Abstract
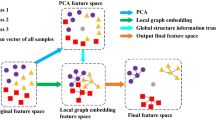
Effective and robust recognition and tracking of objects are the key problems in visual surveillance systems. Most existing object recognition methods were designed with particular objects in mind. This study presents a general moving objects recognition method using global features of targets. Targets are extracted with an adaptive Gaussian mixture model and their silhouette images are captured and unified. A new objects silhouette database is built to provide abundant samples to train the subspace feature. This database is more convincing than the previous ones. A more effective dimension reduction method based on graph embedding is used to obtain the projection eigenvector. In our experiments, we show the effective performance of our method in addressing the moving objects recognition problem and its superiority compared with the previous methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins, R.T., Lipton, A.J., Kanade, T., Fujiyoshi, H., Duggins, D., Tsin, Y., Tolliver, D., Enomoto, N., Hasegawa, O., Burt, P., et al., 2000. A system for video surveillance and monitoring. Tech. Rep., CMU-RI-TR-00-12, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA.
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., Meer, P., 2000. Real-time Tracking of Non-rigid Objects Using Meanshift. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.142–149.
Cutler, R., Davis, L.S., 2000. Robust real-time periodic motion detection, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 22(8):781–796. [doi:10.1109/34.868681]
Duque, D., Santos, H., Cortez, P., 2007. Prediction of Abnormal Behaviors for Intelligent Video Surveillance Systems. Proc. IEEE Symp. on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining, p.362–367. [doi:10.1109/CIDM.2007.368897]
El Baf, F., Bouwmans, T., Vachon, B., 2007. Comparison of Background Subtraction Methods for a Multimedia Application. 6th EURASIP Conf. on Speech and Image Processing, Multimedia Communications and Services, p.385–388. [doi:10.1109/IWSSIP.2007.4381122]
Ghobadi, S.E., Hartmann, K., 2006. Detection and Classification of Moving Objects-Stereo or Time-of-flight Images. Int. Conf. on Computational Intelligence and Security, p.11–16. [doi:10.1109/ICCIAS.2006.294082]
Haritaoglu, I., Harwood, D., Davis, L.S., 2000. W4: Real-time surveillance of people and their activities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 22(8):809–830. [doi:10.1109/34.868683]
Hu, W.M., Tan, T.N., 2004. A survey on visual surveillance of object motion and behaviors. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.-Part C: Appl. Rev., 34(3):334–352. [doi:10. 1109/TSMCC.2004.829274]
Javed, O., Ali, S., 2005. Online Detection and Classification of Moving Objects Using Progressively Improving Detectors. Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.696–701.
Lipton, A.J., Fujiyoshi, H., Patil, R.S., 1998. Moving Target Classification and Tracking from Real-time Video. 4th IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, p.8–14. [doi:10.1109/ACV.1998.732851]
Liu, X.D., Su, G.D., 2000. A New Network-based Intelligent Surveillance System. 5th Int. Conf. on Signal Processing Proc., p.1187–1192.
Martinez, A.M., Kak, A.C., 2001. PCA versus LDA. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 23(2):228–233. [doi:10.1109/34.908974]
Munder, S., Gavrila, D.M., 2006. An experimental study on pedestrian classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 28(11):1–6. [doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2006.217]
Rivlin, E., Rudzsky, M., 2002. A Real-time System for Classification of Moving Objects. 16th Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition, p.688–691.
Stauffer, C., 1999. Automatic Hierarchical Classification Using Time-base Co-occurrences. Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.335–339.
Stauffer, C., Grimson, W.E.L, 1999. Adaptive Background Mixture Models for Real-time Tracking. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p.246–252.
Wang, L., Tan, T.N., 2003. Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 25(12):1505–1518. [doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1251144]
Yan, S.C., Xu, D., Zhang, B.Y., 2007. Graph embedding and extensions: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 29(1): 40–51. [doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2007.250598]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 60805001) partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, J. & Liu, K. General moving objects recognition method based on graph embedding dimension reduction algorithm. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 10, 976–984 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820489
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820489
Key words
- Moving objects recognition
- Adaptive Gaussian mixture model
- Principal component analysis
- Linear discriminant analysis
- Marginal Fisher analysis