Abstract
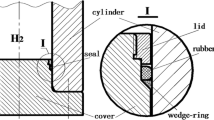
The charge valve is an important element in the charging port of a high-pressure hydrogen storage cylinder (HP-HSC). It is normally closed after the HP-HSC is filled with hydrogen. If the seal of the charge valve is damaged, it will seriously affect the stable operation of the hydrogen supply system and may even cause safety problems. Therefore, the seal performance of the charge valve is important. In this paper, finite element analysis (FEA) is carried out to analyze the seal contact performance of hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) gaskets in the seal pair of a charge valve. The effects of different pre-compressions, seal widths, and hydrogen pressures on the seal contact performance of the charge valve are analyzed. The contact pressure on the seal surface increases with the increase of pre-compression. With a pre-compression of 2.5 mm, the maximum contact pressure without and with hydrogen pressure are 68.51 and 107.38 MPa, respectively. A contact gap appears in the inner ring of the seal surface with pre-compression below 0.15 mm. The contact gap occurs between the entire seal surface with a seal width of 1 mm. The contact pressure on the seal surface and the width of the separation area between the seal surfaces increase with the increase of the seal width. The contact gap between the seal surfaces is zero with a width of 2.5 mm. The width of the separation area between the seal surfaces decreases with the decrease of the hydrogen pressure. The width of the separation area is reduced from 0.5 mm at 35 MPa to 0.17 mm at 15 MPa. This work can be useful for improvement of the seal performance and of the design of the charge valve used in the HP-HSC.
概要
目的:充氢阀阀座良好的软密封性能是保障高压储氢瓶氢气不泄漏的一个关键因素。本文旨在探讨密封预压缩量、密封宽度和氢气压力对软密封元件接触压力和接触间隙的影响规律。 创新点:建立非线性有限元分析模型,在不同预压缩量、密封宽度和氢气压力下对密封接触特性进行动态分析。 方法:1. 建立不同预压缩量的数值模型,比较分析在不同密封预压缩量下接触间隙和接触压力在密封面上的分布(图6);2. 建立不同密封宽度的数值模型,对比分析在不同密封宽度下密封间隙和密封压力的动态变化过程(图9);3. 改变氢气压力值,比较在不同氢气压力下软密封的应力强度和接触特性(图10和11)。 结论:1. 密封面上的接触压力随着预压缩量的增加而增大;当预紧压缩量减小到一定值时会出现接触间隙大于零的区域。2. 随着密封宽度的增加,密封面上的接触压力和密封面之间分离区域的宽度也随之增加。3. 随着氢气压力的降低,密封面之间的分离区域的宽度相应减小。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderezzak B, Busawon K, Binns R, 2017. Flows consumption assessment study for fuel cell vehicles: towards a popularization of FCVs technology. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(17):12905–12911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.152
Bai YF, Zhang CZ, Duan H, et al., 2021. Modeling and optimal control of fast filling process of hydrogen to fuel cell vehicle. Journal of Energy Storage, 35:102306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.102306
Ben Jemaa MC, Mnif R, Fehri K, et al., 2012. Design of a new tribometer for tribological and viscoelasticity studies of PTFE valve seats. Tribology Letters, 45(1):177–184.
Cao C, Zhao JY, Li GL, et al., 2019. Dynamic and static sealing performance of elastic check valve spool. The Journal of Engineering, 2019(13):28–31. https://doi.org/10.1049/joe.2018.8979
Chen FQ, Ren XD, Hu B, et al., 2019. Parametric analysis on multi-stage high pressure reducing valve for hydrogen decompression. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(59):31263–31274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.10.004
Cheng J, Xiao JS, Bénard P, et al., 2017. Estimation of final hydrogen temperatures during refueling 35 MPa and 70 MPa tanks. Energy Procedia, 105:1363–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.505
Dev B, Samudrala O, Wang JF, 2016. Characterization of leak rates in thermoplastic barrier valve seals under high static and cyclic pressure loads. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 145:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2016.05.016
Gorash Y, Dempster W, Nicholls WD, et al., 2016. Study of mechanical aspects of leak tightness in a pressure relief valve using advanced FE-analysis. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 43:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2016.04.009
Hong BK, Kim SH, 2018. (Invited) recent advances in fuel cell electric vehicle technologies of Hyundai. ECS Transactions, 86(13):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1149/08613.0003ecst
Jayanath S, Achuthan A, Mashue A, et al., 2016. A subscale experimental test method to characterize extrusion-based elastomer seals. Journal of Tribology, 138(3):032201. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4032175
Kan BA, Ding JN, 2016. Criterion for non-interference of solid metal seal pair in double-offset butterfly valve. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 38(6):1745–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0544-4
Kovač A, Paranos M, Marciuš D, 2021. Hydrogen in energy transition: a review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(16):10016–10035.
Kwak HS, Seong H, Kim C, 2019. Design of laminated seal in cryogenic triple-offset butterfly valve used in LNG marine engine. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 20(2):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00056-6
Li JQ, Myoung NS, Kwon JT, et al., 2020. A theoretical analysis of temperature rise of hydrogen in high-pressure storage cylinder during fast filling process. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 12(12). https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814020971920
Lin ZH, Ou SQ, Elgowainy A, et al., 2018. A method for determining the optimal delivered hydrogen pressure for fuel cell electric vehicles. Applied Energy, 216:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.041
Lin ZH, Li XJ, Jin ZJ, et al., 2020. Fluid-structure interaction analysis on membrane behavior of a microfluidic passive valve. Membranes, 10(10):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100300
Marckmann G, Verron E, 2006. Comparison of hyperelastic models for rubber-like materials. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 79(5):835–858. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547969
Nie SL, Guo M, Yin FL, et al., 2021. Research on fluid-structure interaction for piston/cylinder tribopair of seawater hydraulic axial piston pump in deep-sea environment. Ocean Engineering, 219:108222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108222
Özbek E, Yalin G, Ekici S, et al., 2020. Evaluation of design methodology, limitations, and iterations of a hydrogen fuelled hybrid fuel cell mini UAV. Energy, 213:118757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118757
Peláez-Peláez S, Colmenar-Santos A, Pérez-Molina C, et al., 2021. Techno-economic analysis of a heat and power combination system based on hybrid photovoltaic-fuel cell systems using hydrogen as an energy vector. Energy, 224:120110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120110
Qian JY, Chen MR, Gao ZX, et al., 2019. Mach number and energy loss analysis inside multi-stage tesla valves for hydrogen decompression. Energy, 179:647–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.05.064
Romanik G, Jaszak P, Rogula J, 2019. Cooperation of the PTFE sealing ring with the steel ball of the valve subjected to durability test. Open Engineering, 9(1):321–328. https://doi.org/10.1515/eng-2019-0028
Shet SP, Priya SS, Sudhakar K, et al., 2021. A review on current trends in potential use of metal-organic framework for hydrogen storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(21):11782–11803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.01.020
Song XG, Wang L, Park YC, 2009. Analysis and optimization of nitrile butadiene rubber sealing mechanism of ball valve. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 19(S1): S220–S224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60274-9
Staffell I, Scamman D, Abad AV, et al., 2019. The role of hydrogen and fuel cells in the global energy system. Energy & Environmental Science, 12(2):463–491. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EE01157E
Wu SJ, Yang CJ, Chen Y, et al., 2010. A study of the sealing performance of a new high-pressure cone valve for deep-sea gas-tight water samplers. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 132(4):041601. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4001204
Zheng CX, Wang L, Li R, et al., 2013. Fatigue test of carbon epoxy composite high pressure hydrogen storage vessel under hydrogen environment. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 14(6):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1200297
Zhou CL, Chen GH, Liu PF, 2018. Finite element analysis of sealing performance of rubber D-ring seal in high-pressure hydrogen storage vessel. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 18(4):846–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-018-0472-y
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52175067), the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2021C01021), China, and the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by China Association for Science and Technology (No. YESS20200154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhen-hao LIN and Jin-yuan QIAN designed the research. Zhen-hao LIN, Long-jie YU, and Ting-feng HUA processed the corresponding data. Zhen-hao LIN wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Long-jie YU and Ting-feng HUA helped to organize the manuscript. Zhi-jiang JIN and Jin-yuan QIAN revised and edited the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
Zhen-hao LIN, Long-jie YU, Ting-feng HUA, Zhi-jiang JIN, and Jin-yuan QIAN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Zh., Yu, Lj., Hua, Tf. et al. Seal contact performance analysis of soft seals on high-pressure hydrogen charge valves. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 23, 247–256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2100395
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2100395
Key words
- Charge valve
- Seal contact performance
- High-pressure hydrogen storage cylinder (HP-HSC)
- Finite element analysis (FEA)