Abstract
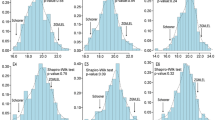
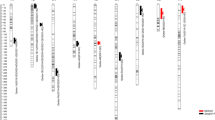
High malting quality of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) relies on many traits, such as β-amylase and limit dextrinase activities and β-glucan and protein fraction contents. In this study, interval mapping was utilized to detect quantitative trait loci (QTLs) affecting these malting quality parameters using a doubled haploid (DH) population from a cross of CM72 (six-rowed) by Gairdner (two-rowed) barley cultivars. A total of nine QTLs for eight traits were mapped to chromosomes 3H, 4H, 5H, and 7H. Five of the nine QTLs mapped to chromosome 3H, indicating a possible role of loci on chromosome 3H on malting quality. The phenotypic variation accounted by individual QTL ranged from 8.08% to 30.25%. The loci of QTLs for β-glucan and limit dextrinase were identified on chromosomes 4H and 5H, respectively. QTL for hordeins was coincident with the region of silica eluate (SE) protein on 3HS, while QTLs for albumins, globulins, and total protein exhibited overlapping. One locus on chromosome 3H was found to be related to β-amylase, and two loci on chromosomes 5H and 7H were found to be associated with glutelins. The identification of these novel QTLs controlling malting quality may be useful for marker-assisted selection in improving barley malting quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arends, A.M., Fox, G.P., Henry, R.J., Marschke, R.J., Symons, M.H., 1995. Genetic and environmental variation in the diastatic power of Australian barley. J. Cereal Sci., 21(1): 63–70. [doi:10.1016/S0733-5210(95)80009-3]
Bamforth, C.W., 1982. Barley β-glucans: their role in malting and brewing. Brew. Dig., 57(6):22–27.
Baxter, E.D., 1981. Hordein in barley and malt. A review. J. Inst. Brew., 87(2):173–176.
Bradford, M.M., 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem., 72(1–2):248–254. [doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3]
Celus, I., Brijs, K., Delcour, J.A., 2006. The effects of malting and mashing on barley protein extractability. J. Cereal Sci., 44(2):203–211. [doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.06.003]
Clancy, J.A., Han, F., Ullrich, S.E., 2003. Comparative mapping of beta-amylase activity loci among three barley crosses. Crop Sci., 43(3):1043–1052.
Delcour, J.A., Verschaeve, S.G., 1987. Malt diastatic power. Part II. A modified EBC diastatic power assay for the selective estimation of β-amylase activity. Time and temperature dependence of the release of reducing sugars. J. Inst. Brew., 93(4):296–301.
Dellaporta, S.L., Wood, J., Hicks, J.B., 1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 1(4): 19–21. [doi:10.1007/BF02712670]
Emebiri, L.C., Moody, D.B., Horsley, R., Panozzo, J.F., Read, B.J., 2005. The genetic control of grain protein content variation in a doubled haploid population derived from a cross between Australian and North American two-rowed barley lines. J. Cereal Sci., 41(1):107–114. [doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2004.08.012]
Georg-kraemer, J.E., Mundstock, E.C., Cavalli-Molina, L., 2001. Developmental expression of amylase during barley malting. J. Cereal Sci., 33(3):279–288. [doi:10.1006/jcrs.2001.0367]
Han, F., Ullrich, S.E., Chirat, S., Menteur, S., Jestin, L., Sarrafi, A., Hayes, P.M., Jones, B.L., Blake, T.K., Wesenberg, D.M., et al., 1995. Mapping of β-glucan content and β-glucanase activity loci in barley grain and malt. Theor. Appl. Genet., 91(6–7):921–927. [doi:10.1007/BF00223901]
Hayes, P.M., Jones, B.L., 2000. Malting Quality from a QTL Perspective. In: Logue, S. (Ed.), Proceedings of the Eighth International Barley Genet. Symp., p.99–106.
Hayes, P.M., Cerono, J., Witsenboer, H., Kuiper, M., Zabeau, M., Sato, K., Kleinhofs, A., Kudrna, D., Killian, A., Saghai-Maroof, M., Hoffman, D., the North American Barley Genome Mapping Project, 1997. Characterizing and exploiting genetic diversity and quantitative traits in barley (Hordeum vulgare) using AFLP markers. J. Quant. Trait Loci, 3(1):1–15.
Hayes, P.M., Castro, A., Marquez-Cedillo, L., Corey, A., Henson, C., Jones, B., Kling, J., Mather, D., Matus, I., Rossi, C., Sato, K., 2001. A Summary of Published Barley QTL Reports. Available from: http://www.barleyworld.org/northamericanbarley/qtlsummary.php (access at Mar. 28, 2005).
Holme, D.J., Peck, H., 1998. Analytical Biochemistry, 3rd Ed. Addison Wesley Longman, New York, p.388–393.
Langridge, P., Karakousis, A., Kretschmer, J., Manning, S., Logue, S., 1996. Barley Mapping and QTL Analysis of Three Populations from the University of Adelaide. Available on line through GrainGenes. Available from: http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/maps.html (access at Dec. 19, 2002).
Li, C.D., Zhang, X.Q., Eckstein, P., Rossnagel, B.G., Scoles, G.H., 1999. A polymorphic microsatellite in the limit dextrinase gene of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Mol. Breeding, 5(6):569–577. [doi:10.1023/A:1009692207966]
Li, J.Z., Huang, X.Q., Heinrichs, F., Ganal, M.W., Röder, M.S., 2005. Analysis of QTLs for yield, yield components, and malting quality in a BC3-DH population of spring barley. Theor. Appl. Genet., 110(2):356–363. [doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1847-x]
Liu, Z.H., Cheng, F.M., Cheng, W.D., Zhang, G.P., 2005. Positional variations in phytic acid and protein content within a panicle of japonica rice. J. Cereal Sci., 41(3): 297–303. [doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2004.09.010]
Manly, K.F., Cudmore, R.H., Meer, J.M., 2001. Map manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm. Genome, 12(12):930–932. [doi:10.1007/s00335-001-1016-3]
Mather, D.E., Tinker, N.A., LaBerge, D.E., Edney, M., Jones, B.L., Rossnagel, B.G., Legge, W.G., Briggs, K.G., Irvine, R.B., Falk, D.E., et al., 1997. Regions of the genome that affect grain and malt quality in a North American two-row barley cross. Crop Sci., 37(2):544–554.
McCleary, B.V., 1992. Measurement of the content of limit dextrinase in cereal flours. Carbohydr. Res., 227(1): 257–268. [doi:10.1016/0008-6215(92)85076-C]
McCleary, B.V., Codd, R., 1989. Measurement of beta-amylase in cereal flours and commercial enzyme preparations. J. Cereal Sci., 9(1):17–33. [doi:10.1016/S0733-5210(89)80018-9]
McCleary, B.V., Codd, R., 1991. Measurement of (1-3),(1-4)-β-D-glucan in barley and oats: a streamlined enzymic procedure. J. Sci. Food Agric., 55(2):303–312. [doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740550215]
McCouch, S.R., Cho, Y.G., Yano, M., Paul, E., Blinstrub, M., 1997. Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet. Newslett., 14:11–13.
Oziel, A., Hayes, P.M., Chen, F.Q., Jones, B., 1996. Application of quantitative trait locus mapping to the development of winter-habit malting barley. Plant Breeding, 115(1):43–51. [doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.1996.tb00869.x]
Panozzo, J.F., Eckermann, P.J., Mather, D.E., Moody, D.B., Black, C.K., Collins, H.M., Barr, A.R., Lim, P., Cullis, B.R., 2007. QTL analysis of malting quality traits in two barley populations. Aust. J. Agric. Res., 58(9):858–866. [doi:10.1071/AR06203]
Rasmusson, D.C., Glass, R.L., 1965. Effectiveness of early generation selection for four quality characters in barley. Crop Sci., 5(2):389–391.
Robinson, L.H., Healy, P., Stewart, D.C., Eglinton, J.K., Ford, C.M., Evans, D.E., 2007. The identification of a barley haze active protein that influences beer haze stability: the genetic basis of a barley malt haze active protein. J. Cereal Sci., 45(3):335–342. [doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.08.013]
Shewry, P.R., 1993. Barley Seed Proteins. In: MacGregor, A.W., Bhatty, R.S. (Eds.), Barley: Chemistry and Technology. American Society of Cereal Chemists, Minnesota, USA, p.131–197.
von Korff, M., Wang, H.J., Léon, J., Pillen, K., 2008. AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: III. Identification of exotic alleles for the improvement of malting quality in spring barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Mol. Breeding, 21(1):81–93.
Wang, D.L., Zhu, J., Li, Z.K., Paterson, A.H., 1999. Mapping QTLs with epistatic effects and QTL×environment interactions by mixed linear model approaches. Theor. Appl. Genet., 99(7–8):1255–1264. [doi:10.1007/s001220051331]
Wang, J.M., Zhang, G.P., Chen, J.X., Wu, F.B., 2004. The changes of β-glucan content and β-glucanase activity in barley before and after malting and their relationships to malt qualities. Food Chem., 86(2):223–228. [doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.08.020]
Wang, X.D., Yang, J., Zhang, G.P., 2006. Genotypic and environmental variation in barley limit dextrinase activity and its relation to malt quality. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B., 7(5):386–392. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.B0386]
Yang, J., Hu, C.C., Ye, X.Z., Zhu, J., 2005. QTLNetwork 2.0. Institute of Bioinformatics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. Available from: http://ibi.zju.edu.cn/software/qtlnetwork
Yin, C., Zhang, G.P., Wang, J.M., Chen, J.X., 2002. Variation of β-amylase activity in barley as affected by cultivar and environment and its relation to protein content and grain weight. J. Cereal Sci., 36(3):307–312. [doi:10.1006/jcrs.2002.0467]
Zale, J.M., Clancy, J.A., Ullrich, S.E., Jones, B.L., Hayes, P.M., 2000. North American barley genome project. Summary of barley malting-quality QTLs mapped in various populations. Barley Genet. Newslett., 30:44–54.
Zhang, G.P., Chen, J.X., Dai, F., Wang, J.M., Wu, F.B., 2006. The effect of cultivar and environment on beta-amylase activity is associated with the change of protein content in barley grains. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 192(1):43–49. [doi:10.1111/j.1439-037X.2006.00181.x]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30630047 and 30771281), the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program (863) of China (No. 2006AA10Z1C3), and the Ministry of Education and the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs (111 Project) of China (No. B06014)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, K., Xue, Dw., Huang, Yz. et al. Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with β-amylase and limit dextrinase activities and β-glucan and protein fraction contents in barley. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 10, 839–846 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0920135
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0920135
Key words
- Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
- Quantitative trait locus
- β-amylase
- Limit dextrinase
- β-glucan
- Protein fraction