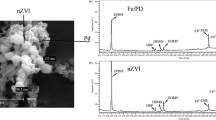
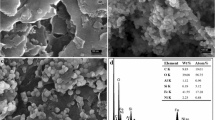
Abstract
The remediation of groundwater which contains chlorinated organic compounds (COCs) by nanoscale bimetallic catalysts has received increasing interest in recent years. This report presents the dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) by Pd-Fe bimetallic nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid (HA) to investigate the feasibility of using Pd-Fe for the in situ remediation of contaminated groundwater. Our experimental results indicated that HA had an adverse effect on the dechlorination of 2,4-DCP by Pd-Fe nanoparticles. The rate constant k values of 2,4-DCP dechlorination were 0.017, 0.013, 0.009, 0.006 and 0.004 min−1 for HA concentrations of 0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 mg/L, respectively. The relationship between HA dosage and k values can be described as a linear model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen-King, R.M., Halket, R.M., Burris, D.R., 1997. Reductive transformation and sorption of cis-and trans-1,2-dichloroethene in a metallic iron-water system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 16(3):424–429. [doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1997)016〈0424:RTASOC〉2.3.CO;2]
Burris, D.R., Campbell, T.J., Manoranjan, V.S., 1995. Sorption of trichloroethylene and etrachloroethylene in a batch reactive metallic iron-water system. Environ. Sci. Technol., 29(11):2850–2855. [doi:10.1021/es00011a022]
Cheng, S.F., Wu, S.C., 2001. Feasibility of using metals to remediate water containing TCE. Chemosphere, 43(8):1023–1028. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00263-0]
Coq, B., Figueras, F., 2001. Bimetallic palladium catalysts: influence of the co-metal on the catalyst performance. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem., 173(1–2):117–134. [doi:10.1016/S1381-1169(01)00148-0]
Gurtis, G.P., Reinhard, M., 1994. Reductive dehalogenation of hexachloroethane, carbon tetrachloride, and bromoform by anthrahydroquinone disulfate and humic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol., 28(13):2393–2401. [doi:10.1021/es00062a026]
Doong, R.A., Lai, Y.L., 2005. Dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene by palladized iron in the presence of humic acid. Water Res., 39(11):2309–2318. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.036]
Doong, R.A., Lai, Y.L., 2006. Effect of metal ions and humic acid on the dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene by zerovalent iron. Chemosphere, 64(3):371–378. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.038]
He, F., Zhao, D., 2005. Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39(9):3314–3320. [doi:10.1021/es048743y]
Johnson, T.L., Fish, W., Gorby, Y.A., Tratnyek, P.G., 1998. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride by iron metal: complexation effects on the oxide surface. J. Contam. Hydrol., 29(4):379–398. [doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(97)00063-6]
Lien, H.L., Zhang, W.X., 2001. Nanoscale iron particles for complete reduction of chlorinated ethenes. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 191:97–105.
Muftikian, R., Nebesny, K., Fernando, Q., Korte, N., 1996. X-ray photoelectron spectra of the palladium-iron bimetallic surface used for the rapid dechlorination of chlorinated organic environmental contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol., 30(12):3593–3596. [doi:10.1021/es960289d]
Murphy, E.M., Zachara, J.M., Smith, S.C., 1990. Influence of mineral-bound humic substances on the sorption of hydrophobic organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol., 24(10):1507–1516. [doi:10.1021/es00080a009]
Oliver, B.G., Nicol, K.D., 1982. Chlorobenzenes in sediments, water, and selected fish from Lakes Superior, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. Environ. Sci. Technol., 16(8):532–536. [doi:10.1021/es00102a019]
Schrick, B., Blough, J.L., Jones, A.D., Mallouk, T.E., 2002. Hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene to hydrocarbons using bimetallic nickel-iron nanoscales. Chem. Mater., 14(12):5140–5147. [doi:10.1021/cm020737i]
Schwarzenbach, R.P., Molnar-Kubica, E., Giger, W., Wakeham, S.G., 1979. Distribution, residence time, and fluxes of tetrachloroethylene and 1,4-dichlorobenzene in Lake Zurich, Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol., 13(11): 1367–1373. [doi:10.1021/es60159a013]
Tratnyek, P.G., Schere, M.M., Hu, S., 2001. Effects of natural organic matter anthropogenic surfactants, and model quinones on the reduction of contaminants by zerovalent iron. Water Res., 35(18):4435–4443. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00165-8]
Wang, C.Y., Chen, Z.Y., Cheng, B., Zhu, Y.R., Liu, H.J., 1999. The preparation, surface modification, and characterization of metallic α-Fe nanoparticles. Chin. J. Chem. Physics, 12:670–674.
Wei, J.J., Liu, Y., Wang, D.H., 2006. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over nanoscale Pd/Fe: reaction pathway and some experimental parameters. Water Res., 40(2):348–354. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.017]
Wu, L.F., Stephen, M.C., 2006. Removal of trichloroethylene from water by cellulose acetate supported bimetallic Ni/Fe nanoscales. Chemosphere, 63(2):285–292. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.021]
Xie, L., Shang, C., 2005. Role of humic acid and quinone model compounds in bromate reduction by zerovalent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39(4):1092–1100. [doi:10.1021/es049027z]
Xu, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., He, P., Wang, D.H., 2005a. Catalytic dechlorination kinetics of p-dichlorobenzene over Pd/Fe catalysts. Chemosphere, 58(8):1135–1140. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.010]
Xu, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Wang, D.H., 2005b. Structure relationship for catalytic dechlorination rate of dichlorobenzenes in water. Chemosphere, 58(11):1497–1502. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.071]
Zhang, W.X., Wang, C.B., Lien, H.L., 1998. Treatment of chlorinated organic contaminants with nanoscale bimetallic particles. Catal. Today, 40(4):387–395. [doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00067-4]
Zhu, B.W., Lim, T.T., Feng, J., 2006. Reductive dechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene with palladized nanoscale Fe0 particles supported on chitosan and silica. Chemosphere, 65(7):1137–1146. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.012]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20407015) and the Program for the New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-06-0525), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wo, Jj., Cissoko, N. et al. Kinetics of 2,4-dichlorophenol dechlorination by Pd-Fe bimetallic nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 118–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071313
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071313