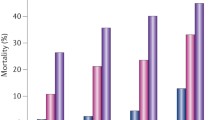
Abstract
Reperfusion is the key strategy in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) care, and it is time-dependent. Shortening the time from symptom to reperfusion and choosing the optimal reperfusion strategy for STEMI patients are great challenges in practice. We need to improve upon the problems of low reperfusion rate, non-standardized treatment, and economic burden in STEMI care. This article briefly reviews the current status of reperfusion strategy in STEMI care, and also introduces what we will do to bridge the gap between the guidelines and implementation in the clinical setting through the upcoming China STEMI early reperfusion program.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Treatment Strategy with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (ASSENT-4 PCI) Investigators, 2006. Primary versus tenecteplase-facilitated percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction (ASSENT-4 PCI): randomised trial. Lancet, 367(9510):569–578. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68147-6]
China Society of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology, 2010. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Chin. J. Cardiol., 38(8):675–690 (in Chinese).
D’souza, S.P., Mamas, M.A., Fraser, D.G., Fath-Ordoubadi, F., 2011. Routine early coronary angioplasty versus ischaemia-guided angioplasty after thrombolysis in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J., 32(8):972–982. [doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq398]
Eagle, K.A., Nallamothu, B.K., Mehta, R.H., Granger, C.B., Steg, P.G., van de Werf, F., López-Sendón, J., Goodman, S.G., Quill, A., Fox, K.A., 2008. Trends in acute reperfusion therapy for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction from 1999 to 2006: we are getting better but we have got a long way to go. Eur. Heart J., 29(5):609–617. [doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn069]
Ellis, S.G., Tendera, M., de Belder, M.A., van Boven, A.J., Widimsky, P., Janssens, L., Andersen, H.R., Betriu, A., Savonitto, S., Adamus, J., et al., 2008. Facilitated PCI in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med., 358(21):2205–2217. [doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0706816]
Huo, Y., 2010. Current status and development of percutaneous coronary intervention in China. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B (Biomed. & Biotechnol.), 11(8):631–633. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B1001012]
Keeley, E.C., Boura, J.A., Grines, C.L., 2003. Primary angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: a quantitative review of 23 randomised trials. Lancet, 361(9351):13–20. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12113-7]
Stettler, C., Wandel, S., Allemann, S., Kastrati, A., Morice, M.C., Schömig, A., Pfisterer, M.E., Stone, G.W., Leon, M.B., de Lezo, J.S., et al., 2007. Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet, 370(9591):937–948. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61444-5]
Widimsky, P., Wijns, W., Fajadet, J., de Belder, M., Knot, J., Aaberge, L., Andrikopoulos, G., Baz, J.A., Betriu, A., Claeys, M., et al., 2010. Reperfusion therapy for ST elevation acute myocardial infarction in Europe: description of the current situation in 30 countries. Eur. Heart J., 31(8):943–957. [doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp492]
Wijns, W., Kolh, P., Danchin, N., di Mario, C., Falk, V., Folliguet, T., Garg, S., Huber, K., James, S., Knuuti, J., et al., 2010. Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J., 31(20):2501–2555. [doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq277]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Huo, Y. Early reperfusion strategy for acute myocardial infarction: a need for clinical implementation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 629–632 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1101010
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1101010
Key words
- Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
- Reperfusion
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Fibrinolysis