Abstract
Objective
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are correlated with a more malignant phenotype in many cancers. This study was designed to evaluate the predictive value of the expression of MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2), as the key regulatory mechanism of the MAPKs, in lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
Methods
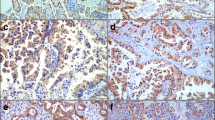
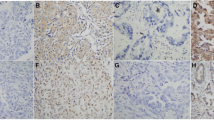
We assessed the expressions of MKP-1 and p-ERK1/2 in twenty subjects at different differentiation degree of SCC and five normal lungs by immunohistochemistry and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis.
Results
Immunohistochemistry and real-time RT-PCR assay showed that the expression of MKP-1 was gradually decreased as tissue type went from normal lung tissues to increasingly undifferentiated carcinoma, and it was negatively correlated with tumor differentiation (P<0.01). However, the expression of p-ERK1/2 or ERK1/2 was gradually increased as tissue type went from normal lung tissues to increasingly undifferentiated carcinoma, and it was positively correlated with tumor differentiation (P<0.01).
Conclusions
Our data indicates the relevance of MKP-1 and p-ERK1/2 in SCC as a potential positive and negative prognostic factor. The imbalanced expression of MKP-1 and p-ERK1/2 may play a role in the development of SCC and these two molecules may be new targets for the therapy and prognosis of SCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeyinka, A., Nui, Y., Cherlet, T., Snell, L., Watson, P.H., Murphy, L.C., 2002. Activated mitogen-activated protein kinase expression during human breast tumorigenesis and breast cancer progression. Clin. Cancer Res., 8(6): 1747–1753.
Bermudez, O., Pages, G., Gimond, C., 2010. The dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases: critical roles in development and cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 299(2):C189–C202. [doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00347.2009]
Blackhall, F.H., Pintilie, M., Michael, M., Leighl, N., Feld, R., Tsao, M.S., Shepherd, F.A., 2003. Expression and prognostic significance of kit, protein kinase B, and mitogen-activated protein kinase in patients with small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res., 9(6):2241–2247.
Bogoyevitch, M.A., 2006. The isoform-specific functions of the c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs): differences revealed by gene targeting. Bioessays, 28(9):923–934. [doi:10.1002/bies.20458]
Bogoyevitch, M.A., Arthur, P.G., 2008. Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases: JuNK no more? Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1784(1):76–93. [doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.013]
Chang, L.F., Karin, M., 2001. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature, 410(6824):37–40. [doi:10.1038/35065000]
Chen, H., Zhu, G., Li, Y., Padia, R.N., Dong, Z., Pan, Z.K., Liu, K., Huang, S., 2009. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway regulates breast cancer cell migration by maintaining slug expression. Cancer Res., 69(24): 9228–9235. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1950]
Denkert, C., Schmitt, W.D., Berger, S., Reles, A., Pest, S., Siegert, A., Lichtenegger, W., Dietel, M., Hauptmann, S., 2002. Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in primary human ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer, 102(5):507–513. [doi:10.1002/ijc.10746]
Dickinson, R.J., Keyse, S.M., 2006. Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases. J. Cell Sci., 119(22):4607–4615. [doi:10.1242/jcs.03266]
Dunn, K.L., Espino, P.S., Drobic, B., He, S., Davie, J.R., 2003. The Ras-MAPK signal transduction pathway, cancer and chromatin remodeling. Biochem. Cell Biol., 83(1):1–14. [doi:10.1139/o04-121]
Eralp, Y., Derin, D., Ozluk, Y., Yavuz, E., Guney, N., Saip, P., Muslumanoglu, M., Igci, A., Kücücük, S., Dincer, M., Aydiner, A., Topuz, E., 2008. MAPK overexpression is associated with anthracycline resistance and increased risk for recurrence in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol., 19(4):669–674. [doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm522]
Farooq, A., Zhou, M.M., 2004. Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell. Signal., 16(7):769–779. [doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2003.12.008]
Gailhouste, L., Ezan, F., Bessard, A., Frémin, C., Rageul, J., Langouët, S., Baffet, G., 2010. RNAi-mediated MEK1 knock-down prevents ERK1/2 activation and abolishes human hepatocarcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer, 126(6):1367–1377. [doi:10.1002/ijc.24950]
Greenberg, A.K., Basu, S., Hu, J., Yie, T.A., Tchou-Wong, K.M., Rom, W.N., Lee, T.C., 2002. Selective p38 activation in human non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 26(5):558–564.
Herbst, R.S., Heymach, J.V., Lippman, S.M., 2008. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med., 359(13):1367–1380. [doi:10.1056/NEJMra0802714]
Hu, J.A., Li, Y., Fang, J., 2010. Effect of ERK inhibitor on pulmonary metastasis of inoculated human adenoid cystic carcinoma cells in nude mice. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod., 109(1):117–123. [doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.052]
Huang, D., Ding, Y., Luo, W.M., Bender, S., Qian, C.N., Kort, E., Zhang, Z.F., VandenBeldt, K., Duesbery, N.S., Resau, J.H., Teh, B.T., 2008. Inhibition of MAPK kinase signaling pathways suppressed renal cell carcinoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res., 68(1):81–88. [doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5311]
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Hao, Y., Xu, J., Thun, M.J., 2009. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer. J. Clin., 59(4): 225–249. [doi:10.3322/caac.20006]
Johnson, G.L., Lapadat, R., 2002. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science, 298(5600):1911–1912. [doi:10.1126/science.1072682]
Mavria, G., Vercoulen, Y., Yeo, M., Paterson, H., Karasarides, M., Marais, R., Bird, D., Marshall, C.J., 2006. ERK-MAPK signaling opposes Rho-kinase to promote endothelial cell survival and sprouting during angiogenesis. Cancer Cell, 9(1):33–44. [doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.12.021]
Moro, L., Arbini, A.A., Marra, E., Greco, M., 2007. Constitutive activation of MAPK/ERK inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation through upregulation of BRCA2. Int. J. Oncol., 30(1):217–224.
Mukohara, T., Kudoh, S., Yamauchi, S., Kimura, T., Yoshimura, N., Kanazawa, H., Hirataa, K., Wanibuchib, H., Fukushimab, S., Inouec, K., et al., 2003. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and downstream-activated peptides in surgically excised non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer, 41(2): 123–130. [doi:10.1016/S0169-5002(03)00225-3]
Murphy, L.O., Blenis, J., 2006. MAPK signal specificity: the right place at the right time. Trends Biochem. Sci., 31(5):268–275. [doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.03.009]
Owens, D.M., Keyse, S.M., 2007. Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene, 26(22):3203–3213. [doi:10.1038/sj. onc.1210412]
Roux, P.P., Blenis, J., 2004. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 68(2): 320–344. [doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.2.320-344.2004]
Serini, S., Trombino, S., Oliva, F., Piccioni, E., Monego, G., Resci, F., Boninsegna, A., Picci, N., Ranelletti, F.O., Calviello, G., 2008. Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells by increasing MKP-1 and down-regulating p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 expression. Apoptosis, 13(9):1172–1183. [doi:10.1007/s10495-008-0246-1]
Shaul, Y.D., Seger, R., 2007. The MEK/ERK cascade: from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1773(8):1213–1226. [doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.005]
Tsujita, E., Taketomi, A., Gion, T., Kuroda, Y., Endo, K., Watanabe, A., Nakashima, H., Aishima, S., Kohnoe, S., Maehara, Y., 2005. Suppressed MKP-1 is an independent predictor of outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology, 69(4):342–347. [doi:10.1159/000089766]
Wada, T., Penninger, J.M., 2004. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene, 23(16): 2838–2849. [doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207556]
Ward, Y., Wang, W., Woodhouse, E., Linnoila, I., Liotta, L., Kelly, K., 2001. Signal pathways which promote invasion and metastasis: critical and distinct contributions of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Ral-specific guanine exchange factor pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol., 21(17): 5958–5969. [doi:10.1128/MCB.21.17.5958-5969.2001]
Widmann, C., Gibson, S., Jarpe, M.B., Johnson, G.L., 1999. Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol. Rev., 79(1):143–180.
Wong, H.R., Dunsmore, K.E., Page, K., Shanley, T.P., 2005. Heat shock-mediated regulation of MKP-1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 289(5):C1152–C1158. [doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00138.2005]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30900654), the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2009R10031), and the Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province (No. 2009QN010), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Zhang, M., Qian, Yy. et al. Imbalanced expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 828–834 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100165
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100165
Key words
- Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1)
- Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
- Lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Prognostic factor