Abstract
Objective
The age-related change is important part of degenerative disc disease. However, no appropriate animal model or objective evaluation index is available. This study aimed to investigate the features of intervertebral disc degeneration in aging process of rats.
Methods
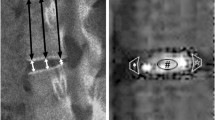
22-month-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were used as spontaneously occurring intervertebral disc degeneration models and 6-month-old rats as young controls. Expression of collagen types II and X was measured by immunohistochemistry. Degenerations of intervertebral discs were scored according to Miyamoto’s method. Numbers and areas of afferent vascular buds were measured. The thicknesses of non-calcified and calcified layers were measured and statistically analyzed.
Results
There were less collagen type II expression and more collagen type X expression in the calcified layer of the cartilage endplates and nucleus pulposus in the rats of the aged group than in the young control. There were fewer and smaller afferent vascular buds in the rats of the aged group than in the young control group. The ratio of the non-calcified to the calcified layers in the rats of the aged group significantly decreased, compared with that of the young control group (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Rats can spontaneously establish intervertebral disc age-related degeneration. The expression of collagen types II and X, numbers and areas of afferent vascular buds, the ratio of the non-calcified to the calcified layers, and water and glycosaminoglycan contents in the nucleus pulposus are sensitive indexes of intervertebral disc degeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsan, R., Tajima, N., Chosa, E., Sugamata, M., Sumida, M., Hamada, M., 2001. Biochemical and morphological changes in herniated human intervertebral disc. J. Orthop. Sci., 6(6):510–518. [doi:10.1007/s007760100006]
Ala-Kokko, L., 2002. Genetic risk factors for lumbar disc disease. Ann. Med., 34(1):42–47. [doi:10.1080/078538902317338634]
Annunen, S., Paassilta, P., Lohiniva, J., Perälä, M., Pihlajamaa, T., Karppinen, J., Tervonen, O., Kröger, H., Lähde, S., Vanharanta, H., et al., 1999. An allele of COL9A2 associated with intervertebral disc disease. Science, 285(5426):409–412. [doi:10.1126/science.285.5426.409]
Antoniou, J., Steffen, T., Nelson, F., Winterbottom, N., Hollander, A.P., Poole, R.A., Aebi, M., Alini, M., 1996. The human lumbar intervertebral disc: evidence for changes in the biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with growth, maturation, ageing, and degeneration. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 98(4):996–1003. [doi:10.1172/JCI118884]
Boos, N., Nerlich, A.G., Wiest, I., von der Mark, K., Aebi, M., 1997. Immunolocalization of type X collagen in human lumbar intervertebral discs during ageing and degeneration. Histochem. Cell Biol., 108(6):471–480. [doi:10.1007/s004180050187]
Boos, N., Weissbach, S., Rohrbach, H., Weiler, C., Spratt, K.F., Nerlich, A.G., 2002. Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo award in basic science. Spine, 27(23):2631–2644. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200212010-00002]
Cs-Szabo, G., Ragasa-San Juan, D., Turumella, V., Masuda, K., Thonar, E.J., An, H.S., 2002. Changes in mRNA and protein levels of proteoglycans of the anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus during intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine, 27(20):2212–2219. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200210150-00006]
Diwan, A.D., Parvataneni, H.K., Khan, S.N., Sandhu, H.S., Girardi, F.P., Cammisa, F.P.Jr., 2000. Current concepts in intervertebral disc restoration. Orthop. Clin. North Am., 31(3):453–464. [doi:10.1016/S0030-5898(05)70163-2]
Farndale, R.W., Sayers, C.A., Barrett, A.J., 1982. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res., 9(4):247–248.
Feng, L., Song, Y., 2004. Pathological development of researches on intervertebral disc degeneration. Sheng Wu Yi. Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi, 21(5):867–870 (in Chinese).
Götz, W., Barnert, S., Bertagnoli, R., Miosge, N., Kresse, H., Herken, R., 1997. Immunohistochemical localization of the small proteoglycans decorin and biglycan in human intervertebral discs. Cell Tissue Res., 289(1):185–190. [doi:10.1007/s004410050864]
Gruber, H.E., Johnson, T., Norton, H.J., Hanley, E.N.Jr., 2002. The sand rat model for disc degeneration: radiologic characterization of age-related changes. Spine, 27(3):230–234. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200202010-00004]
Hansson, T., Holm, S., 1991. Clinical implications of vibration-induced changes in the lumbar spine. Orthop. Clin. North Am., 22(2):247–253.
He, H.L., Wu, Z.H., Zhang, J.G., Wang, Y.P., Zhou, Y., Xu, Y.Q., Yuan, J.G., Qiu, G.X., 2004. Primary study on collagen X gene expression in the apical disc of idiopathic scoliosis. Chinese Medical Journal, 84(20):1681–1685 (in Chinese).
Kaila-Kangas, L., Leino-Arjas, P., Riihimäki, H., Luukkonen, R., Kirjonen, J., 2003. Smoking and overweight as predictors of hospitalization for back disorders. Spine, 28(16):1860–1868. [doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000083284.47176.80]
Katz, M.M., Hargens, A.R., Garfin, S.R., 1986. Intervertebral disc nutrition. Diffusion versus convection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 210:243–245.
Lipson, S.J., Muri, H., 1981. 1980 Volvo award in basic science. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine, 6(3):194–210. [doi:10.1097/00007632-198105000-00002]
Luoma, K., Riihimäki, H., Luukkonen, R., Raininko, R., Viikari-Juntura, E., Lamminen, A., 2000. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine, 25(4):487–492. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200002150-00016]
Miller, J.A., Schmatz, C., Schultz, A.B., 1988. Lumbar disc degeneration: correlation with age, sex, and spine level in 600 autopsy specimens. Spine, 13(2):173–178. [doi:10.1097/00007632-198802000-00008]
Miyamoto, S., Yonenobu, K., Ono, K., 1991. Experimental cervical spondylosis in the mouse. Spine, 16(10 Suppl.):S495–S500.
Reginato, A.M., Tuan, R.S., Ono, T., Jimenez, S.A., Jacenko, O., 1993. Effects of calcium deficiency on chondrocyte hypertrophy and type X collagen expression in chick embryonic sternum. Dev. Dynamics, 198(4):284–295.
Schmid, T.M., Bonen, D.K., Luchene, L., Linsenmayer, T.F., 1991. Late events in chondrocyte differentiation: hypertrophy, type X collagen synthesis and matrix calcification. In Vivo, 5(5):533–540.
Turgut, M., Uslu, S., Uysal, A., Yurtseven, M.E., Ustün, H., 2003. Changes in vascularity of cartilage endplate of degenerated intervertebral discs in response to melatonin administration in rats. Neurosurg. Rev., 26(2):133–138. [doi:10.1007/s10143-003-0259-8]
Urban, J.P., Smith, S., Fairbank, J.C., 2004. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine, 29(23):2700–2709. [doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000146499.97948.52]
Virtanen, I.M., Karppinen, J., Taimela, S., Ott, J., Barral, S., Kaikkonen, K., Heikkilä, O., Mutanen, P., Noponen, N., Männikkö, M., Tervonen, O., Natri, A., Ala-Kokko, L., 2007. Occupational and genetic risk factors associated with intervertebral disc disease. Spine, 32(10):1129–1134. [doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000261473.03274.5c]
Zhang, Y.G., Guo, X., Xu, P., Kang, L.L., Li, J., 2005. Bone mesenchymal stem cells transplanted into rabbit intervertebral discs can increase proteoglycans. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 430:219–226. [doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000146534.31120.cf]
Zhang, Y., Sun, Z., Liu, J., Guo, X., 2008. Advances in susceptibility genetics of intervertebral degenerative disc disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci., 4(5):283–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 30400163) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yg., Sun, Zm., Liu, Jt. et al. Features of intervertebral disc degeneration in rat’s aging process. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 10, 522–527 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0820295
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0820295