Abstract
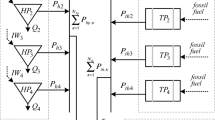
This study presents a robust design method for autonomous photovoltaic (PV)-wind hybrid power systems to obtain an optimum system configuration insensitive to design variable variations. This issue has been formulated as a constraint multi-objective optimization problem, which is solved by a multi-objective genetic algorithm, NSGA-II. Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) method, combined with Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), is applied to evaluate the stochastic system performance. The potential of the proposed method has been demonstrated by a conceptual system design. A comparative study between the proposed robust method and the deterministic method presented in literature has been conducted. The results indicate that the proposed method can find a large mount of Pareto optimal system configurations with better compromising performance than the deterministic method. The trade-off information may be derived by a systematical comparison of these configurations. The proposed robust design method should be useful for hybrid power systems that require both optimality and robustness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis, A.N., Wilson, J.R., 1996. Integrated variance reduction strategies for simulation. Operations Research, 44(2):327–346.
Bernal-Agustín, J.L., Dufo-López, R., Rivas-Ascaso, D.M., 2006. Design of isolated hybrid systems minimizing costs and pollutant emissions. Renewable Energy, 31(14):2227–2244. [doi:10.1016/j.renene.2005.11.002]
Celik, A.N., 2003. Techno-economic analysis of autonomous PV-wind hybrid energy systems using different sizing methods. Energy Conversion and Management, 44(12):1951–1968. [doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00223-6]
Deb, K., 2000. An efficient constraint handling method for genetic algorithms. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 186(2–4):311–338. [doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(99)00389-8]
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., Meyariva, T., 2002. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(2):182–197. [doi:10.1109/4235.996017]
Kellogg, W., Nehrir, M.H., Venkataramannan, G., Gerez, V., 1996. Optimal unit sizing for a hybrid wind/photovoltaic generating system. Electric Power Systems Research, 39(1):35–38. [doi:10.1016/S0378-7796(96)01096-6]
Kicinger, R., Arciszewski, T., de Jong, K., 2005. Evolutionary computation and structural design: A survey of the state-of-the-art. Computers and Structures, 83(23–24):1943–1978. [doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2005.03.002]
Lagaros, N.D., Plevris, V., Papadrakakis, M., 2005. Multi-objective design optimization using cascade evolutionary computations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 194(30–33):3496–3515. [doi:10.1016/j.cma.2004.12.029]
Notton, G., Muselli, M., Poggi, P., 1998. Costing of a stand-alone photovoltaic system. Energy, 23(4):289–308. [doi:10.1016/S0360-5442(97)00092-3]
Notton, G., Muselli, M., Poggi, P., Louche, A., 2001. Decentralized wind energy systems providing small electrical loads in remote areas. International Journal of Energy Research, 25(2):141–164. [doi:10.1002/er.670]
Protogeropoulos, C., Brinkworth, B.J., Marshall, R.H., 1997. Sizing and techno-economical optimization for hybrid solar photovoltaic/wind power systems with battery storage. International Journal of Energy Research, 21(6):465–479. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-114X(199705)21:6«465::AID-ER273»3.0.CO;2-L]
Shi, J.H., Zhu, X.J., Cao, G.Y., 2007. Design and techno-economical optimization for stand-alone hybrid power systems with multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. International Journal of Energy Research, 31(3):315–328. [doi:10.1002/er.1247]
Wichert, B., 1997. PV-diesel hybrid energy systems for remote area power generation—A review of current practice and future developments. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 1(3):209–228. [doi:10.1016/S1364-0321(97)00006-3]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Jh., Zhong, Zd., Zhu, Xj. et al. Robust design and optimization for autonomous PV-wind hybrid power systems. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 401–409 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071317
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071317
Key words
- PV-wind power system
- Robust design
- Constraint multi-objective optimizations
- Multi-objective genetic algorithms
- Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS)
- Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS)