Abstract
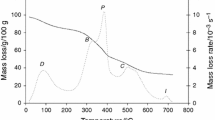
Incineration is considered one of the most readily available techniques for sewage sludge disposal, including tannery sludge, which often contains significant amounts of volatile heavy metals. The combustion characteristics and kinetic analysis of tannery sludge were investigated using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) at a heating rate of 30 °C/min in 50–950 °C. In addition to confirming that tannery sludge has a high content of volatile material and ash, it was further discovered that almost all the zinc (Zn) in tannery sludge is volatilized at 900 °C. The degree of volatilization for heavy metals at 900 °C followed the order of Zn>Cd>Cu>Mn>Pb>Cr. Moreover, the volatilization of these heavy metals increased with temperature. It is thus concluded that, to avoid heavy metal volatization during incineration disposal, 800 °C is a reasonable incineration temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu, M.A., Toffoli, S.M., 2009. Characterization of a chromium-rich tannery waste and its potential use in ceramics. Ceramics International, 35(6):2225–2234. [doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2008.12.011]
Amand, L.E., Leckner, B., 2004. Metal emissions from co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal/wood in fluidized bed. Fuel, 83(13):1803–1821. [doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2004.01.014]
Bakoglu, M., Karademir, A., Ayberk, S., 2003. Partitioning characteristics of targeted heavy metals in IZAYDAS hazardous waste incinerator. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 99(1):89–105. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00009-8]
Corella, J., Toledo, J.M., 2000. Incineration of doped sludges in fluidized bed: Fate and partitioning of six targeted heavy metals. I. Pilot plant used and results. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 80(1–3):81–105. [doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(00)00280-6]
Dai, J.Y., Xu, M.Q., Chen, J.P., Yang, X.P., Ke, Z.S., 2007. PCDD/F, PAH and heavy metals in the sewage sludge from six wastewater treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 66(2):353–361. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.072]
Ferrasse, J.H., Chavez, S., Arlabosse, P., Dupuy, N., 2003. Chemometrics as a tool for the analysis of evolved gas during the thermal treatment of sewage sludge using coupled TG-FTIR. Thermochimica Acta, 404(1–2): 97–108. [doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00064-9]
Hu, R.Z., 2001. Thermal Analysis Kinetics. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Jensen, J., Jepsen, S.E., 2005. The production, use and quality of sewage sludge in Denmark. Waste Management, 25(3):239–247. [doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2004.08.011]
Lopes, M.H., Abelha, P., Lapa, N., Oliveira, J.S., Cabrita, I., Gulyurtlu, I., 2003. The behaviour of ashes and heavy metals during the co-combustion of sewage sludges in a fluidised bed. Waste Management, 23(9):859–870. [doi:10.1016/S0956-053X(03)00025-4]
Lopes, M.H., Gulyurtlu, I., Cabrita, I., 2004. Control of pollutants during FBC combustion of sewage sludge. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 43(18): 5540–5547. [doi:10.1021/ie049765w]
Magalhães, W.L.E., Job, A.E., Ferreira, C.A., da Silva, H.D., 2008. Pyrolysis and combustion of pulp mill lime sludge. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 82(2): 298–303. [doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2008.05.005]
Mahesh, S., Prasad, B., Mall, I.D., Mishra, I.M., 2006. Electrochemical degradation of pulp and paper mill wastewater. Part 2. Characterization and analysis of sludge. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45(16): 5766–5774. [doi:10.1021/ie0603969]
Marani, D., Braguglia, C.M., Mininni, G., Maccioni, F., 2003. Behaviour of Cd, Cr, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn in sewage sludge incineration by fluidised bed furnace. Waste Management, 23(2):117–124. [doi:10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00044-2]
Miller, B.B., Kandiyoti, R., Dugwell, D.R., 2004. Trace element behavior during co-combustion of sewage sludge with polish coal. Energy & Fuels, 18(4):1093–1103.
Ogada, T., Werther, J., 1996. Combustion characteristics of wet sludge in a fluidized bed release and combustion of the volatiles. Fuel, 75(5):617–626. [doi:10.1016/0016-2361(95)00280-4]
Saxena, S.C., Jotshi, C.K., 1996. Management and combustion of hazardous wastes. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 22(5):401–425. [doi:10.1016/S0360-1285(96)00007-X]
Seames, W.S., Fernandez, A., Wendt, J.O.L., 2002. A study of fine particulate emissions from combustion of treated pulverized municipal sewage sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(12):2772–2776. [doi:10.1021/es0113091]
Swarnalatha, S., Ramani, K., Karthi, A.G., Sekaran, G., 2006. Starved air combustion-solidification/stabilization of primary chemical sludge from a tannery. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137(1):304–313. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.006]
Toribio, M., Romanya, J., 2006. Leaching of heavy metals (Cu, Ni and Zn) and organic matter after sewage sludge application to Mediterranean forest soils. Science of the Total Environment, 363(1–3):11–21. [doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv. 2005.10.004]
US EPA3050, 1992. Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods, SW-846 (3rd Ed.), Method 3050. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Wang, K.S., Chiang, K.Y., Lin, S.M., Tsai, C.C., Sun, C.J., 1999. Effects of chlorides on emissions of toxic compounds in waste incineration: study on partitioning characteristics of heavy metal. Chemosphere, 38(8):1833–1849. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00398-1]
Yao, H., Naruse, I., 2005. Combustion characteristics of dried sewage sludge and control of trace-metal emission. Energy & Fuels, 19(6):2298–2303. [doi:10.1021/ef0501039]
Yao, H., Mkilaha, I.S.N., Naruse, I., 2004. Screening of sorbents and capture of lead and cadmium compounds during sewage sludge combustion. Fuel, 83(7–8):1001–1007. [doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2003.10.022]
Yao, H., Luo, G.Q., Xu, M.H., 2006. Mercury emissions and species during combustion of coal and waste. Energy & Fuels, 20(5):1946–1950. [doi:10.1021/ef060100b]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National High-Tech Research and Development (863) Program of China (Nos. 2007AA061302 and 2007AA06Z336), the Key Project of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2007C13084), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. X506312 and R107532), the Project on Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province (No. 2008C23090), China, the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-05-0524), and the Y. C. TANG Disciplinary Development Fund of Zhejiang University, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Xg., Li, Cy., Fei, Zw. et al. Combustion characteristics of tannery sludge and volatilization of heavy metals in combustion. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 11, 530–537 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900414
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0900414
Key words
- Tannery sludge
- Combustion
- Heavy metal volatilization
- Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
- Combustion kinetics