Abstract
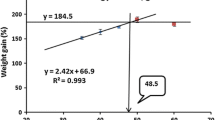
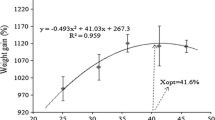
We investigated the effects of fish protein hydrolysate (FPH) on growth performance and humoral immune response of the large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea R.). One thousand and two hundred large yellow croakers [initial average weight: (162.75±23.85) g] were divided into four groups and reared in floating sea cages (3 m×3 m×3 m). The animals were fed with 4 diets: basal diet only (control) or diets supplemented with 5%, 10% and 15% (w/w) FPH. The results show that dietary FPH levels significantly influenced the growth and immunity of the large yellow croaker. Compared with the control group, total weight gain (TWG) in all treatment groups, relative weight gain (RWG) and specific growth rate (SGR) in fish fed with diets supplemented with 10% and 15% FPH were significantly increased (P<0.05). Similar results were observed in immune parameters [lysozyme activity, serum complements, immunoglobulin M (IgM)]. Lysozyme activity, complement C4 and IgM were also significantly increased (P<0.05) in fish fed with diets supplemented with 10% and 15% FPH, while complement C3 level was significantly increased (P<0.05) in all treatment groups. In general, with the supplementation of FPH, particularly at dose of 10%, the growth performance and immunity of the large yellow croaker can be improved effectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibi, S.A., 1997. The oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in human intestine: biology and function. Gastroenterology, 113(1):332–340. [doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(97)70112-4]
Adler-Nissen, J., 1986. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, New York.
Aguila, J., Cuzon, G., Pascual, C., Dominguesd, P.M., Gaxiolac, G., Sánchezc, A., Maldonadoe, T., Rosas, C., 2007. The effects of fish hydrolysate (CPSP) level on Octopus maya (Voss and Solis) diet: digestive enzyme activity, blood metabolites, and energy balance. Aquaculture, 273(4):641–655. [doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.07.010]
Alcorn, S.W., Murray, A.L., Pascho, R.J., 2002. Effects of rearing temperature on immune functions in sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Fish Shellfish Immunol., 12(4):303–334. [doi:10.1006/fsim.2001.0373]
Bachère, E., 2000. Shrimp immunity and disease control. Aquaculture, 191(1–3):3–11. [doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00413-0]
Bagni, M., Archetti, L., Amadori, M., Marino, G., 2000. Effect of long-term administration of an immunostimulant diet on innate immunity in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Vet. Med. B, 47(10):745–751. [doi:10.1046/j.1439-0450.2000.00412.x]
Berge, G.M., Storebakken, T., 1996. Fish protein hydrolyzate in starter diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fry. Aquaculture, 145(1–4):205–212. [doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01355-5]
Bøgwald, J., Dalmo, R., Leifson, R.M., Stenbern, E., GildBerg, A., 1996. The stimulatory effect of a muscle protein hydrolysate from Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. on Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., head kidney leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 6(1):3–16. [doi:10.1006/fsim.1996.0002]
Cahu, C.L., Zambonino Infante, J.L., Quazuguel, P., Le Gall, M.M., 1999. Protein hydrolysate vs. fish meal in compound diets for 10-day old sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax larvae. Aquaculture, 171(1–2):109–119. [doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00428-1]
Carvalho, A.P., Escaffre, A.M., Oliva Teles, A., Bergot, P., 1997. First feeding of common carp larvae on diets with high levels of protein hydrolysates. Aquac. Int., 5(4):361–367. [doi:10.1023/A:1018368208323]
Cook, M.T., Hayball, P.J., Hutchinson, W., Nowak, B.F., Hayball, J.D., 2003. Administration of a commercial immunostimulant preparation, EcoActiva™ as a feed supplement enhances macrophage respiratory burst and the growth rate of snapper (Pagrus auratus, Sparidae (Bloch and Schneider)) in winter. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 14(4):333–345. [doi:10.1006/fsim.2002.0441]
Cuesta, A., Meseguer, J., Esteban, M.A., 2004. Total serum immunoglobulin M levels are affected by immunomodulators in seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol., 101(3–4):203–210. [doi:10.1016/j.vetimm.2004.04.021]
Duan, Q., Mai, K., Zhong, H., Si, L., Wang, X., 2001. Studies on the nutrition of the large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea R. I: growth response to graded levels of dietary protein and lipid. Aquac. Res., 32(Suppl. 1):46–52. [doi:10.1046/j.1355-557x.2001.00048.x]
Duarte, J., Vinderola, G., Ritz, B., Perdigón, G., Matar, C., 2006. Immunomodulating capacity of commercial fish protein hydrolysate for diet supplementation. Immunobiology, 211(5):341–350. [doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2005.12.002]
Ellis, A.E., 1990. Lysozyme Assays. In: Stolen, J.S., Fletcher, D.P., Anderson, B.S., Roberson, B.S. (Eds.), Techniques in Fish Immunology. SOS Publications, Fair Haven, USA, p.101–103.
Gasque, P., 2004. Complement: a unique innate immune sensor for danger signals. Mol. Immunol., 41(11):1089–1098. [doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2004.06.011]
Holland, M.C.H., Lambris, J.D., 2002. The complement system in teleosts. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 12(5):399–420. [doi:10.1006/fsim.2001.0408]
Klompong, V., Benjakul, S., Kantachote, D., Shahidi, F., 2007. Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem., 102(4):1317–1327. [doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.016]
Kolkovski, S., Tandler, A., 2000. The use of squid protein hydrolysate as a protein source in microdiets for gilthead seabream Sparus aurata larvae. Aquac. Nutr., 6(1):11–15. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2095.2000.00125.x]
Kotzamanis, Y.P., Gisbert, E., Gatesoupe, F.J., Zambonino Infante, J., Cahu, C., 2007. Effects of different dietary levels of fish protein hydrolysates on growth, digestive enzymes, gut microbiota, and resistance to Vibrio anguillarum in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol., 147(1):205–214. [doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.12.037]
Liang, M., Wang, J., Chang, Q., Mai, K., 2006. Effects of different levels of fish protein hydrolysate in the diet on the nonspecific immunity of Japanese sea bass, Lateolabrax japonicus (Cuvieret Valenciennes, 1928). Aquac. Res., 37(1):102–106. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2005.01392.x]
Liaset, B., Espe, M., 2008. Nutritional composition of soluble and insoluble fractions obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of fish-raw materials. Process Biochem., 43(1):42–48. [doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2007.10.007]
Mai, K., Wan, J., Ai, Q., Xu, W., Liufu, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Li, H., 2006. Dietary methionine requirement of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea R. Aquaculture, 253(1–4):564–572. [doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.08.010]
Murray, A.L., Ponald, J.P., Alcorn, S.W., Fairgrieve, W.T., Shearer, K.D., Roley, D., 2003. Effects of various feed supplements containing fish protein hydrolysate or fish processing by products on the innate immune functions of juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquaculture, 220(1–4):643–653. [doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00426-X]
Oliva-Teles, A., Cerqueira, A.L., Goncalves, P., 1999. The utilization of diets containing high levels of fish protein hydrolysate by turbot (Scophthalamus maximus) juveniles. Aquaculture, 179(1–4):195–201. [doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00162-3]
Ouellet, D.R., Seoane, J.R., Veira, D.M., Proulx, J.G., 1997. Effects of supplementation with fish meal or fish protein hydrolysate on growth, nutrient digestibility and rumen fermentation of growing cattle fed grass silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol., 68(3–4):307–326. [doi:10.1016/S0377-8401(97)00035-7]
Pascual, C., Zenteno, E., Cuzon, G., Sánchez, A., Gaxiola, G., Taboada, G., Suárez, J., Maldonado, T., Rosas, C., 2004. Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles energetic balance and immunological response to dietary protein. Aquaculture, 236(1–4):431–450. [doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.015]
Puangkaew, J., Kiron, V., Somamoto, T., Okamoto, N., Satoh, S., Takeuchi, T., Watanabe, T., 2004. Nonspecific immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) in relation to different status of vitamin E and highly unsaturated fatty acids. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 16(1):25–39. [doi:10.1016/S1050-4648(03)00028-7]
Refstie, S., Olli, J.J., Standal, H., 2004. Feed intake, growth, and protein utilisation by post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in response to graded levels of fish protein hydrolysate in the diet. Aquaculture, 239(1–4):331–349. [doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.06.015]
Ross, D.A., Wilson, M.R., Miller, N.W., Clem, L.W., Warr, G.W., 1998. Evolutionary variation of immunoglobulin μ-heavy chain RNA processing pathways: origins, effects, and implications. Immunol. Rev., 166(1):143–151. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1998.tb01259.x]
Siwicki, A.K., Anderson, D.P., 1993. Nonspecific Defense Mechanisms Assay in Fish. II. Potential Killing Activity of Neutrophils and Macrophages, Lysozyme Activity in Serum and Organs and Total Immunoglobulin Level in Serum. In: Siwicki, A.K., Anderson, D.P., Waluga, J. (Eds.), Fish Disease Diagnosis and Prevention Methods. Olsztyn, Poland, p.105–112.
Song, Z., Wu, T., Cai, L., Zhang, L., Zheng, X., 2006. Effects of dietary supplementation with Clostridium butyricum on the growth performance and humoral immune response in Miichthys miiuy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 7(7):596–602. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.B0596]
Tesser, M.B., Terjesen, B.F., Zhang, Y., Portella, M.C., Dabrowski, K., 2005. Free-and peptide-based dietary arginine supplementation for the South American fish pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). Aquac. Nutr., 11(6):443–453. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2095.2005.00373.x]
Thiansilakul, Y., Benjakul, S., Shahidi, F., 2007. Compositions, functional properties and antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi). Food Chem., 103(4):1385–1394. [doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.055]
Watts, M., Munday, B.L., Burke, C.M., 2001. Isolation and partial characterisation of immunoglobulin from southern bluefin tuna Thunnus maccoyii Castelnau. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 11(6):491–503. [doi:10.1006/fsim.2000.0329]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2006C12098) supported by the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Hg., Wu, Tx., Zhao, Zy. et al. Effects of fish protein hydrolysate on growth performance and humoral immune response in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea R.). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 9, 684–690 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0820088
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0820088