Abstract
Objective
To study whether Tongxinluo (TXL) can induce angiogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and to investigate the underlying mechanism.
Methods
Bone marrow MSCs were obtained from male Sprague-Dawley rats. We established an angiogenesis model in vitro via matrigel experiment. MSCs were seeded on matrigel coated 24-well plates, and treated by TXL 50 and 100 mg/L. After 24 h, we observed the tube formations of MSCs in the matrigel. Cell migration ability was examined by wound scratch test and transwell assay. Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fetal liver kinase-1 (Flk-1), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) were analyzed at the protein level by Western blot. Gelatin zymography assay was applied to investigating the MSC paracrine abilities of pro-MMP-2 and activated MMP-2.
Results
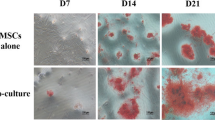
TXL promoted MSC tube formation in matrigel. The ratio of TXL 100 mg/L treated-MSC tubular length was increased 3.04-fold compared to the control group (P<0.05). Scratch test and transwell assay showed that TXL could improve the cell migration ability of MSCs. Western blot experiments showed that TXL promoted MSC synthesis of MMP-2, but it had no influence on the expressions of MMP-9 and TIMP-2. This effect was confirmed by gelatin zymography assay, which showed that TXL increased MSC secretion of pro-MMP-2 and activated MMP-2. VEGF expression of TXL treated-MSCs was increased compared to the control group. The expression of Flk-1 was not different among the groups.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that TXL can promote the tube formation of MSCs, and the underlying mechanisms are associated with increased migration ability of MSCs and the up-regulation of MMP-2 and VEGF expressions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, B.M., Kassem, M., 2008. Human mesenchymal stem cells: from basic biology to clinical applications. Gene Ther., 15(2):109–116. [doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3303067]
Baksh, D., Song, L., Tuan, R.S., 2004. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med., 8(3): 301–316. [doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00320.x]
Behfar, A., Yamada, S., Crespo-Diaz, R., Nesbitt, J.J., Rowe, L.A., Perez-Terzic, C., Gaussin, V., Homsy, C., Bartunek, J., Terzic, A., 2010. Guided cardiopoiesis enhances therapeutic benefit of bone marrow human mesenchymal stem cells in chronic myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 56(9):721–734. [doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.03.066]
Birkedal-Hansen, H., Moore, W.G., Bodden, M.K., Windsor, L.J., Birkedal-Hansen, B., DeCarlo, A., Engler, J.A., 1993. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med., 4(2):197–250.
Dai, J., Rabie, A.B., 2007. VEGF: an essential mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondral ossification. J. Dent. Res., 86(10):937–950. [doi:10.1177/154405910708601006]
Gao, F., He, T., Wang, H., Yu, S., Yi, D., Liu, W., Cai, Z., 2007. A promising strategy for the treatment of ischemic heart disease: mesenchymal stem cell-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer in rats. Can. J. Cardiol., 23(11):891–898. [doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(07)70845-0]
Kim, T.S., Kim, Y.B., 1999. Correlation between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and angiogenesis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. J. Korean Med. Sci., 14:263–270.
Lamalice, L., Le Boeuf, F., Huot, J., 2007. Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ. Res., 100(6):782–794. [doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000259593.07661.1e]
Li, X.D., Yang, Y.J., Geng, Y.J., Jin, C., Hu, F.H., Zhao, J.L., Zhang, H.T., Cheng, Y.T., Qian, H.Y., Wang, L.L., et al., 2010. Tongxinluo reduces myocardial no-reflow and ischemia-reperfusion injury by stimulating the phosphorylation of eNOS via the PKA pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 299(4):H1255–H1261. [doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00459.2010]
Liang, J.Q., Wu, K., Jia, Z.H., Liu, C., Ding, J., Huang, S.N., Yin, P.P., Wu, X.C., Wei, C., Wu, Y.L., et al., 2011. Chinese medicine Tongxinluo modulates vascular endothelial function by inducing eNOS expression via the PI-3K/Akt/HIF-dependent signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol., 133(2):517–523. [doi:10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.031]
Matsumoto, R., Omura, T., Yoshiyama, M., Hayashi, T., Inamoto, S., Koh, K.R., Ohta, K., Izumi, Y., Nakamura, Y., Akioka, K., et al., 2005. Vascular endothelial growth factor-expressing mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 25(6):1168–1173. [doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000165696.25680.ce]
Nagase, H., Woessner, J.J., 1999. Matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem., 274(31):21491–21494. [doi:10.1074/jbc.274.31.21491]
Nguyen, B.K., Maltais, S., Perrault, L.P., Tanguay, J.F., Tardif, J.C., Stevens, L.M., Borie, M., Harel, F., Mansour, S., Noiseux, N., 2010. Improved function and myocardial repair of infarcted heart by intracoronary injection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived growth factors. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res., 3(5):547–558. [doi:10.1007/s12265-010-9171-0]
Ohno-Matsui, K., Uetama, T., Yoshida, T., Hayano, M., Itoh, T., Morita, I., Mochizuki, M., 2003. Reduced retinal angiogenesis in MMP-2-deficient mice. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 44(12):5370–5375. [doi:10.1167/iovs.03-0249]
Olsson, A.K., Dimberg, A., Kreuger, J., Claesson-Welsh, L., 2006. VEGF receptor signalling—in control of vascular function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 7(5):359–371. [doi:10.1038/nrm1911]
Orlic, D., Kajstura, J., Chimenti, S., Bodine, D.M., Leri, A., Anversa, P., 2003. Bone marrow stem cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Pediatr. Transplant., 7(Suppl. 3): 86–88. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-3046.7.s3.13.x]
Pittenger, M.F., Mackay, A.M., Beck, S.C., Jaiswal, R.K., Douglas, R., Mosca, J.D., Moorman, M.A., Simonetti, D.W., Craig, S., Marshak, D.R., 1999. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science, 284(5411):143–147. [doi:10.1126/science.284.5411.143]
Qian, H.Y., Yang, Y.J., Huang, J., Gao, R.L., Dou, K.F., Yang, G.S., Li, J.J., Shen, R., He, Z.X., Lu, M.J., et al., 2007. Effects of Tongxinluo-facilitated cellular cardiomyoplasty with autologous bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells on postinfarct swine hearts. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.), 120(16):1416–1425.
Raffetto, J.D., Khalil, R.A., 2008. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem. Pharmacol., 75(2):346–359. [doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.004]
Stetler-Stevenson, W.G., 2008. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in cell signaling: metalloproteinase-independent biological activities. Sci. Signal., 1(27):re6. [doi:10.1126/scisignal.127re6]
Tomita, S., Li, R.K., Weisel, R.D., Mickle, D.A.G., Kim, E.J., Sakai, T., Jia, Z.Q., 1999. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow cells improves damaged heart function. Circulation, 100(Suppl. II):247–256. [doi:10.1161/01.CIR.100.suppl_2.II-247]
Tse, H.F., Yiu, K.H., Lau, C.P., 2007. Bone marrow stem cell therapy for myocardial angiogenesis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol., 5(2):103–112. [doi:10.2174/157016107780368299]
Wang, H.J., Huang, Y.W., Sun, J., 2003. Effect of tongxinluo capsule on function of vascular endothelium in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Chin. J. Integr. Trad. West. Med., 23(8):587–589 (in Chinese).
Wang, J.A., Chen, T.L., Jiang, J., Shi, H., Gui, C., Luo, R.H., Xie, X.J., Xiang, M.X., Zhang, X., 2008. Hypoxic preconditioning attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 29(1):74–82. [doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00716.x]
Wu, T., Harrison, R.A., Chen, X., Ni, J., Zhou, L., Qiao, J., Wang, Q., Wei, J., Xin, D., Zheng, J., 2006. Tongxinluo (Tong xin luo or Tong-xin-luo) capsule for unstable angina pectoris. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., (4): CD004474. [doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004474.pub2]
Xu, F., Shi, J., Yu, B., Ni, W., Wu, X., Gu, Z., 2010. Chemokines mediate mesenchymal stem cell migration toward gliomas in vitro. Oncol. Rep., 23(6):1561–1567. [doi:10.3892/or_00000796]
Zhang, H.T., Jia, Z.H., Zhang, J., Ye, Z.K., Yang, W.X., Tian, Y.Q., Jia, X., Li, W., Wu, Y.L., Yang, Y.J., 2010. No-reflow protection and long-term efficacy for acute myocardial infarction with Tongxinluo: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trial (ENLEAT Trial). Chin. Med. J. (Engl.), 123(20):2858–2864.
Zhu, F., Guo, G.H., Chen, W., Wang, N.Y., 2010. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells engraftment on vascular endothelial cell growth factor in lung tissue and plasma at early stage of smoke inhalation injury. World J. Emerg. Med., 1:224–228.
Zisa, D., Shabbir, A., Suzuki, G., Lee, T., 2009. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a key therapeutic trophic factor in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac repair. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 390(3):834–838. [doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.058]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Project supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. Y2090308), the Traditional Chinese Medicine Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 391030-W50806), and the Key Lab of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Zhejiang Province, China (No. ZK23812)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Xy., Wang, Wx., Yu, Mj. et al. Tongxinluo promotes mesenchymal stem cell tube formation in vitro. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 644–651 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1101005
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1101005