy, also predict a patient’s response to treatment (Montero et al., 2012).
Factors that induce MDSC expansion include granulocyte-macrophage (GM)-CSF, PGE2, IL-6, stem cell factor (SCF), VEGF, and CCL5, while IFN-γ, ligands of toll-like receptors, IL-13, and IL-4 are associated with MDSC activation (Gabrilovich and Nagaraj, 2009; Zhang Y. et al., 2013a). TGF-β- induced miR-494 was recently shown to facilitate MDSC accumulation and promote their suppressive function in breast cancers (Liu et al., 2012). MDSCs suppress CD8+ T cells by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and arginase 1 (ARG1) enzymes (Gabrilovich et al., 2012). Through nitration of tyrosines in the T cell receptor (TCR)-CD8 complexes, MDSCs also directly disrupt the binding of specific peptide-MHC dimers to CD8+ T cells. This prevents cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) from binding to the peptide-MHC complex and therefore inhibits antitumor activity (Nagaraj et al., 2007). MDSCs can also induce nitration of MHC class I molecules expressed on breast cancer cells, making them unable to effectively present specific peptides and thus rendering tumor cells resistant to antigen-specific CTLs (Lu et al., 2011). More recently, MDSCs were shown to suppress T cell function through STAT3-mediated indolea-mine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) production (Yu J. et al., 2013). In addition to acting as potent T cell suppressors, MDSCs also promote immunosuppression by inducing Treg cell proliferation and inhibiting NK cell activity (Huang et al., 2006; Mauti et al., 2011). Other studies have shown that reduction of the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs is required for induction of the anti-breast tumor immune response (Sinha et al., 2005; Morales et al., 2009; Steding et al., 2011; Thakur et al., 2012). These studies further demonstrate that MDSCs negatively regulate the antitumor immune response, and that MDSC suppression may enhance immunosurveillance against breast cancer cells.
2.4 Th17 cells
Based on the cytokines they produce, CD4+ T helper cells are classically divided into either Th1 or Th2 cells. Th17 is a recently discovered type of CD4+ T helper cell, characterized by the production of IL-17 (Korn et al., 2009). The Th17 cell is well recognized for its role in autoimmunity (Harrington et al., 2005; Dong, 2006). The role of Th17 cells in the microenvironment of various tumors has been studied in recent years. Both antitumor and tumor-promoting functions have been identified in Th17 cells, depending on the tumor type (Zou and Restifo, 2010). Breast cancer-produced PGE2 was shown to induce the expression of IL-23, which then promotes Th17 cell survival and expansion (Qian et al., 2013). Chen et al. (2013) showed that a high number of IL-17 producing cells in breast tumors correlate with high histological grade, negative ER/PR status, and triple-negative phenotype. Moreover, patients with high IL-17 have shorter disease-free survival. Novitskiy et al. (2011) demonstrated a strong association between IL-17 expression and poor outcomes in lymph node-positive, ER-negative, and luminal B subtype breast cancers. A positive correlation between FOXP3+ Treg cells and IL-17-producing Th17 cells was shown in human breast tumors. It was suggested that Th17 cells promote breast cancer progression through the induction of angiogenic factors such as VEGF, MMP9, and IL-8 (Benevides et al., 2013). IL-17 may also promote breast cancer progression by enhancing the protumorigenic functions of MDSCs and TAMs. Interestingly, treatment with an anti-IL17 antibody decreased tumor growth and metastatic burden (Novitskiy et al., 2011). Although these data strongly suggest that IL-17-producing Th17 cells may act as tumor-promoting T helper cells in breast cancer, Yang et al. (2012) showed that the Th17 cell is associated with a favorable prognosis and may display antitumor activity. This suggests plasticity of Th17 cells in breast cancer progression (Coussens et al., 2013). In summary, the Th17 cell likely acts as a tumor-promoting CD4+ T helper cell in breast cancer, but in some clinical settings, it may act as a tumor suppressor. More research is needed to further identify the role that Th17 cells play in different stages of breast cancer development, and only then may Th17 cells be considered a promising therapeutic target.
3 Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines
The role of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-6, IL-1, IL-8, TNF-α, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), CCL5, and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL12), in breast cancer has been extensively studied and reviewed (Ben-Baruch, 2003; Goldberg and Schwertfeger, 2010; Baumgarten and Frasor, 2012). Here, only the most recent findings will be discussed.
IL-6 is a key inflammatory cytokine in a number of diseases. Circulating IL-6 levels are positively associated with clinical tumor stage, lymph node infiltration, and number of distant metastases in breast cancer patients (Salgado et al., 2003; Dethlefsen et al., 2013). However, no correlation between breast cancer risk and the functional polymorphism of the IL-6 gene promoter was observed in a meta-analysis (Yu et al., 2010). Rokavec et al. (2012) showed that the transient induction of IL-6 by monocyte-derived MCP-1 drives a feed-forward inflammatory signaling path-way that leads to constitutive IL-6 production and breast cancer cell transformation and tumorigenesis, revealing a novel mechanistic link between IL-6 and breast cancer initiation. In vitro IL-6 can either promote or inhibit breast cancer cell growth depending on hormone receptor status (Dethlefsen et al., 2013). In TNBC, autocrine expressions of IL-6 and IL-8 are critical for their anchorage-independent growth and resistance to apoptosis (Hartman et al., 2013). IL-6 not only regulates breast CSC self-renewal (Marotta et al., 2011), but also promotes CSC survival and proliferation through the activation of Notch, Wnt, Hedgehog, and TGF-β signaling pathways (Dethlefsen et al., 2013). IL-6 also promotes breast cancer metastasis through the induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Korkaya et al., 2012; Xie et al., 2012; Hwang et al., 2013). These studies suggest that IL-6 may promote breast cancer progression, metastasis, and resistance to treatment by acting on the CSC population and initiating EMT.
IL-8 is highly expressed in ER− breast cancers and increases the invasiveness and metastatic potential of both ER+ and ER− breast cancer cells (Todorović- Raković and Milovanović, 2013). IL-8 promotes CSC self-renewal and invasion by binding to its cognate receptor CXCR1 on CSCs (Charafe-Jauffret et al., 2009). It also affects breast CSC activity measured ex vivo using patient-derived breast cancer samples, through a CXCR1/2-dependent but HER2-independent pathway (Singh et al., 2013). Upregulation of IL-8 through leukotriene B4 receptor 2 (BLT2) activation also promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness (Kim et al., 2012). HER2/HER3 co-expression induced IL-8 autocrine signaling is responsible for breast cancer cell invasiveness (Aceto et al., 2012). Li S. et al. (2012) showed that TWIST1-induced IL-8 also promotes breast cancer cell invasion. Targeting both the JAK2 and STAT5 signaling pathways diminishes IL-8 expression, which in turn decreases tumor metastasis and improves survival (Britschgi et al., 2012). These studies suggest that inhibition of the IL-8 signaling pathway may diminish breast cancer invasiveness and metastasis by acting on breast cancer cells and CSCs.
A recent preclinical study showed that chemotherapy-induced inflammation is one of the main contributors to chemo-resistance and metastasis (Acharyya et al., 2012). Profiles of cytokines and chemokines in the tumor microenvironment showed that chemotherapy strikingly induces endothelial cell production of TNF-α. This enhances tumor cell CXCL1/2 production, which in turn facilitates recruitment of CD11b+Gr1+ MDSCs. These cells release S100A8/9, an inflammatory modulator that activates the p70S6K and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and provides a survival advantage for both primary and metastatic tumor cells (Acharyya et al., 2012). TNF-α also promotes breast cancer metastasis by inducing EMT through the NF-κB-mediated transcriptional activation of TWIST1 (Li C.W. et al., 2012). It was recently shown that targeting transmembrane TNF-α was effective in delaying tumor growth and inhibiting tumor metastasis (Yu M. et al., 2013). TNF-α inhibition may synergize with anti-HER2 therapy to improve treatment outcomes (Ceran et al., 2012). These studies suggest that TNF-α may play a significant role in breast tumor progression not only by directly acting on breast cancer cells, but also by recruiting and activating suppressive immune cells.
CXCL12 is a chemokine that has been shown to be associated with breast cancer metastasis (Boimel et al., 2012; Wendel et al., 2012; Mukherjee and Zhao, 2013). Targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling by using the oncolytic virus therapy strategy inhibits breast cancer metastasis (Gil et al., 2013). It was recently shown that a pair of microRNAs, miR-126 and miR-126*, suppresses breast cancer metastasis by inhibiting the recruitment of tumor promoting mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). CXCL12 was identified as a target gene of miR-126 and miR-126* (Zhang Y. et al., 2013b). These two studies suggest a role for the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in breast cancer metastasis. However, Williams et al. (2010) showed that CXCL12 expression in the primary tumor site may prevent or attenuate breast cancer metastasis by recruiting antitumor immune cells. This suggests that a differential targeting strategy for CXCL12 in the primary tumor site compared to metastatic sites might be needed for the best clinical outcome.
It was recently shown that hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α-mediated paracrine signaling pathways (i.e., CXCL10/CXCR3 and CCL5/CCR5) between MSCs and breast cancer cells promoted metastasis (Chaturvedi et al., 2013). This suggests that hypoxia of the tumor microenvironment may promote metastasis through the synergistic effect of HIF-1α and proinflammatory mediators. In addition to proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, immunosuppressive molecules such as TGF-β, IL-10, and PGE2 are often present in abundant levels in the tumor microenvironment (Wrzesinski et al., 2007; Chen and Smyth, 2011; Hamidullah et al., 2012; Basu et al., 2013). Other suppressive factors produced by breast cancer cells, such as soluble forms of the ligand, soluble major histocompatibility complex class I-related- chain A (sMICA) and IDO, have also been shown to suppress antitumor NK cells and CD8+ T cells (Groh et al., 2002; Uyttenhove et al., 2003; Muller et al., 2005).
Taken together, tumorigenic cytokines, chemokines, and immunosuppressive soluble factors produced by cancer cells or stromal cells promote chronic inflammation in the breast tumor microenvironment. These molecules, in turn, enhance tumor growth and metastasis by directly acting on tumor cells, facilitating recruitment and activation of suppressive immune cells, and suppressing antitumor effector cells.
4 Immunotherapeutic strategies
Escape of tumor cells from immunosurveillance often results from diminished effector cell function and the immune suppressive tumor microenvironment (Schreiber et al., 2011; Vesely et al., 2011). Therefore, the goal of an effective immunotherapy is to boost the antitumor immunity of effector cells and to neutralize tumor-promoting chronic inflammation (Coussens et al., 2013). The proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines and suppressive immune cells present in the breast tumor microenvironment are potential therapeutic targets, as discussed above. Several other immunotherapeutic strategies have been successfully tested in preclinical and/or clinical studies and will be discussed here (Fig. 2).
Scheme of immunotherapeutic strategies
Antitumor immunity can be boosted by antagonizing suppressive factors, such as TGF-ß, IL-10, IDO, and PGE2, inhibition of immune checkpoints, and therapeutic vaccines. Proinflammatory mediators, such as IL-6, IL-8, IL-1, TNF-a, CCL5, CCL2, CXCL10 and CXCL12, can also be targeted. Moreover, depleting or reprogramming suppressive immune cells, such as Treg cells, TAM, or B cells, can also indirectly boost antitumor immunity. Immunotherapy combined with conventional therapies will likely improve the overall therapeutic efficacy. Abbreviations: TGF, transforming growth factor; IL, interleukin; PG, prostaglandin; IDO, indoleamine- pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; CCL, CC chemokine ligand; CSF, colony stimulating factor; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
4.1 Immune checkpoint blockade
The CD8+ T cell is a major antitumor effector cell in breast cancer (Jiang and Shapiro, 2014). CD8+ T cell infiltration is associated with better overall patient outcomes, independent of other prognostic factors such as tumor grade, lymph node stage, size, vascular invasion, and HER2 status (Mahmoud et al., 2011). However, the net effect of CD8+ T cell mediated cytotoxicity is regulated by the balance between costimulatory and inhibitory signals (i.e., immune checkpoints) (Greenwald et al., 2005; Zou and Chen, 2008). One of the most extensively studied immune checkpoint receptors is cytotoxic Tlymphocyte- associated antigen 4 (CTLA4) (Pardoll, 2012). Ipilimumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that suppresses CTLA4 signaling and was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat melanoma in 2011 (Emens, 2012). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from breast cancer patients express higher levels of CTLA4, are less responsive to phytohae-magglutinin (PHA) stimulation, and produce lower levels of IL-2, suggesting that CTLA4 expression in immune cells may be responsible for immune evasion of breast cancer cells (Mao et al., 2010). CTLA4 polymorphisms may also be associated with breast cancer susceptibility and progression in Chinese women (Wang et al., 2007). Fractionated radiotherapy was shown to synergize with anti-CTLA4 therapy to induce antitumor T cell immunity and inhibit the growth of tumors outside the radiation field (i.e., an abscopal effect) (Dewan et al., 2009). This suggests that the anti-CTLA4 antibody may be effective in breast cancer treatment when combined with conventional therapies.
Another well characterized immune checkpoint receptor is programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). A recently completed phase I trial showed that treatment with an anti-PD-1 antibody was safe and produced durable tumor regression in 6%‒17% of patients with melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, or renal cancer (Brahmer et al., 2012). Programmed death-1-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression on breast cancer cells has been shown to inhibit T cell proliferation and induce their apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2008). The presence of PD-1+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is associated with a significantly worse overall survival, and further subtype analysis showed that this is associated with worse survival in luminal B and basal-like sub-types (Muenst et al., 2013). A very recent preclinical study showed that COX-2 deficient breast cancer cells express lower levels of PD-L1, which leads to suppression of tumor growth in immune competent mice (Markosyan et al., 2013). Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy has been shown to enhance the response to radiotherapy and DC vaccines in established breast cancers (Verbrugge et al., 2012; Ge et al., 2013). Anti-PD-1 antibody also significantly improves the effectiveness of the anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in immunocompetent mice (Stagg et al., 2011). Together, these studies suggest that anti-PD-1 may be used in combination with other therapies to improve the overall treatment efficacy in breast cancer.
4.2 Therapeutic vaccines
Therapeutic cancer vaccine is another strategy to boost the host immune system to suppress tumor growth. The principle is to utilize tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) to induce targeted immune attack against tumor cells. Numerous preclinical and clinical studies have shown that cancer vaccines are safe and have extremely low levels of toxicity (i.e., mostly limited to grade I and grade II). The most effective outcome is often observed when patients are treated with vaccines in combination with other therapeutic regimens (Schlom, 2012). A large number of early phase breast cancer vaccine clinical trials have been carried out with HER2 TAAs (Emens, 2012; Wiedermann et al., 2013). Miles et al. (2011) showed that the therapeutic vaccine, sialyl-TN-keyhole limpet hemocyanin (STn-KLH), alone did not affect time to progression (TTP) or overall survival. However, a very recent multicenter, double blinded, randomized phase III clinical trial showed that patients with metastatic breast cancer receiving STn-KLH plus endocrine therapy had significantly longer TTP and overall survival (Ibrahim et al., 2013). Another small clinical trial showed that metastatic breast cancer patients treated with a vaccine comprising human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) peptide plus anti-CD25 anti-body had much higher OS than those treated with hTERT vaccine alone (Rech et al., 2012). This suggests that the efficacy of breast cancer vaccines can be enhanced by depleting suppressive components of the tumor microenvironment, such as Treg cells. Antigen- loaded DC vaccines, engineered to produce antibodies against CTLA-4 and glucocorticoid-induced TNFR- related protein (GITR), induced stronger CD8+ T cell immunity against breast cancer cells (Pruitt et al., 2011), suggesting that breast cancer vaccines combined with immune checkpoint inhibition may produce stronger antitumor immunity in vivo. Enhanced HER2/neu-specific immune responses were achieved when breast cancer patients received both the vaccine and the HER2/neu inhibiting monoclonal antibody, trastuzumab (Disis et al., 2009). Low-dose paclitaxel was also able to enhance DC function in preclinical studies (Pfannenstiel et al., 2010). Together, these data suggest that breast cancer vaccines may have the highest efficacy when combined with other therapeutic modalities.
Consistent with earlier findings showing an inverse correlation between prior chemotherapy and the efficacy of vaccine treatment (von Mehren et al., 2000; 2001), a recently reported pilot study of a MUC-1/CEA/TRICOM poxviral-based vaccine showed that only 1 of 12 patients with breast cancer had an objective complete response, whereas all the others had rapid progression of disease (Mohebtash et al., 2011). The only responder was a patient who had minimal disease and was not as heavily pretreated as the others, suggesting that breast cancer vaccine monotherapy in patients with heavy tumor burdens or extensive prior treatment with chemotherapy is not likely to produce a significant clinical benefit. This finding also suggests that breast cancer therapeutic vaccines should be used as early as possible to prevent recurrence and dissemination of tumors (Wiedermann et al., 2013).
5 Concluding remarks
Chronic inflammation in the breast cancer microenvironment, comprised of proinflammatory mediators, immunosuppressive factors, and suppressive immune cells, may represent intrinsic negative feedback in response to a tumor-inhibiting acute immune reaction. The studies reviewed above demonstrate that the immune network plays a significant role in the development and progression of breast cancer. In the future, incorporating some of these factors into the traditional classification scheme may be helpful in determining prognosis and treatment options. Identification of genetic variations that affect inflammation and immunity may provide better therapeutic targets for breast cancer patients, which may allow for a more personalized approach to management. Moreover, identification of these variations may also be useful for designing new preventive approaches for populations with a high risk of developing breast cancer.
In summary, compelling preclinical and clinical studies have shown that the inflammatory microenvironment not only promotes breast cancer progression and metastasis, but also enhances treatment resistance and accelerates recurrence. This knowledge has identified numerous novel targets for breast cancer immunotherapies that include depletion or reprogramming of suppressive immune cells, neutralization of proinflammatory mediators, inhibition of immune checkpoints and immunosuppressive factors, and therapeutic vaccines. A combination of these strategies with conventional breast cancer therapies will likely improve overall treatment efficacy.
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to gratefully acknowledge Dr. Yon SUNG (Stanford University, USA) for critically reading and editing this manuscript.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Xinguo JIANG declares that he has no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
References
Aceto, N., Duss, S., Macdonald, G., et al., 2012. Co-expression of HER2 and HER3 receptor tyrosine kinases enhances invasion of breast cells via stimulation of interleukin-8 autocrine secretion. Breast Cancer Res., 14(5):R131. [doi:10.1186/bcr3329]
Acharyya, S., Oskarsson, T., Vanharanta, S., et al., 2012. A CXCL1 paracrine network links cancer chemoresistance and metastasis. Cell, 150(1):165–178. [doi:10.1016/j. cell.2012.04.042]
Basu, S., Nachat-Kappes, R., Caldefie-Chezet, F., et al., 2013. Eicosanoids and adipokines in breast cancer: from molecular mechanisms to clinical considerations. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 18(3):323–360. [doi:10.1089/ars.2011.4408]
Bates, G.J., Fox, S.B., Han, C., et al., 2006. Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of highrisk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J. Clin. Oncol., 24(34):5373–5380. [doi:10.1200/JCO.2006. 05.9584]
Baumgarten, S.C., Frasor, J., 2012. Minireview: Inflammation: an instigator of more aggressive estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers. Mol. Endocrinol., 26(3):360–371. [doi:10.1210/me.2011-1302]
Ben-Baruch, A., 2003. Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: inflammatory cells, cytokines and chemokines in breast cancer progression: reciprocal tumor-microenvironment interactions. Breast Cancer Res., 5(1):31–36. [doi:10.1186/bcr554]
Benevides, L., Cardoso, C.R., Tiezzi, D.G., et al., 2013. Enrichment of regulatory T cells in invasive breast tumor correlates with the upregulation of IL-17A expression and invasiveness of the tumor. Eur. J. Immunol., 43(6):1518–1528. [doi:10.1002/eji.201242951]
Biswas, S.K., Mantovani, A., 2010. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat. Immunol., 11(10):889–896. [doi:10.1038/ni. 1937]
Bohling, S.D., Allison, K.H., 2008. Immunosuppressive regulatory T cells are associated with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes: a potential therapeutic target. Mod. Pathol., 21:1527–1532. [doi:10.1038/modpathol.2008.160]
Boimel, P.J., Smirnova, T., Zhou, Z.N., et al., 2012. Contribution of CXCL12 secretion to invasion of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res., 14(1):R23. [doi:10.1186/ bcr3108]
Brahmer, J.R., Tykodi, S.S., Chow, L.Q., et al., 2012. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med., 366:2455–2465. [doi:10. 1056/NEJMoa1200694]
Bray, F., Jemal, A., Grey, N., et al., 2012. Global cancer transitions according to the Human Development Index (2008‒2030): a population-based study. Lancet Oncol., 13(8):790–801. [doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70211-5]
Britschgi, A., Andraos, R., Brinkhaus, H., et al., 2012. JAK2/STAT5 inhibition circumvents resistance to PI3K/mTOR blockade: a rationale for cotargeting these pathways in metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Cell, 22(6):796–811. [doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.10.023]
Campbell, M.J., Tonlaar, N.Y., Garwood, E.R., et al., 2011. Proliferating macrophages associated with high grade, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and poor clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 128(3):703–711. [doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1154-y]
Ceran, C., Cokol, M., Cingoz, S., et al., 2012. Novel anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies: synergy and antagonism with tumor necrosis factor-α. BMC Cancer, 12(1):450. [doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-450]
Charafe-Jauffret, E., Ginestier, C., Iovino, F., et al., 2009. Breast cancer cell lines contain functional cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular signature. Cancer Res., 69(14):1302–1313. [doi:10.1158/ 0008-5472.CAN-08-2741]
Chaturvedi, P., Gilkes, D.M., Wong, C.C., et al., 2013. Hypoxia- inducible factor-dependent breast cancer-mesenchymal stem cell bidirectional signaling promotes metastasis. J. Clin. Invest., 123:189–205. [doi:10.1172/JCI64993]
Chen, E.P., Smyth, E.M., 2011. COX-2 and PGE2-dependent immunomodulation in breast cancer. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat., 96(1-4):14–20. [doi:10.1016/j. prostaglandins.2011.08.005]
Chen, Q., Zhang, X.H., Massague, J., 2011. Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell., 20(4):538–549. [doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.08.025]
Chen, W.C., Lai, Y.H., Chen, H.Y., et al., 2013. Interleukin- 17-producing cell infiltration in the breast cancer tumour microenvironment is a poor prognostic factor. Histopathology, 63(2):225–233. [doi:10.1111/his.12156]
Coussens, L.M., Pollard, J.W., 2011. Leukocytes in mammary development and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 3(3):a003285. [doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a003285]
Coussens, L.M., Zitvogel, L., Palucka, A.K., 2013. Neutralizing tumor-promoting chronic inflammation: a magic bullet. Science, 339(6117):286–291. [doi:10.1126/science. 1232227]
Dalotto-Moreno, T., Croci, D.O., Cerliani, J.P., et al., 2013. Targeting galectin-1 overcomes breast cancer-associated immunosuppression and prevents metastatic disease. Cancer Res., 73(3):1107–1117. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472. CAN-12-2418]
DeNardo, D.G., Coussens, L.M., 2007. Inflammation and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: crosstalk between adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res., 9(4):212. [doi:10. 1186/bcr1746]
DeNardo, D.G., Brennan, D.J., Rexhepaj, E., et al., 2011. Leukocyte complexity predicts breast cancer survival and functionally regulates response to chemotherapy. Cancer Discov., 1(1):54–67. [doi:10.1158/2159-8274.CD-10-0028]
de Palma, M., Lewis, C.E., 2013. Macrophage regulation of tumor responses to anticancer therapies. Cancer Cell, 23(3):277–286. [doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.013]
Dethlefsen, C., Hojfeldt, G., Hojman, P., 2013. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 138(3):657–664. [doi:10.1007/ s10549-013-2488-z]
Dewan, M.Z., Galloway, A.E., Kawashima, N., et al., 2009. Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Clin. Cancer Res., 15(17):5379–5388. [doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0265]
Diaz-Montero, C.M., Salem, M.L., Nishimura, M.I., et al., 2009. Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 58(1):49–59. [doi:10. 1007/s00262-008-0523-4]
Ding, J., Jin, W., Chen, C., et al., 2012. Tumor associated macrophage×cancer cell hybrids may acquire cancer stem cell properties in breast cancer. PLoS ONE, 7(7):e41942. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041942]
Dirkx, A.E., Oude Egbrink, M.G.A., Wagstaff, J., et al., 2006. Monocyte/macrophage infiltration in tumors: modulators of angiogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol., 80(3):1183–1196. [doi: 10.1189/jlb.0905495]
Disis, M.L., Wallace, D.R., Gooley, T.A., et al., 2009. Concurrent trastuzumab and HER2/neu-specific vaccination in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol., 27(28):4685–4692. [doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.6789]
Dong, C., 2006. Diversification of T-helper-cell lineages: finding the family root of IL-17-producing cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 6(4):329–333. [doi:10.1038/nri1807]
Emens, L.A., 2012. Breast cancer immunobiology driving immunotherapy: vaccines and immune checkpoint blockade. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther., 12(12):1597–1611. [doi:10.1586/era.12.147]
Finak, G., Bertos, N., Pepin, F., et al., 2008. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat. Med., 14(5):518–527. [doi:10.1038/nm1764]
Gabrilovich, D.I., Nagaraj, S., 2009. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 9(3):162–174. [doi:10.1038/nri2506]
Gabrilovich, D.I., Ostrand-Rosenberg, S., Bronte, V., 2012. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 12:253–268. [doi:10.1038/nri3175]
Gautier, E.L., Shay, T., Miller, J., et al., 2012. Gene-expression profiles and transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nat. Immunol., 13:1118–1128. [doi:10.1038/ni. 2419]
Ge, Y., Xi, H., Ju, S., et al., 2013. Blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint during DC vaccination induces potent protective immunity against breast cancer in hu-SCID mice. Cancer Lett., 336(2):253–259. [doi:10. 1016/j.canlet.2013.03.010]
Gil, M., Seshadri, M., Komorowski, M.P., et al., 2013. Targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling with oncolytic virotherapy disrupts tumor vasculature and inhibits breast cancer metastases. PNAS, 110(14):E1291–E1300. [doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220580110]
Gobert, M., Treilleux, I., Bendriss-Vermare, N., et al., 2009. Regulatory T cells recruited through CCL22/CCR4 are selectively activated in lymphoid infiltrates surrounding primary breast tumors and lead to an adverse clinical outcome. Cancer Res., 69(5):2000–2009. [doi:10.1158/ 0008-5472.CAN-08-2360]
Goldberg, J.E., Schwertfeger, K.L., 2010. Proinflammatory cytokines in breast cancer: mechanisms of action and potential targets for therapeutics. Curr. Drug Targets, 11(9):1133–1146. [doi:10.2174/138945010792006799]
Greenwald, R.J., Freeman, G.J., Sharpe, A.H., 2005. The B7 family revisited. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 23(1):515–548. [doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115611]
Groh, V., Wu, J., Yee, C., et al., 2002. Tumour-derived soluble MIC ligands impair expression of NKG2D and T-cell activation. Nature, 419(6908):734–738. [doi:10.1038/ nature01112]
Hamidullah, Changkija, B., Konwar, R., 2012. Role of interleukin-10 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 133(1):11–21. [doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1855-x]
Hanahan, D., Weinberg, R.A., 2011. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 144(5):646–674. [doi:10.1016/j.cell. 2011.02.013]
Hanks, B.A., Holtzhausen, A., Evans, K.S., et al., 2013. Type III TGF-β receptor downregulation generates an immunotolerant tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Invest., 123(9):3925–3940. [doi:10.1172/JCI65745]
Harrington, L.E., Hatton, R.D., Mangan, P.R., et al., 2005. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol., 6:1123–1132. [doi:10.1038/ni1254]
Hartman, Z.C., Poage, G.M., den Hollander, P., et al., 2013. Growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells relies upon coordinate autocrine expression of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8. Cancer Res., 73(11):3470–3480. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4524-T]
Huang, B., Pan, P.Y., Li, Q., et al., 2006. Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res., 66(2):1123–1131. [doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1299]
Huang, Y., Yuan, J., Righi, E., et al., 2012. Vascular normalizing doses of antiangiogenic treatment reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy. PNAS, 109(43):17561–17566. [doi:10.1073/pnas.1215397109]
Hwang, M.S., Yu, N., Stinson, S.Y., et al., 2013. miR-221/222 targets adiponectin receptor 1 to promote the epithelial- to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. PLoS ONE, 8(6):e66502. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066502]
Ibrahim, N.K., Murray, J.L., Zhou, D., et al., 2013. Survival advantage in patients with metastatic breast cancer receiving endocrine therapy plus sialyl Tn-KLH vaccine: post hoc analysis of a large randomized trial. J. Cancer, 4(7):577–584. [doi:10.7150/jca.7028]
Iliopoulos, D., Hirsch, H.A., Struhl, K., 2009. An epigenetic switch involving NF-κB, Lin28, Let-7 microRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell, 139(4):693–706. [doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.014]
Ishihara, D., Dovas, A., Hernandez, L., et al., 2013. Wiskott- Aldrich syndrome protein regulates leukocyte-dependent breast cancer metastasis. Cell Rep., 4(3):429–436. [doi:10. 1016/j.celrep.2013.07.007]
Jemal, A., Center, M.M., DeSantis, C., et al., 2010. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 19(8):1893–1907. [doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0437]
Jiang, X., Shapiro, D.J., 2014. The immune system and inflammation in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 382(1):673–682. [doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.06.003]
Jiang, X., Orr, B.A., Kranz, D.M., et al., 2006. Estrogen induction of the granzyme B inhibitor, proteinase inhibitor 9, protects cells against apoptosis mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Endocrinology, 147(3):1419–1426. [doi:10.1210/en.2005-0996]
Jiang, X., Ellison, S.J., Alarid, E.T., et al., 2007. Interplay between the levels of estrogen and estrogen receptor controls the level of the granzyme inhibitor, proteinase inhibitor 9 and susceptibility to immune surveillance by natural killer cells. Oncogene, 26:4106–4114. [doi:10. 1038/sj.onc.1210197]
Jiang, X., Patterson, N.M., Ling, Y., et al., 2008. Low concentrations of the soy phytoestrogen genistein induce proteinase inhibitor 9 and block killing of breast cancer cells by immune cells. Endocrinology, 149(11):5366–5373. [doi:10.1210/en.2008-0857]
Joffroy, C.M., Buck, M.B., Stope, M.B., et al., 2010. Antiestrogens induce transforming growth factor β-mediated immunosuppression in breast cancer. Cancer Res., 70(4):1314–1322. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3292]
Kakarala, M., Wicha, M.S., 2008. Implications of the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and therapy. J. Clin. Oncol., 26(17):2813–2820. [doi:10.1200/ JCO.2008.16.3931]
Karavitis, J., Hix, L.M., Shi, Y.H., et al., 2012. Regulation of COX2 expression in mouse mammary tumor cells controls bone metastasis and PGE2-induction of regulatory T cell migration. PLoS ONE, 7(9):e46342. [doi:10.1371/ journal.pone.0046342]
Kim, H., Choi, J.A., Park, G.S., et al., 2012. BLT2 up-regulates interleukin-8 production and promotes the invasiveness of breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE, 7(11):e49186. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049186]
Korkaya, H., Liu, S., Wicha, M.S., 2011. Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Invest., 121(10):3804–3809. [doi:10.1172/ JCI57099]
Korkaya, H., Kim, G.I., Davis, A., et al., 2012. Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2+ breast cancer by expanding the cancer stem cell population. Mol. Cell, 47(4):570–584. [doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.06.014]
Korn, T., Bettelli, E., Oukka, M., et al., 2009. IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 27(1):485–517. [doi:10.1146/ annurev.immunol.021908.132710]
Laoui, D., Movahedi, K., van Overmeire, E., et al., 2011. Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: distinct subsets, distinct functions. Int. J. Dev. Biol., 55(7-8-9):861–867. [doi:10.1387/ijdb.113371dl]
Leek, R.D., Lewis, C.E., Whitehouse, R., et al., 1996. Association of macrophage infiltration with angiogenesis and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res., 56(20):4625–4629.
Leek, R.D., Hunt, N.C., Landers, R.J., et al., 2000. Macrophage infiltration is associated with VEGF and EGFR expression in breast cancer. J Pathol., 190(4):430–436. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200003)190:4<430::AID- PATH538>3.3.CO;2-Y]
Lewis, J.S., Landers, R.J., Underwood, J.C., et al., 2000. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by macrophages is up-regulated in poorly vascularized areas of breast carcinomas. J. Pathol., 192(2):150–158. [doi:10. 1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH687>3.0.CO;2-G]
Li, C.W., Xia, W., Huo, L., et al., 2012. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TNF-α requires NF-κB-mediated transcriptional upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res., 72(5):1290–1300. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472. CAN-11-3123]
Li, J., Zhang, B.N., Fan, J.H., et al., 2011. A nation-wide multicenter 10-year (1999-2008) retrospective clinical epidemiological study of female breast cancer in China. BMC Cancer, 11(1):364. [doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-364]
Li, S., Kendall, S.E., Raices, R., et al., 2012. TWIST1 associates with NF-κB subunit RELA via carboxyl-terminal WR domain to promote cell autonomous invasion through IL8 production. BMC Biol., 10(1):73. [doi:10.1186/ 1741-7007-10-73]
Liu, Y., Lai, L., Chen, Q., et al., 2012. MicroRNA-494 is required for the accumulation and functions of tumor-expanded myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting of PTEN. J. Immunol., 188(11):5500–5510. [doi:10. 4049/jimmunol.1103505]
Lu, T., Ramakrishnan, R., Altiok, S., et al., 2011. Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells induce tumor cell resistance to cytotoxic T cells in mice. J. Clin. Invest., 121(10):4015–4029. [doi:10.1172/JCI45862]
Mahmoud, S.M., Paish, E.C., Powe, D.G., et al., 2011. Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol., 29(15):1949–1955. [doi:10. 1200/JCO.2010.30.5037]
Mahmoud, S.M., Lee, A.H., Paish, E.C., et al., 2012. Tumour-infiltrating macrophages and clinical outcome in breast cancer. J. Clin. Pathol., 65(2):159–163. [doi:10.1136/ jclinpath-2011-200355]
Mantovani, A., Allavena, P., Sica, A., et al., 2008. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature, 454(7203):436–444. [doi: 10.1038/nature07205]
Mao, H., Zhang, L., Yang, Y., et al., 2010. New insights of CTLA-4 into its biological function in breast cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets, 10(7):728–736.
Markosyan, N., Chen, E.P., Evans, R.A., et al., 2013. Mammary carcinoma cell derived cyclooxygenase 2 suppresses tumor immune surveillance by enhancing intratumoral immune checkpoint activity. Breast Cancer Res., 15(5):R75. [doi:10.1186/bcr3469]
Markowitz, J., Wesolowski, R., Papenfuss, T., et al., 2013. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 140(1):13–21. [doi:10.1007/s10549- 013-2618-7]
Marotta, L.L., Almendro, V., Marusyk, A., et al., 2011. The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44+CD24− stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J. Clin. Invest., 121(7):2723–2735. [doi:10. 1172/JCI44745]
Mauti, L.A., Le Bitoux, M.A., Baumer, K., et al., 2011. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells are implicated in regulating permissiveness for tumor metastasis during mouse gestation. J. Clin. Invest., 121(7):2794–2807. [doi:10. 1172/JCI41936]
Miles, D., Roche, H., Martin, M., et al., 2011. Phase III multicenter clinical trial of the sialyl-TN (STn)-keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) vaccine for metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist, 16(8):1092–1100. [doi:10.1634/ theoncologist.2010-0307]
Mohebtash, M., Tsang, K.Y., Madan, R.A., et al., 2011. A pilot study of MUC-1/CEA/TRICOM poxviral-based vaccine in patients with metastatic breast and ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res., 17(22):7164–7173. [doi:10.1158/1078-0432. CCR-11-0649]
Montero, A.J., Diaz-Montero, C.M., Deutsch, Y.E., et al., 2012. Phase 2 study of neoadjuvant treatment with NOV-002 in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel in patients with HER-2 negative clinical stage II‒IIIc breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 132(1):215–223. [doi:10.1007/ s10549-011-1889-0]
Morales, J.K., Kmieciak, M., Graham, L., et al., 2009. Adoptive transfer of HER2/neu-specific T cells expanded with alternating gamma chain cytokines mediate tumor regression when combined with the depletion of myeloid- derived suppressor cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 58(6):941–953. [doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0609-z]
Muenst, S., Soysal, S.D., Gao, F., et al., 2013. The presence of programmed death 1 (PD-1)-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 139(3):667–676. [doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2581-3]
Mukherjee, D., Zhao, J., 2013. The role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in breast cancer metastasis. Am. J. Cancer Res., 3(1):46–57.
Muller, A.J., DuHadaway, J.B., Donover, P.S., et al., 2005. Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1, potentiates cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Med., 11(3):312–319. [doi:10.1038/nm1196]
Murray, P.J., Wynn, T.A., 2011. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 11(11):723–737. [doi:10.1038/nri3073]
Na, Y.R., Yoon, Y.N., Son, D.I., et al., 2013. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition blocks M2 macrophage differentiation and suppresses metastasis in murine breast cancer model. PLoS ONE, 8(5):e63451. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone. 0063451]
Nagaraj, S., Gupta, K., Pisarev, V., et al., 2007. Altered recognition of antigen is a mechanism of CD8+ T cell tolerance in cancer. Nat. Med., 13(7):828–835. [doi:10. 1038/nm1609]
Novitskiy, S.V., Pickup, M.W., Gorska, A.E., et al., 2011. TGF-β receptor II loss promotes mammary carcinoma progression by Th17-dependent mechanisms. Cancer Discov., 1(5):430–441. [doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11- 0100]
Obeid, E., Nanda, R., Fu, Y.X., et al., 2013. The role of tumor- associated macrophages in breast cancer progression (review). Int. J. Oncol., 43(1):5–12. [doi:10.3892/ijo. 2013.1938]
Ohara, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Matsuura, K., et al., 2009. Possible involvement of regulatory T cells in tumor onset and progression in primary breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 58(3):441–447. [doi:10.1007/s00262-008- 0570-x]
Olkhanud, P.B., Damdinsuren, B., Bodogai, M., et al., 2011. Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4+ T cells to T-regulatory cells. Cancer Res., 71(10):3505–3515. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4316]
Osborne, C.K., Schiff, R., 2011. Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu. Rev. Med., 62(1):233–247. [doi:10.1146/annurev-med-070909-182917]
O’Sullivan, C., Lewis, C.E., Harris, A.L., et al., 1993. Secretion of epidermal growth factor by macrophages associated with breast carcinoma. Lancet, 342(8864):148–149. [doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)91348-P]
Pardoll, D.M., 2012. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 12(4):252–264. [doi:10.1038/nrc3239]
Pfannenstiel, L.W., Lam, S.S., Emens, L.A., et al., 2010. Paclitaxel enhances early dendritic cell maturation and function through TLR4 signaling in mice. Cell. Immunol., 263(1):79–87. [doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.03.001]
Pruitt, S.K., Boczkowski, D., de Rosa, N., et al., 2011. Enhancement of anti-tumor immunity through local modulation of CTLA-4 and GITR by dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol., 41(12):3553–3563. [doi:10.1002/eji.201141383]
Qian, B.Z., Pollard, J.W., 2010. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell, 141(1):39–51. [doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014]
Qian, X., Gu, L., Ning, H., et al., 2013. Increased Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment is mediated by IL-23 via tumor-secreted prostaglandin E2. J. Immunol., 190(11):5894–5902. [doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203141]
Rech, A.J., Mick, R., Martin, S., et al., 2012. CD25 blockade depletes and selectively reprograms regulatory T cells in concert with immunotherapy in cancer patients. Sci. Transl. Med., 4(134):134ra62. [doi:10.1126/scitranslmed. 3003330]
Ribatti, D., Nico, B., Crivellato, E., et al., 2007. Macrophages and tumor angiogenesis. Leukemia, 21:2085–2089. [doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404900]
Rokavec, M., Wu, W., Luo, J.L., 2012. IL6-mediated suppression of miR-200c directs constitutive activation of inflammatory signaling circuit driving transformation and tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell, 45(6):777–789. [doi:10.1016/j. molcel.2012.01.015]
Ruffell, B., Affara, N.I., Coussens, L.M., 2012. Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol., 33(3):119–126. [doi:10.1016/j. it.2011.12.001]
Ryan, B.M., Konecny, G.E., Kahlert, S., et al., 2006. Survivin expression in breast cancer predicts clinical outcome and is associated with HER2, VEGF, urokinase plasminogen activator and PAI-1. Ann. Oncol., 17(4):597–604. [doi:10. 1093/annonc/mdj121]
Sakaguchi, S., Miyara, M., Costantino, C.M., et al., 2010. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 10(7):490–500. [doi:10.1038/nri2785]
Salgado, R., Junius, S., Benoy, I., et al., 2003. Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer, 103(5):642–646. [doi:10. 1002/ijc.10833]
Schlom, J., 2012. Therapeutic cancer vaccines: current status and moving forward. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 104(8):599–613. [doi:10.1093/jnci/djs033]
Schreiber, R.D., Old, L.J., Smyth, M.J., 2011. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science, 331(6024):1565–1570. [doi:10.1126/science.1203486]
Shevach, E.M., 2009. Mechanisms of Foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity, 30(5):636–645. [doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.010]
Shin, M.S., Kim, H.S., Lee, S.H., et al., 2001. Mutations of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 1 (TRAIL-R1) and receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2) genes in metastatic breast cancers. Cancer Res., 61:4942–4946.
Singh, J.K., Farnie, G., Bundred, N.J., et al., 2013. Targeting CXCR1/2 significantly reduces breast cancer stem cell activity and increases the efficacy of inhibiting HER2 via HER2-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Clin. Cancer Res., 19(3):643–656. [doi:10.1158/1078-0432. CCR-12-1063]
Sinha, P., Clements, V.K., Ostrand-Rosenberg, S., 2005. Interleukin-13-regulated M2 macrophages in combination with myeloid suppressor cells block immune surveillance against metastasis. Cancer Res., 65(24):11743–11751. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0045]
Sisirak, V., Faget, J., Gobert, M., et al., 2012. Impaired IFN-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells favors regulatory T-cell expansion that may contribute to breast cancer progression. Cancer Res., 72(20):5188–5197. [doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3468]
Spranger, S., Spaapen, R.M., Zha, Y., et al., 2013. Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and Tregs in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8+ T cells. Sci. Transl. Med., 5(200):200ra116. [doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3006504]
Stagg, J., Allard, B., 2013. Immunotherapeutic approaches in triple-negative breast cancer: latest research and clinical prospects. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol., 5(3):169–181. [doi: 10.1177/1758834012475152]
Stagg, J., Loi, S., Divisekera, U., et al., 2011. Anti-ErbB-2 mAb therapy requires type I and II interferons and synergizes with anti-PD-1 or anti-CD137 mAb therapy. PNAS, 108(17):7142–7147. [doi:10.1073/pnas.1016569108]
Steding, C.E., Wu, S.T., Zhang, Y., et al., 2011. The role of interleukin-12 on modulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells, increasing overall survival and reducing metastasis. Immunology, 133(2):221–238. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567. 2011.3429.x]
Tan, W., Zhang, W., Strasner, A., et al., 2011. Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL-RANK signalling. Nature, 470(7335):548–553. [doi:10.1038/nature09707]
Tang, X., 2013. Tumor-associated macrophages as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Cancer Lett., 332(1):3–10. [doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013. 01.024]
Thakur, A., Schalk, D., Sarkar, S.H., et al., 2012. A Th1 cytokine-enriched microenvironment enhances tumor killing by activated T cells armed with bispecific antibodies and inhibits the development of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 61(4):497–509. [doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1116-1]
Todorović-Raković, N., Milovanović, J., 2013. Interleukin-8 in breast cancer progression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res., 33(10):563–570. [doi:10.1089/jir.2013.0023]
Tsutsui, S., Yasuda, K., Suzuki, K., et al., 2005. Macrophage infiltration and its prognostic implications in breast cancer: the relationship with VEGF expression and microvessel density. Oncol. Rep., 14(2):425–431.
Uyttenhove, C., Pilotte, L., Theate, I., et al., 2003. Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nat. Med., 9:1269–1274. [doi:10.1038/nm934]
Verbrugge, I., Hagekyriakou, J., Sharp, L.L., et al., 2012. Radiotherapy increases the permissiveness of established mammary tumors to rejection by immunomodulatory antibodies. Cancer Res., 72(13):3163–3174. [doi:10.1158/ 0008-5472.CAN-12-0210]
Vesely, M.D., Kershaw, M.H., Schreiber, R.D., et al., 2011. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 29(1):235–271. [doi:10.1146/annurev- immunol-031210-101324]
von Mehren, M., Arlen, P., Tsang, K.Y., et al., 2000. Pilot study of a dual gene recombinant avipox vaccine containing both carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and B7. 1 transgenes in patients with recurrent CEA-expressing adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res., 6(6):2219–2228.
von Mehren, M., Arlen, P., Gulley, J., et al., 2001. The influence of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and prior chemotherapy on the immunological response to a vaccine (ALVAC-CEA B7. 1) in patients with metastatic carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res., 7(5):1181–1191.
Wang, B., He, M., Wang, L., et al., 2013. Breast cancer screening among adult women in China, 2010. Prev. Chronic Dis., 10:130136. [doi:10.5888/pcd10.130136]
Wang, L., Li, D., Fu, Z., et al., 2007. Association of CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms with sporadic breast cancer in Chinese Han population. BMC Cancer, 7(1):173. [doi:10. 1186/1471-2407-7-173]
Weiss, V.L., Lee, T.H., Song, H., et al., 2012. Trafficking of high avidity HER-2/neu-specific T cells into HER-2/neu- expressing tumors after depletion of effector/memory- like regulatory T cells. PLoS ONE, 7(2):e31962. [doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031962]
Wendel, C., Hemping-Bovenkerk, A., Krasnyanska, J., et al., 2012. CXCR4/CXCL12 participate in extravasation of metastasizing breast cancer cells within the liver in a rat model. PLoS ONE, 7(1):e30046. [doi:10.1371/journal. pone.0030046]
Wiedermann, U., Davis, A.B., Zielinski, C.C., 2013. Vaccination for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer with special focus on Her-2/neu peptide vaccines. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 138(1):1–12. [doi:10.1007/s10549- 013-2410-8]
Williams, S.A., Harata-Lee, Y., Comerford, I., et al., 2010. Multiple functions of CXCL12 in a syngeneic model of breast cancer. Mol. Cancer, 9(1):250. [doi:10.1186/ 1476-4598-9-250]
Wolford, C.C., McConoughey, S.J., Jalgaonkar, S.P., et al., 2013. Transcription factor ATF3 links host adaptive response to breast cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Invest., 123(7):2893–2906. [doi:10.1172/JCI64410]
Wrzesinski, S.H., Wan, Y.Y., Flavell, R.A., 2007. Transforming growth factor-β and the immune response: implications for anticancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res., 13:5262–5270. [doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1157]
Wynn, T.A., Chawla, A., Pollard, J.W., 2013. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature, 496(7446):445–455. [doi:10.1038/nature12034]
Xie, G., Yao, Q., Liu, Y., et al., 2012. IL-6-induced epithelial- mesenchymal transition promotes the generation of breast cancer stem-like cells analogous to mammosphere cultures. Int. J. Oncol., 40(4):1171–1179. [doi:10.3892/ ijo.2011.1275]
Yan, M., Jene, N., Byrne, D., et al., 2011. Recruitment of regulatory T cells is correlated with hypoxia-induced CXCR4 expression, and is associated with poor prognosis in basal-like breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res., 13(2):R47. [doi:10.1186/bcr2869]
Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Chen, C., et al., 2013a. MicroRNA-19a-3p inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization through downregulated expression of Fra-1 proto-oncogene. Oncogene, online. [doi:10.1038/onc.2013.258]
Yang, J., Liao, D., Chen, C., et al., 2013b. Tumor-associated macrophages regulate murine breast cancer stem cells through a novel paracrine EGFR/Stat3/Sox-2 signaling pathway. Stem Cells, 31(2):248–258. [doi:10.1002/stem. 1281]
Yang, L., Qi, Y., Hu, J., et al., 2012. Expression of Th17 cells in breast cancer tissue and its association with clinical parameters. Cell Biochem. Biophys., 62(1):153–159. [doi:10.1007/s12013-011-9276-3]
Yu, J., Du, W., Yan, F., et al., 2013. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells suppress antitumor immune responses through IDO expression and correlate with lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer. J. Immunol., 190(7):3783–3797. [doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201449]
Yu, K.D., Di, G.H., Fan, L., et al., 2010. Lack of an association between a functional polymorphism in the interleukin-6 gene promoter and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis involving 25703 subjects. Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 122(2):483–488. [doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0706-5]
Yu, M., Zhou, X., Niu, L., et al., 2013. Targeting transmembrane TNF-α suppresses breast cancer growth. Cancer Res., 73(13):4061–4074. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN- 12-3946]
Zhang, P., Su, D.M., Liang, M., et al., 2008. Chemopreventive agents induce programmed death-1-ligand 1 (PD-L1) surface expression in breast cancer cells and promote PD-L1-mediated T cell apoptosis. Mol. Immunol., 45(5):1470–1476. [doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.08.013]
Zhang, X., Tian, W., Cai, X., et al., 2013. Hydrazinocurcumin encapsuled nanoparticles "re-educate" tumor-associated macrophages and exhibit anti-tumor effects on breast cancer following STAT3 suppression. PLoS ONE, 8(6):e65896. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065896]
Zhang, Y., Lv, D., Kim, H.J., et al., 2013a. A novel role of hematopoietic CCL5 in promoting triple-negative mammary tumor progression by regulating generation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cell Res., 23(3):394–408. [doi:10.1038/cr.2012.178]
Zhang, Y., Yang, P., Sun, T., et al., 2013b. miR-126 and miR-126* repress recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells and inflammatory monocytes to inhibit breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol., 15(3):284–294. [doi:10.1038/ ncb2690]
Zou, W., Chen, L., 2008. Inhibitory B7-family molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 8(6):467–477. [doi:10.1038/nri2326]
Zou, W., Restifo, N.P., 2010. TH17 cells in tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 10(4):248–256. [doi:10.1038/nri2742]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X. Harnessing the immune system for the treatment of breast cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 15, 1–15 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1300264
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1300264