Abstract
Optimizing the operation of coal-fired power plants to reduce nitrogen oxide (NO x ) emissions requires accurate modeling of the NO x emission process. The careful selection of input parameters not only forms the basis of accurate modeling, but can also be used to reduce the complexity of the model. The present study employs the least squares support vector machine-supervised learning method to model NO x emissions based on historical real time data obtained from a 1000-MW once-through boiler. The initial input parameters are determined by expert knowledge and operational experience, while the final input parameters are obtained by sensitivity analysis, where the variation in model accuracy for a given set of data is analyzed as one or several input parameters are successively omitted from the calculations, while retaining all other parameters. Here, model accuracy is evaluated according to the mean relative error (MRE). This process reduces the parameters required for NO x emission modeling from an initial number of 33 to 7, while the corresponding MRE is reduced from 3.09% to 2.23%. Moreover, a correlation of 0.9566 between predicted and measured values was obtained by applying the model with just these seven input parameters to a validation dataset. As such, the proposed method for selecting input parameters serves as a reference for related studies.
概要
目的
采用最小二乘支持向量机建立煤粉锅炉NOx 排放 模型,即建立输入参数与NOx 之间的关系。合理 选择输入参数不仅会降低模型的复杂度,而且会 提高模型的精度。为此,本文探讨各输入参数对 模型的影响,并最终保留合适数量的输入参数建 立NOx 排放模型。
创新点
1. 采用最小二乘支持向量机建立NOx 排放模型; 2. 通过敏感性分析确定模型的最终输入参数。
方法
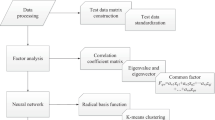
1. 根据专家知识及运行经验确定NOx 排放模型的 初始输入参数(图2);2. 根据锅炉的运行历史数 据,采用最小二乘支持向量机建立NOx排放模型; 3. 采用敏感性分析方法确定NOx排放模型的最终 输入参数(图11),并用其进行建模以验证模型 的有效性。
结论
1. 采用最小二乘支持向量机建立的1000 MW 超 超临界前后墙对冲锅炉NOx 排放模型,可靠性和 精度较高;2. 经过敏感性分析,NOx 排放模型的 输入参数由初始的33 个降为7 个,模型的复杂度 降低且精度提高。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi MA, 2015. Connectionist approach estimates gas–oil relative permeability in petroleum reservoirs: application to reservoir simulation. Fuel, 140:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.09.058
Ahmadi MA, Ebadi M, 2014. Evolving smart approach for determination dew point pressure through condensate gas reservoirs. Fuel, 117:1074–1084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.10.010
Ahmadi MA, Bahadori A, 2015a. A LSSVM approach for determining well placement and conning phenomena in horizontal wells. Fuel, 153:276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.094
Ahmadi MA, Bahadori A, 2015b. Prediction performance of natural gas dehydration units for water removal efficiency using a least square support vector machine. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 37(5):486–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2015.1004105
Ahmadi MA, Ebadi M, Hosseini SY, 2014a. Prediction breakthrough time of water coning in the fractured reservoirs by implementing low parameter support vector machine approach. Fuel, 117:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.071
Ahmadi MA, Ebadi M, Marghmaleki PS, et al., 2014b. Evolving predictive model to determine conden sate-togas ratio in retrograded condensate gas reservoirs. Fuel, 124:241–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.01.073
Ahmadi MA, Ebadi M, Yazdanpanah A, 2014c. Robust intelligent tool for estimation dew point pressure in retrograded condensate gas reservoirs: application of particle swarm optimization. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 123:7–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2014.05.023
Ahmadi MA, Masoumi M, Askarinezhad R, 2014d. Evolving connectionist model to monitor the efficiency of an in situ combustion process: application to heavy oil recovery. Energy Technology, 2(9–10): 811–818. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201402043
Ahmadi MA, Zahedzadeh M, Shadizadeh SR, et al., 2015a. Connectionist model for predicting minimum gas miscibility pressure: application to gas injection process. Fuel, 148:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.044
Ahmadi MA, Masoumi M, Askarinezhad R, 2015b. Evolving smart model to predict the combustion front velocity for in situ combustion. Energy Technology, 3(2):128–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201402104
Ahmadi MA, Hasanvand MZ, Bahadori A, 2015c. A leastsquares support vector machine approach to predict temperature drop accompanying a given pressure drop for the natural gas production and processing systems. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 38(2):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2015.1055515
Ahmadi MA, Lee M, Bahadori M, 2015d. Prediction of a solid desiccant dehydrator performance using least squares support vector machines algorithm. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 50:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.004
Ahmadi MH, Ahmadi MA, Sadatsakkak SA, et al., 2015. Connectionist intelligent model estimates output power and torque of stirling engine. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 50:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.185
Ahmed F, Cho HJ, Kim JK, et al., 2015. A real-time model based on least squares support vector machines and output bias update for the prediction of NOx emission from coal-fired power plant. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 32(6):1029–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0301-2
Cen KF, Yao Q, Luo ZY, et al., 2003. Advanced Combustion. Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou, China (in Chinese).
Choi CR, Kim CN, 2009. Numerical investigation on the flow, combustion and NOx emission characteristics in a 500 MWe tangentially fired pulverized-coal boiler. Fuel, 88(9):1720–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.04.001
Choi GP, Yoo KHY, Back JH, et al., 2017. Estimation of LOCA break size using cascaded fuzzy neural networks. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 49(3):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2016.11.001
Eberhart RC, Shi Y, Kennedy J, 2001. Swarm Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, USA.
Fan WD, Lin ZC, Li YY, et al., 2010. Experimental flow field characteristics of OFA for large-angle counter flow of fuel-rich jet combustion technology. Applied Energy, 87(8):2737–2745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.02.012
Fletcher R, 1987. Practical Methods of Optimization. John Wiley & Son, Chichester and New York.
Gu YP, Zhao WJ, Wu ZS, 2011. Online adaptive least squares support vector machine and its application in utility boiler combustion optimization systems. Journal of Process Control, 21(7):1040–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2011.06.001
Hattori Y, Otsuka M, 2013. Modeling of feed-forward control using the partial least squares regression method in the tablet compression process. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 524(1–2): 407–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.004
Hill SC, Smoot LD, 2000. Modeling of nitrogen oxides formation and destruction in combustion systems. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 26(4–6): 417–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(00)00011-3
IEA (International Energy Agency), 2015. Key World Energy Statistic. IEA.
Ilamathi P, Selladurai V, Balamurugan K, 2013. Modeling and optimization of unburned carbon in coal-fired boiler using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 135(3):032201. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4023328
Junhom C, Weerapreeyakul N, Tanthanuch W, et al., 2017. Partial least squares regression and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) microspectroscopy for prediction of resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Experimental Cell Research, 351(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.12.027
Kennedy J, Eberhart R, 1995. Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95–International Conference on Neural Networks, p.1942-1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Khajehsharifi H, Eskandari Z, Sareban N, 2017. Using partial least squares and principal component regression in simultaneous spectrophotometric analysis of pyrimidine bases. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10(S1): S141–S147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.07.015
Khajehzadeh M, Taha MR, El-shafie A, et al., 2011. Modified particle swarm optimization for optimum design of spread footing and retaining wall. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 12(6):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1000252
Kuang M, Li ZQ, Wang ZH, et al., 2014. Combustion and NOx emission characteristics with respect to staged-air damper opening in a 600 MWe down-fired pulverized coal furnace under deep-air-staging conditions. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(1):837–844. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403165f
Laurain V, Tóth R, Piga D, et al., 2015. An instrumental least squares support vector machine for nonlinear system identification. Automatica, 54:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2015.02.017
Li ZQ, Liu ZC, Chen ZC, et al., 2013. Effect of angle of arch-supplied overfire air on flow, combustion characteristics and NOx emissions of a down-fired utility boiler. Energy, 59:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.06.020
Liu FD, He H, Zhang CB, et al., 2011. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over environmental-friendly iron titanate catalyst. Catalysis Today, 175(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.02.049
Lv Y, Liu JZ, Yang TT, et al., 2013. A novel least squares support vector machine ensemble model for NOx emission prediction of a coal-fired boiler. Energy, 55:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.02.062
Lv Y, Yang TT, Liu JZ, 2015. An adaptive least squares support vector machine model with a novel update for NOx emission prediction. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 145:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.04.006
Malegori C, Malegori EJN, de Freitas ST, et al., 2017. Comparing the analytical performances of micro-NIR and FT-NIR spectrometers in the evaluation of acerola fruit quality, using PLS and SVM regression algorithms. Talanta, 165:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.12.035
Modlinski N, 2015. Numerical simulation of SNCR (selective non-catalytic reduction) process in coal fired grate boiler. Energy, 92:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.03.124
Rezaei H, Nazir R, Momeni E, 2016. Bearing capacity of thin-walled shallow foundations: an experimental and artificial intelligence-based study. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 17(4):273–285. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500033
Samui P, Kim D, Aiyer BG, 2015. Pullout capacity of small ground anchor: a least square support vector machine approach. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 16(4):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1200260
Smrekar J, Potočnik P, Senegačnik A, 2013. Multi-step-ahead prediction of NOx emissions for a coal-based boiler. Applied Energy, 106:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.056
Song JG, Romero CE, Yao Z, et al., 2017. A globally enhanced general regression neural network for on-line multiple emissions prediction of utility boiler. Knowledge-Based Systems, 118:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.11.003
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J, 1999. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Processing Letters, 9(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018628609742
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J, de Moor B, 2001. Optimal control by least squares support vector machine. Neural Networks, 14(1):23–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(00)00077-0
Suykens JAK, Gestel TV, Brabanter JD, et al., 2002. Least squares support vector machines. Euphytica, 2(2):1599–1604.
Tang Y, Ma X, Lai Z, et al., 2012. NOx and SO2 emissions from municipal solid waste (MSW) combustion in CO2/O2 atmosphere. Energy, 40(1):300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.070
Thissen U, Pepers M, Üstün B, et al., 2004. Comparing support vector machines to PLS for spectral regression applications. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 73(2):169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2004.01.002
Wang QC, Zhang JZ, 2011. Wiener model identification and nonlinear model predictive control of a pH neutralization process based on Laguerre filters and least squares support vector machines. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE C (Computers & Electronics), 12(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C0910779
Wang ZH, Zhou JH, Zhang YW, et al., 2005. Experiment and mechanism investigation on advanced reburning for NOx reduction: influence of CO and temperature. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE, 6B(3):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0187
Wei ZB, Li XL, Xu LJ, et al., 2013. Comparative study of computational intelligence approaches for NOx reduction of coal-fired boiler. Energy, 55:683–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.04.007
Wei ZS, Du ZY, Lin ZH, et al., 2007. Removal of NOx by microwave reactor with ammonium bicarbonate and Ga-A zeolites at low temperature. Energy, 32(8):1455–1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2006.11.007
Wu F, Zhou H, Ren T, et al., 2009. Combining support vector regression and cellular genetic algorithm for multiobjective optimization of coal-fired utility boilers. Fuel, 88(10):1864–1870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.04.023
Xiang J, Wang PY, Su S, et al., 2015. Control of NO and Hg0 emissions by SCR catalysts from coal-fired boiler. Fuel Processing Technology, 135:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.12.044
Xu YY, Zhang Y, Liu FN, et al., 2014. CFD analysis on the catalyst layer breakage failure of an SCR-DeNOx system for a 350 MW coal-fired power plant. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 69:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2014.07.012
Yin F, Luo ZH, Li Y, et al., 2017. Coal type identification based on the emission spectra of a furnace flame. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 18(2):113–123. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500306
Zhang JH, Liu Y, 2017. Application of complete ensemble intrinsic time-scale decomposition and least-square SVM optimized using hybrid DE and PSO to fault diagnosis of diesel engines. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology), 18(3):272–286. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600315
Zhang Y, Li H, Wang ZH, et al., 2015. A preliminary study on time series forecast of fair-weather atmospheric electric field with WT-LSSVM method. Journal of Electrostatics, 75:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elstat.2015.03.005
Zhou H, Cen KF, Fan JR, 2004. Modeling and optimization of the NOx emission characteristics of a tangentially fired boiler with artificial neural networks. Energy, 29(1):167–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2003.08.004
Zhou H, Zhao JP, Zheng LG, et al., 2012. Modeling NOx emissions from coal-fired utility boilers using support vector regression with ant colony optimization. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 25(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2011.08.005
Zhou H, Yang Y, Dong K, et al., 2014. Influence of the gas particle flow characteristics of a low-NOx swirl burner on the formation of high temperature corrosion. Fuel, 134: 595–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.06.027
Zhou H, Yang Y, Wang YY, 2015. Numerical investigation of gas-particle flow in the primary air pipe of low NOx swirl burner–the DEM-CFD method. Particuology, 19:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2014.04.017
Zhou H, Li Y, Tang Q, et al., 2017. Combining flame monitoring techniques and support vector machine for the online identification of coal blends. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 18(9):677–689. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1600454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014C33018), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yl., Ma, Zy., You, Hh. et al. Development of a NO x emission model with seven optimized input parameters for a coal-fired boiler. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 19, 315–328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1600787
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1600787
Keywords
- Nitrogen oxide (NO x )
- Coal-fired boiler
- Least squares support vector machine
- Input parameters
- Sensitivity analysis