Abstract
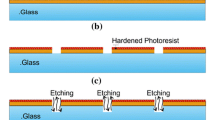
This paper presents a novel micro fabrication method based on the laminar characteristics of micro-scale flows. Therein the separator and etchant are alternatively arranged in micro channels to form multiple laminar streams, and the etchant is located at the site where the reaction is supposed to occur. This new micro fabrication process can be used for the high aspect ratio etching inside a microchannel on glass substrates. Furthermore, the topography of microstructure patterned by this method can be controlled by changing the flow parameters of the separator and etchant. Experiments on the effects of flow parameters on the aspect ratio, side wall profile and etching rate were carried out on a glass substrate. The effect of flow rates on the etching rate and the micro topography was analyzed. In addition, experiments with dynamical changes of the flow rate ratio of the separator and etchant showed that the verticality of the side walls of microstructures can be significantly improved. The restricted flowing etching technique not only abates the isotropic effect in the traditional wet etching but also significantly reduces the dependence on expensive photolithographic equipment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atencia, J., Beebe, D.J., 2005. Controlled microfluidic interfaces. Nature, 437(7059):648–655. [doi:10.1038/nature04163]
Dittrich, P.S., Tachikawa, K., Manz, A., 2006. Micro total analysis systems. Latest advancements and trends. Analytical Chemistry, 78(12):3887–3908. [doi:10.1021/ac0605602]
Fu, X., Liu, S.F., Ruan, X.D., Yang, H.Y., 2006. Research on staggered oriented ridges static micromixers. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 114(2):618–624. [doi:10.1016/j.snb.2005.06.023]
Geissler, M., Xia, Y., 2004. Patterning: Principles and some new developments. Advanced Materials, 16(15):1249–1269. [doi:10.1002/adma.200400835]
Howlader, M.M.R., Suehara, S., Suga, T., 2006. Room temperature wafer level glass/glass bonding. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 127(1):31–36. [doi:10.1016/j.sna.2005.11.003]
Kenis, P.J.A., Ismagilov, R.F., Whitesides, G.M., 1999. Microfabrication inside capillaries using multiphase laminar flow patterning. Science, 285(5424):83–85. [doi:10.1126/science.285.5424.83]
Kenis, P.J.A., Ismagilov, R.F., Takayama, S., Whitesides, G.M., 2000. Fabrication inside microchannels using fluid flow. Accounts of Chemical Research, 33(12):841–847. [doi:10.1021/ar000062u]
Khademhosseini, A., Suh, K.Y., Jon, S., 2004. A soft lithographic approach to fabricate patterned microfluidic channels. Analytical Chemistry, 76(13):3675–3681. [doi:10.1021/ac035415s]
Kim, K., Par, S., Lee, J.B., Manohara, H., Desta, Y., Murphy, M., Ahn, C.H., 2002. Rapid replication of polymeric and metallic high aspect ratio microstructures using PDMS and LIGA technology. Microsystem Technologies, 9(1–2):5–10. [doi:10.1007/s00542-002-0194-6]
Lee, G.B., Kuo, T.Y., Wu, W.Y., 2002. A novel micromachined flow sensor using periodic flapping motion of a planar jet impinging on a V-shaped plate. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 26(5):435–444. [doi:10.1016/S0894-1777(02)00155-3]
Lee, G.B., Chang, C.C., Huang, S.B., Yang, R.J., 2006. The hydrodynamic focusing effect inside rectangular microchannels. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 16(5):1024–1032. [doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/020]
Malek, C.K., Saile, V., 2004. Applications of LIGA technology to precision manufacturing of high-aspect-ratio microcomponents and systems. Microelectronics Journal, 35(2):131–143. [doi:10.1016/j.mejo.2003.10.003]
Manz, A., Harrison, D.J., Verpoorte, E.M.J., 1992. An international journal devoted to research and development of chemical transducers. Journal of Chromatography A, 593(1–2):253–258. [doi:10.1016/0021-9673(92)80293-4]
Paul, K.E., Breen, T.L., Hadzik, T., Whitesidesa, G.M., 2005. Imaging patterns of intensity in topographically directed photolithography. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 23(3):918–925. [doi:10.1116/1.1924415]
Stroock, A.D., Whitesides, G.M., 2003. Controlling flows in microchannels with patterned surface charge and topography. Accounts of Chemical Research, 36(8):597–604. [doi:10.1021/ar0202870]
Urbanski, J.P., Thies, W., Rhodes, C., Amarasinghe, S., 2006. Digital microfluidics using soft lithography. Lab on a Chip, 6(1):96–104. [doi:10.1039/b510127a]
Verpoorte, E., Rooij, N.F.D., 2003. Microfluidics meets MEMS. Proceedings of the IEEE, 91(6):930–953. [doi:10.1109/JPROC.2003.813570]
Weibel, D.B., Whitesides, G.M., 2006. Applications of microfluidics in chemical biology. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 10(6):584–591. [doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.10.016]
Whitesides, G.M., 2006. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature, 442(7101):368–373. [doi:10.1038/nature05058]
Wouden, E.J.V., Heuser, T., Hermes, D.C., Oosterbroek, R.E., Gardeniers, J.G.E., Berg, A.V., 2005. Field-effect control of electro-osmotic flow in microfluidic networks. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 267(1–3):110–116. [doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.06.048]
Yoon, S.K., Mitchell, M., Chobanb, E.R., Kenis, P.J.A., 2005. Gravity-induced reorientation of the interface between two liquids of different densities flowing laminarly through a microchannel. Lab on a Chip, 5(11):1259–1263. [doi:10.1039/b508680a]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 50705081) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Hb., Zheng, Y., Fan, Yr. et al. A novel restricted-flow etching method for glass. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 10, 1601–1608 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820818
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820818