Abstract
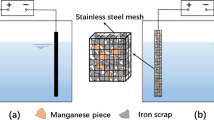
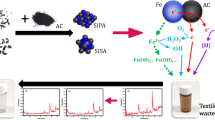
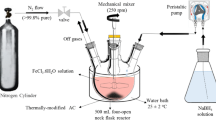
Micro-electrolysis (ME) technology is investigated for improving the efficiency of removal of pentavalent antimony (Sb(V)) from the environment. In this study, an ME system composed of scrap iron filings, waste manganese fillings, and activated carbon (Fe-Mn-C ME) was used to efficiently remove Sb(V). The results proved that, compared with conventional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis (Fe-C ME), Fe-Mn-C ME significantly enhances the removal rate of Sb(V) when the hydraulic retention time is 10–24 h. The Fe-Mn flocs produced by this system were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis, which revealed that the flocs were mostly Mn-substituted FeOOH and had a relatively larger specific surface area, providing better adsorption performance. Furthermore, it was found that the removal rate of Sb(V) decreased as the iron-carbon mass ratio increased, while it first increased and then decreased as the manganese content increased. The reduction of Fe(III) was accelerated with an increase in the addition of manganese, leading to an increase in the concentration of Fe(II). The electron transfer and the formation of Fe(II) were facilitated by the potential difference between manganese and carbon, as well as by the formation of microcells between iron and manganese, which improved the reduction ability of Sb(V). From our thorough investigation and research, this is the first report that has proposed Fe-Mn-C ME for removing antimony. It provides a novel approach and technological support for removing Sb(V) efficiently.
摘要
目的
近年来锑污染日益严重, 因此亟需探索出经济有效的方法除锑。本文旨在提出一种经济环保、操作简单、效果稳定的微电解除锑技术, 并探究其去除效果、影响因素及去除机理。
创新点
1. 提出了基于铁锰碳填料的微电解系统除锑;2. 探究了铁锰碳微电解体系除锑的主要机理(包括氧化还原作用、吸附和共沉淀作用)。
方法
1. 在不同水力停留时间、铁碳质量比和锰含量的情况下, 探究铁锰碳微电解去除性能的变化;2. 对微电解产生的絮体进行X射线衍射、能量色散X射线光谱、比表面积测试、X射线光电子能谱等微观结构分析, 探究铁锰复合双氢氧化物的形成和Sb(V)去除的机理。
结论
1. 当水力停留时间为10~24 h、填料投加量为250 g/L、pH值为6.5、铁碳比为1.6:1、Sb(V)初始浓度为1 mg/L时, 铁锰碳微电解的Sb(V)平均去除率比铁碳微电解高7.60%~9.67%。2. 最佳实验工况下, 铁锰碳微电解法的Sb(V)去除率可达91.85%。3. 机理分析表明, 在铁锰碳微电解反应中, 部分Sb(V)被反应生成的具有良好吸附性能的铁锰复合双氢氧化物絮体吸附去除, 而另一部分被还原为Sb(III), 并在混凝过程中生成Sb(OH)3沉淀, 进而被絮体的吸附和共沉淀反应去除。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao D, Zeng HB, Yang B, et al., 2017. Mn assisted electrochemical generation of two-dimensional Fe-Mn layered double hydroxides for efficient Sb(V) removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 336:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.034
Cao D, Guo T, Zhao X, 2019. Treatment of Sb(V) and CO(II) containing wastewater by electrocoagulation and enhanced Sb(V) removal with CO(II) presence. Separation and Purification Technology, 227:115649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.05.091
Chen F, Li XX, Luo ZB, et al., 2018. Advanced treatment of copper smelting wastewater by the combination of internal micro-electrolysis and electrocoagulation. Separation Science and Technology, 53(16):2639–2646. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1463265
Duan C, Huang X, Gao J, et al., 2022. Iron-carbon (Fe-C) microelectrolysis coupling with anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (A2/O) process: nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance and microbial characteristics. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(2):107235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107235
Fei JC, Min XB, Wang ZX, et al., 2017. Health and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in an antimony mining region: a case study from South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(35):27573–27586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0310-x
Gannon K, Wilson DJ, 1986. Removal of antimony from aqueous systems. Separation Science and Technology, 21(5):475–493. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496398608056130
Gomes JAG, Daida P, Kesmez M, et al., 2007. Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using combined Al–Fe electrode system and characterization of products. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 139(2):220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.108
Guo XJ, Wu ZJ, He MC, 2009. Removal of antimony(V) and antimony(III) from drinking water by coagulation–flocculation–sedimentation (CFS). Water Research, 43(17):4327–4335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.033
Hasan MB, Al-Tameemi IM, Abbas MN, 2021. Orange peels as a sustainable material for treating water polluted with antimony. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 22(2):25–35. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/130632
Holt PK, Barton GW, Mitchell CA, 2005. The future for electrocoagulation as a localised water treatment technology. Chemosphere, 59(3):355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.023
Huang JZ, Zhang HC, 2020. Redox reactions of iron and manganese oxides in complex systems. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 14(5):76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1255-8
Jiang HR, Shyy W, Wu MC, et al., 2019. A bi-porous graphite felt electrode with enhanced surface area and catalytic activity for vanadium redox flow batteries. Applied Energy, 233–234:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.033
Jiang YH, Li M, Yan AP, 2017. Enhanced manganese-carbon microelectrolysis for pretreatment of gasification wastewater from synthetic ammonia industry. Environmental Engineering Science, 34(4):291–298. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2016.0187
Kang M, Kamei T, Magara Y, 2003. Comparing polyaluminum chloride and ferric chloride for antimony removal. Water Research, 37(17):4171–4179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00351-8
Kumarasinghe D, Pettigrew L, Nghiem LD, 2009. Removal of heavy metals from mining impacted water by an electrocoagulation-ultrafiltration hybrid process. Desalination and Water Treatment, 11(1–3):66–72. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.844
Li FB, Lin T, Li Q, et al., 2013. Research on cavitation and impinging stream microelectrolysis reactor for treating organic wastewater. Advanced Materials Research, 652–654:1692–1695. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.652-654.1692
Li JY, Zheng BH, He YZ, et al., 2018. Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 156:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.024
Li T, Li TT, Xiong HF, et al., 2015. Factors influencing hydroquinone degradation in aqueous solution using a modified microelectrolysis method. Water Science and Technology, 71(3):397–404. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.534
Liu H, Lu XC, Li M, et al., 2018. Structural incorporation of manganese into goethite and its enhancement of Pb(II) adsorption. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(8):4719–4727. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05612
Long XJ, Wang X, Guo XJ, et al., 2020. A review of removal technology for antimony in aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 90:189–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.12.008
Luo JH, Song GY, Liu JY, et al., 2014. Mechanism of enhanced nitrate reduction via micro-electrolysis at the powdered zero-valent iron/activated carbon interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 435:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.08.043
Meunier N, Drogui P, Gourvenec C, et al., 2004. Removal of metals in leachate from sewage sludge using electrochemical technology. Environmental Technology, 25(2):235–245. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330409355457
Mitsunobu S, Takahashi Y, Terada Y, et al., 2010. Antimony(V) incorporation into synthetic ferrihydrite, goethite, and natural iron oxyhydroxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(10):3712–3718. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903901e
Muniz FTL, Miranda MAR, Dos Santos CM, et al., 2016. The Scherrer equation and the dynamical theory of X-ray diffraction. Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances, 72(3):385–390. https://doi.org/10.1107/S205327331600365x
Nishad PA, Bhaskarapillai A, Velmurugan S, 2017. Towards finding an efficient sorbent for antimony: comparative investigations on antimony removal properties of potential antimony sorbents. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 14(4):777–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1181-2
Ozdemir N, Soylak M, Elci L, et al., 2004. Speciation analysis of inorganic Sb(III) and Sb(V) ions by using mini column filled with amberlite XAD-8 resin. Analytica Chimica Acta, 505(1):37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00353-2
Prasetyaningrum A, Ariyanti D, Widayat W, et al., 2021. Copper and lead ions removal by electrocoagulation: process performance and implications for energy consumption. International Journal of Renewable Energy Development, 10(3):415–424. https://doi.org/10.14710/ijred.2021.31665
Riveros PA, Dutrizac JE, Lastra R, 2008. A study of the ion exchange removal of antimony(III) and antimony(V) from copper electrolytes. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 47(3):307–316. https://doi.org/10.1179/cmq.2008.47.3.307
Saito T, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, et al., 2004. Removal of antimony(III) using polyol-ligand-containing porous hollow-fiber membranes. Separation Science and Technology, 39(13):3011–3022. https://doi.org/10.1081/SS-200033727
Scheinost AC, Stanjek H, Schulze DG, et al., 2001. Structural environment and oxidation state of Mn in goethite-groutite solid-solutions. American Mineralogist, 86(1–2):139–146. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2001-0115
Song PP, Yang ZH, Xu HY, et al., 2014. Investigation of influencing factors and mechanism of antimony and arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using Fe-Al electrodes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 53(33):12911–12919. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie501727a
Song PP, Yang ZH, Zeng GM, et al., 2015. Optimization, kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics studies of antimony removal in electrocoagulation process. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 226(11):380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2615-z
Souza KR, Silva DR, Mata W, et al., 2012. Electrochemical technology for removing heavy metals present in synthetic produced water. Latin American Applied Research, 42(2):141–147.
Stiers W, Schwertmann U, 1985. Evidence for manganese substitution in synthetic goethite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49(9):1909–1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(85)90085-7
Sun XH, Doner HE, Zavarin M, 1999. Spectroscopy study of arsenite [As(III)] oxidation on Mn-substituted goethite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47(4):474–480. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1999.0470409
Sun ZH, Xu ZH, Zhou YW, et al., 2019. Effects of different scrap iron as anode in Fe-C micro-electrolysis system for textile wastewater degradation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(26):26869–26882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05931-3
Tan FK, Hassan J, Wahab ZA, et al., 2016. Electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of manganese and vanadium mixed oxide prepared by conventional solid state method. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 19(4):2081–2087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.08.002
Ungureanu G, Santos S, Boaventura R, et al., 2015. Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 151:326–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.051
Wang YB, Feng MQ, Liu YH, 2018. Preparation and application of aluminum-carbon microelectrolysis materials. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 144(4):04018016. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001351
Wu FC, Fu ZY, Liu BJ, et al., 2011. Health risk associated with dietary co-exposure to high levels of antimony and arsenic in the world’s largest antimony mine area. Science of the Total Environment, 409(18):3344–3351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.033
Wu WC, Wang SL, Tzou YM, et al., 2007. The adsorption and catalytic transformations of chromium on Mn substituted goethite. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 75(3–4):272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.04.026
Wu XY, Lv CX, Yu SF, et al., 2020. Uranium (VI) removal from aqueous solution using iron-carbon micro-electrolysis packing. Separation and Purification Technology, 234:116104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116104
Xiao Y, Shao Y, Luo M, et al., 2021. Optimized study and column experiments on treatment process of metronidazole pharmaceutical wastewater by microelectrolysis and fenton oxidation. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 232(5):182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05117-z
Yamashita T, Hayes P, 2008. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Applied Surface Science, 254(8):2441–2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.063
Yang KL, Liu YL, Li YZ, et al., 2019. Applications and characteristics of Fe-Mn binary oxides for Sb(V) removal in textile wastewater: selective adsorption and the fixed-bed column study. Chemosphere, 232:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.194
Zhang Q, 2015. Treatment of oilfield produced water using Fe/C micro-electrolysis assisted by zero-valent copper and zero-valent aluminium. Environmental Technology, 36(4):515–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.952678
Zhang X, Wu YQ, 2017. Application of coupled zero-valent iron/biochar system for degradation of chlorobenzene-contaminated groundwater. Water Science and Technology, 75(3):571–580. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.503
Zhang XW, Yue QY, Yue DT, et al., 2015. Application of Fe0/C/clay ceramics for decoloration of synthetic Acid Red 73 and Reactive Blue 4 wastewater by micro-electrolysis. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 9(3):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0659-8
Zhou YC, Zheng WX, Zhang WM, et al., 2022. Effective removal of Sb(V) from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation with composite scrap iron-manganese as an anode. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(38):58088–58096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20033-3
Zhu J, Wu FC, Pan XL, et al., 2011. Removal of antimony from antimony mine flotation wastewater by electrocoagulation with aluminum electrodes. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(7):1066–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60550-5
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2019YFC0408400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51878597).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Shangkun DING: conceptualization; investigation; writing–original draft preparation. Saihua HUANG: supervision; writing–reviewing and editing. Yiping ZHANG: methodology; supervision. Yongchao ZHOU: conceptualization; methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Shangkun DING, Saihua HUANG, Yiping ZHANG, and Yongchao ZHOU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Electronic supplementary materials
Tables S1–S5, Figs. S1 and S2, Section S1
Electronic Supplementary Material
11582_2024_552_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electronic Supplementary Materials: Effective removal of Sb(V) from aqueous solutions by micro-electrolysis with composite scrap iron-manganese as filler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, S., Huang, S., Zhang, Y. et al. Effective removal of Sb(V) from aqueous solutions by micro-electrolysis with composite scrap iron-manganese as filler. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2300287
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2300287