Abstract
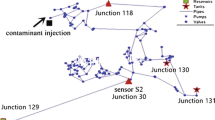
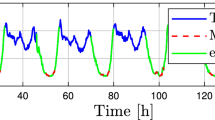
An intrusion of contaminants into the water distribution network (WDN) can occur through storage tanks (via animals, dust-carrying bacteria, and infiltration) and pipes. A sensor network could yield useful observations that help identify the location of the source, the strength, the time of occurrence, and the duration of contamination. This paper proposes a methodology for identifying the contamination sources in a water distribution system, which identifies the key characteristics of contamination, such as location, starting time, and injection rates at different time intervals. Based on simplified hypotheses and associated with a high computational efficiency, the methodology is designed to be a simple and easy-to-use tool for water companies to ensure rapid identification of the contamination sources, The proposed methodology identifies the characteristics of pollution sources by matching the dynamic patterns of the simulated and measured concentrations. The application of this methodology to a literature network and a real WDN are illustrated with the aid of an example. The results showed that if contaminants are transported from the sources to the sensors at intervals, then this method can identify the most possible ones from candidate pollution sources. However, if the contamination data is minimal, a greater number of redundant contamination source nodes will be present. Consequently, more data from different sensors obtained through network monitoring are required to effectively use this method for locating multi-sources of contamination in the WDN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Shalom, Y., Fortmann, T.E., 1988. Tracking and Data Association. Academic Press, San Diego.
Blackman, S.S., Popoli, R., 1999. Design and Analysis of Modern Tracking Systems. Artech House, Norwood, MA.
Deng, Y., Jiang, W., Sadiq, R., 2011. Modeling contaminant intrusion in water distribution networks: A new similarity-based DST method. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(1):571–578. [doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.004]
Di Cristo, C., Leopardi, A., 2008. Pollution source identification of accidental contamination in water distribution networks. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 134(2):197–202. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2008)134:2(197)]
Di Cristo, C., Leopardi, A., 2010. Closure to “DI CRISTO C, LEOPARDI A. 2008). Pollution source identification of accidental contaminations in water distribution networks. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 134 (2)”. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 136(5):292–293. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000048]
Guan, J., Aral, M.M., Maslia, M.L., Grayman, W.M., 2006. Identification of contaminant sources in water distribution systems using simulation—Optimization method: Case study. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 132(4):252–262. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2006)132:4(252)]
Kessler, A., Osfeld, A., Sinai, G., 1998. Detecting accidental contaminations in municipal water networks. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 124(4): 192–198. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1998)124:4(192)]
Kirmeyer, G.J., Friedman, M., Martel, K., Howie, D., 2001. Pathogen Intrusion into Distribution System. Denver, CO: AwwaRF.
Kurien, T., 1990. Issues in the Design of Practical Multi-Target Tracking Algorithms. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Advanced Applications, Bar-Shalom, Y. (Ed.), Artech House, Norwood, MA.
Laird, C.D., Biegler, L.T., van Bloemen Waanders, B.G., Bartlett, R.A., 2005. Contamination source determination for water networks. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 131(2):125–134. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2005)131:2(125)]
Lee, B.H., Deininger, R.A., 1992. Optimal location of monitoring stations in water distribution system. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 118(1):4–16. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1992)118:1(4)]
Lindley, T.R., 2001. A Framework to Protect Water Distribution Systems against Potential Intrusions. MS Thesis, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati.
Liu, L., Ranjithan, R.S., Mahinthakumar, G., 2011. Contamination source identification in water distribution systems using an adaptive dynamic optimization procedure. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 137(2):183–192. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)WR.19435452.0000104]
Preis, A., Ostfeld, A., 2006. Contamination source identification in water systems: A hybrid model trees-linear programming scheme. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 132(4):263–273. [doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2006)132:4(263)]
Preis, A., Ostfeld, A., 2007. A contamination source identification model for water distribution system security. Engineering Optimization, 39(8):941–951. [doi:10.1080/03052150701540670]
Tricarico, C., de Marinis, G., Gargano, R., Leopardi, A., 2007. Peak residential water demand. Proceedings of the ICE-Water Management, 160(2):115–121. [doi:10.1680/wama.2007.160.2.115]
Vermaak, J., Godsill, S.J., Perez, P., 2005. Monte Carlo filtering for multi-target tracking and data association. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 41(1):309–332. [doi:10.1109/TAES.2005.1413764]
Wang, F.X., 2010. The Software and Pre-Warning of Water Quality in Water Distribution Network. MS Thesis, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50908165), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 0400219207), China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, T., Lu, Yj., Fu, X. et al. Identification of sources of pollution and contamination in water distribution networks based on pattern recognition. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 13, 559–570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100286
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100286