Abstract
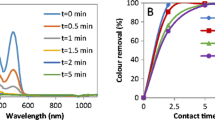
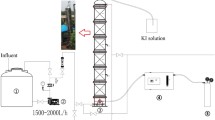
A treatability study of industrial wastewater containing chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds (CNACs) by a catalytic ozonation process (COP) with a modified Mn/Co ceramic catalyst and an aerobic sequencing batch reactor (SBR) was investigated. A preliminary attempt to treat the diluted wastewater with a single SBR resulted in ineffective removal of the color, ammonia, total organic carbon (TOC) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). Next, COP was applied as a pretreatment in order to obtain a bio-compatible wastewater for SBR treatment in a second step. The effectiveness of the COP pretreatment was assessed by evaluating wastewater biodegradability enhancement (the ratio of biology oxygen demand after 5 d (BOD5) to COD), as well as monitoring the evolution of TOC, carbon oxidation state (COS), average oxidation state (AOS), color, and major pollutant concentrations with reaction time. In the COP, the catalyst preserved its catalytic properties even after 70 reuse cycles, exhibiting good durability and stability. The performance of SBR to treat COP effluent was also examined. At an organic loading rate of 2.0 kg COD/(m3·d), with hydraulic retention time (HRT)=10 h and temperature (30±2) °C, the average removal efficiencies of NH3-N, COD, BOD5, TOC, and color in a coupled COP/SBR process were about 80%, 95.8%, 93.8%, 97.6% and 99.3%, respectively, with average effluent concentrations of 10 mg/L, 128 mg/L, 27.5 mg/L, 25.0 mg/L, and 20 multiples, respectively, which were all consistent with the national standards for secondary discharge of industrial wastewater into a public sewerage system (GB 8978-1996). The results indicated that the coupling of COP with a biological process was proved to be a technically and economically effective method for treating industrial wastewater containing recalcitrant CNACs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amat, A.M., Arques, A., Galindo, F., Miranda, M.A., Santos-Juanes, L., Vercher, R.F., Vicente, R., 2007. Acridine yellow as solar photocatalyst for enhancing biodegradability and eliminating ferulic acid as model pollutant. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 73(3–4):220–226. [doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.12.003]
APHA/ AWWA/ WEF, 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Ed. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA.
Ballesteros Martín, M.M., Sánchez Pérez, J.A., Casas López, J.L., Oller, I., Malato Rodríguez, S., 2009. Degradation of a four-pesticide mixture by combined photo-Fenton and biological oxidation. Water Res., 43(3):653–660. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.020]
Beltrán, F.J., Encinar, J.M., Alonso, M.A., 1998. Nitroaromatic hydrocarbon ozonation in water. 1. Single ozonation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 37(1):25–31. [doi:10.1021/ie9704253]
Beltrán, F.J., García-Araya, J.F., Frades, J., Álvarez, P., Gimeno, O., 1999. Effects of single and combined ozonation with hydrogen peroxide or UV radiation on the chemical degradation and biodegradability of debittering table olive industrial wastewaters. Water Res., 33(3):723–732. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00239-5]
Ben, Y., Chen, Z., Xu, Z., Shen, J., 2008. Effect of p-chloronitrobenzen on aerobic sludge activity and pollutants biodegradation kinetics. China Water Wastewater, 24(21):102–105 (in Chinese).
Boon, N., Goris, J., Vos, P.D., Verstraete, W., Top, E.M., 2000. Bioaugmentation of activated sludge by an indigenous 3-chloroaniline-degrading Comamonas testosteroni strain, I2gfp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66(7):2906–2913. [doi:10.1128/AEM.66.7.2906-2913.2000]
Carbajo, M., Beltrán, F.J., Gimeno, O., Acedo, B., Rivas, F.J., 2007. Ozonation of phenolic wastewaters in the presence of a perovskite type catalyst. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 74(3–4):203–210. [doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.02.007]
Christensen, A., Gurol, M.D., Garoma, T., 2009. Treatment of persistent organic compounds by integrated advanced oxidation processes and sequential batch reactor. Water Res., 43(16):3910–3921. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.04.009]
Coca, M., Peña, M., González, G., 2007. Kinetic study of ozonation of molasses fermentation wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater., 149(2):364–370. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.006]
Comninellis, C., Kapalka, A., Malato, S., Parsons, S.A., Poulios, I., Mantzavinos, D., 2008. Advanced oxidation processes for water treatment: advances and trends for R & D. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 83(6):769–776. [doi:10.1002/jctb.1873]
Faria, P.C.C., Órfão, J.J.M., Pereira, M.F.R., 2009. Activated carbon and ceria catalysts applied to the catalytic ozonation of dyes and textile effluents. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 88(3–4):341–350. [doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.11.002]
Farré, M.J., Doménech, X., Peral, J., 2006. Assessment of photo-Fenton and biological treatment coupling for diuron and linuron removal from water. Water Res., 40(13):2533–2540. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.034]
Haag, W.R., Hoigné, J., Bader, H., 1984. Improved ammonia oxidation by ozone in the presence of bromide ion during water treatment. Water Res., 18(9):1125–1128. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(84)90227-6]
Hoigné, J., Bader, H., 1976. The role of hydroxyl radical reaction in ozonation process in aqueous solution. Water Res., 10(5):377–386. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(76)90055-5]
Hoigné, J., Bader, H., 1978. Ozonation of water: kinetics of oxidation of ammonia by ozone and hydroxyl radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol., 12(1):79–84. [doi:10.1021/es60137a005]
Hoigné, J., Bader, H., Haag, W.R., Staehelin, J., 1985. Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water-III. Water Res., 19(8): 993–1004. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(85)90368-9]
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Ziólek, M., Nawrocki, J., 2003. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 46(4):639–669. [doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00326-6]
Lan, B.Y., Nigmatullin, R., Puma, G.L., 2008. Ozonation kinetics of cork-processing water in a bubble column reactor. Water Res., 42(10–11):2473–2482. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.01.030]
Lei, L., Gu, L., Zhang, X., Su, Y., 2007. Catalytic oxidation of highly concentrated real industrial wastewater by integrated ozone and activated carbon. Appl. Catal. A-Gen., 327(2):287–294. [doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2007.05.027]
Li, B., Xu, X., Zhu, L., 2009. Ozonation of chloronitrobenzenes in aqueous solution: kinetics and mechanism. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 84(2):167–175. [doi:10.1002/jctb.2015]
Li, Q., Minami, M., Inagaki, H., 1998. Acute and subchronic immunotoxicity of p-chloronitrobenzene in mice. I. Effect of natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activities and mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte proliferation. Toxicology, 127(1-3):223–232. [doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(98)00027-4]
Li, Q., Minami, M., Hanaoka, T., Yamamura, Y., 1999. Acute immunotoxicity of p-chloronitrobenzene in mice: II. Effect of p-chloronitrobenzene on the immunophenotype of murine splenocytes determined by flow cytometry. Toxicology, 137(1):35–45. [doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(99)00065-7]
Liang, C., 2007. Production situation and market analysis of nitrochlorobenzene. Techno-Economics in Petrochemicals, 23(2):23–26 (in Chinese).
Lin, S.H., Wang, C.H., 2003. Ozonation of phenolic wastewater in a gas-induced reactor with a fixed granular activated carbon bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 42(8): 1648–1653. [doi:10.1021/ie020545x]
Liu, Y., 2009. Citing Electronic Source of Information, China. Available from http://www.ccin.com.cn/front/home/templet/default/ShowArticle.jsp?id=75662 [accessed on Sept. 12, 2009].
Lucas, M.S., Peres, J.A., Lan, B.Y., Puma, G.L., 2009. Ozonation kinetics of winery wastewater in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor. Water Res., 43(6):1523–1532. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.036]
Martínez, N.S.S., Fernández, J.F., Segura, X.F., Ferrer, A.S., 2003. Pre-oxidation of an extremely polluted industrial wastewater by the Fenton’s regent. J. Hazard. Mater., 101(3):315–322. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00207-3]
Melero, J.A., Martínez, F., Botas, J.A., Molina, R., Pariente, M.I., 2009. Heterogeneous catalytic wet peroxide oxidation systems for the treatment of an industrial pharmaceutical wastewater. Water Res., 43(16):4010–4018. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.04.012]
Minero, C., Pelizzetti, E., Piccinini, P., Vincenti, M., 1994. Photocatalyzed transformation of nitrobenzene on TiO2 and ZnO. Chemosphere, 28(6):1229–1244. [doi:10.1016/0045-6535(94)90340-9]
Nair, R.S., Johannsen, F.R., Levinskas, G.J., Terrill, J.B., 1986a. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of p-nitroaniline and p-nitrochlorobenzene in rats. Fund. Appl. Toxicol., 6(4):618–627. [doi:10.1016/0272-0590(86)90174-0]
Nair, R.S., Johannsen, F.R., Levinskas, G.J., Terrill, J.B., 1986b. Assessment of toxicity of o-nitrochlorobenzene in rats following a 4-week inhalation exposure. Fund. Appl. Toxicol., 7(4):609–614. [doi:10.1016/0272-0590(86)90110-7]
Rice, R.G., 1997. Application of ozone for industrial wastewater treatment-a review. Ozone-Sci. Eng., 18(6): 477–515.
Sarasa, J., Cortés, S., Ormad, P., Gracia, R., Ovelleiro, J.L., 2002. Study of the aromatic by-products formed from ozonation of anilines in aqueous solution. Water Res., 36(12):3035–3044. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00003-9]
Sarria, V., Parra, S., Adler, N., Peringer, P., Benitez, N., Pulgarin, C., 2002. Recent developments in the coupling of photoassisted and aerobic biological processes for the treatment of biorecalcitrant compounds. Catal. Today, 76(2–4):301–315. [doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00228-6]
Selçuk, H., Eremektar, G., Meriç, S., 2006. The effect of pre-ozone oxidation on acute toxicity and inert soluble COD fractions of a textile finishing industry wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater., 137(1):254–260. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.055]
Siuda, J.F., DeBernardis, J.F., 1973. Naturally occurring halogenated organic compounds. Lloydia, 36(2):107–143.
Sreethawong, T., Chavadej, S., 2008. Color removal of distillery wastewater by ozonation in the absence and presence of immobilized iron oxide catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater., 155(3):486–493. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.091]
Tanaka, K., Luesaiwong, W., Hisanaga, T., 1997. Photocatalytic degradation of mono-, di- and trinitrophenol in aqueous TiO2 suspension. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem., 122(1):67–74. [doi:10.1016/S1381-1169(96)00509-2]
Tomei, M.C., Annesini, M.C., Bussoletti, S., 2004. 4-nitrophenol biodegradation in a sequencing batch reactor: kinetic study and effect of filling time. Water Res., 38(2):375–384. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.09.023]
Travlos, G.S., Mahler, J., Ragan, H.A., Chou, B.J., Bucher, J.R., 1996. Thirteen-week inhalation toxicity of 2- and 4-chloronitrobenzene in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Fund. Appl. Toxicol., 30(1):75–92. [doi:10.1006/faat.1996.0045]
Volskay, V.T.Jr., Grady, C.P.L.Jr., 1990. Respiration inhibition kinetic analysis. Water Res., 24(7):863–874. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(90)90136-T]
Wei, F. (Ed.), 2002. Analysis of Water and Wastewater. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China.
Wert, E.C., Rosario-Ortiz, F.L., Drury, D.D., Snyder, S.A., 2007. Formation of oxidation byproducts from ozonation of wastewater. Water Res., 41(7):1481–1490. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.020]
Winarno, E.K., Getoff, N., 2002. Comparative studies on the degradation of aqueous 2-chloroaninline by O3 as well as by UV-light and γ-rays in the presence of ozone. Radiat. Phys. Chem., 65(4–5):387–395. [doi:10.1016/S0969-806X(02)00339-0]
Zeng, Y.F., Liu, Z.L., Qin, Z.Z., 2009. Decolorization of molasses fermentation wastewater by SnO2-catalyzed ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater., 162(2–3):682–687. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.094]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50378082) and the Key Project of Science and Technology Plan of Zhejiang Province (No. 2004C23021), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Bz., Xu, Xy. & Zhu, L. Catalytic ozonation-biological coupled processes for the treatment of industrial wastewater containing refractory chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 177–189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900291
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900291