Abstract
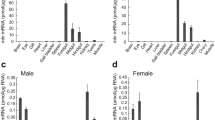
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is one of the most important orexigenic agents in central regulation of feeding behavior, body weight and energy homeostasis in domestic chickens. To examine differences in the hypothalamic NPY between layer-type and meat-type of chickens, which are two divergent kinds of the domestic chickens in feeding behavior and body weight, we detected mRNA levels of NPY in hypothalamic infundibular nucleus (IN), paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) of these two types of chickens using one-step real time RT-PCR. The meat-type chicken had more food daily (about 1.7 folds) and greater body weights (about 1.5 folds) and brain weights than the layer-type chicken at the age of 14 d. In the meat-type of chicken, NPY mRNA levels of the IN and PVN were significantly greater than those of the LHA, and were not significantly different between the IN and PVN. However, in the layer-type of chicken, NPY mRNA levels were significantly greater in the IN than those in the LHA and PVN, and were not significantly different between the PVN and LHA. In all these hypothalamic regions, the layer-type of chicken had significantly higher NPY mRNA levels than the meat-type chicken did. These results suggest the expression of NPY in the hypothalamus has a type-dependent pattern in domestic chickens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aste, N., Viglietti-Panzica, C., Fasolo, A., Andreone, C., Vaudry, H., Pelletier, G., Panzica, G.C., 1991. Localization of neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive cells and fibers in the brain of the Japanese quail. Cell and Tissue Research, 265(2):219–230. [doi:10.1007/BF00398070]
Boswell, T., 2005. Regulation of energy balance in birds by the neuroendocrine hypothalamus. The Journal of Poultry Science, 42(3):161–181. [doi:10.2141/jpsa.42.161]
Boswell, T., Millam, J.R., Li, Q., Dun, I., 1998. Cellular localization of neuropeptide Y mRNA and peptide in the brain of the Japanese quail and domestic chicken. Cell and Tissue Research, 293(1):31–38. [doi:10.1007/s004410051095]
Boswell, T., Dunn, I.C., Corr, S.A., 1999. Hypothalamic neuropeptide Y mRNA is increased after food restriction in growing broilers. Poultry Science, 78(8):1203–1207.
Boswell, T., Li, Q., Takeuchi, S., 2002. Neurons expressing neuropeptide Y mRNA in the infundibular hypothalamus of Japanese quail are activated by fasting and co-express agouti-related protein mRNA. Molecular Brain Research, 100(1–2):31–42. [doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00145-6]
Burnside, J., Cogburn, L.A., 1992. Developmental expression of hepatic growth hormone receptor and insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA in the chicken. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 89(1–2):91–96. [doi:10.1016/0303-7207(92)90214-Q]
Cassy, S., Picard, M., Crochet, S., Derouet, M., Keisler, D.H., Taouis, M., 2004. Peripheral leptin effect on food intake in young chickens is influenced by age and strain. Domestic Animal Endocrinology, 27(1):51–61. [doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2004.01.004]
Denbow, D.M., 1999. Food intake regulation in birds. Journal of Experimental Zoology, 283(4–5):333–338. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990301/01)283:4/5〈333::AID-JEZ3〉3.0.CO;2-R]
Esposito, V., Pelagalli, G.V., DeGirolamo, P., Gargiulo, G., 2001. Anatomical distribution of NPY-like immunoreactivity in the domestic chick brain (Gallus domesticus). Anatomical Record, 263(2):186–201. [doi:10.1002/ar.1089]
Furuse, M., 2002. Central regulation of food intake in the neonatal chick. Animal Science Journal, 73(2):83–94. [doi:10.1046/j.1344-3941.2002.00014.x]
Furuse, M., 2007. Behavioral regulators in the brain of neonatal chicks. Animal Science Journal, 78(3):218–232. [doi:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2007.00429.x]
Furuse, M., Matsumoto, M., Mori, R., Sugahara, K., Kano, K., Hasegawa, S., 1997. Influence of fasting and neuropeptide Y on the suppressive food intake induced by intracerebroventricular injection of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the neonatal chick. Brain Research, 764(1–2):289–292. [doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(97)00623-9]
Hensley, I.E., Lawler, J.E., Alemzadeh, R., Holshouser, S.J., 2001. Diazoxide effects on hypothalamic and extra-hypothalamic NPY content in Zucker rats. Peptides, 22(6):899–908. [doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00415-6]
Jang, M., Romsos, D.R., 1998. Neuropeptide Y and corticotropin-releasing hormone concentrations within specific hypothalamic regions of lean but not ob/ob mice respond to food-deprivation and refeeding. Journal of Nutrition, 128(12):2520–2525.
Kameda, Y., Miura, M., Nishimaki, T., 2001. Localization of neuropeptide Y mRNA and peptide in the chicken hypothalamus and their alterations after food deprivation, dehydration and castration. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 436(3):376–388. [doi:10.1002/cne.1074.abs]
Kuenzel, W.J., Masson, M., 1988. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Brain of the Chick (Gallus domesticus). The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, p.1–10.
Kuenzel, W.J., Fraley, G.S., 1995. Neuropeptide Y: its role in the neural regulation of reproductive function and food intake in avian and mammalian species. Avian and Poultry Biology Reviews, 6(3):185–209.
Kuenzel, W.J., Douglass, L.W., Davison, B.A., 1987. Robust feeding following central administration of neuropeptide Y or peptide YY in chicks, Gallus domesticus. Peptides, 8(5):823–828. [doi:10.1016/0196-9781(87)90066-0]
Kuenzel, W.J., Mary, M.B., Teruyama, R., 1999. Neural sites and pathways regulating food intake in birds: a comparative analysis to mammalian systems. Journal of Experimental Zoology, 283(4–5):348–364. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990301/01)283:4/5〈348::AID-JEZ5〉3.0.CO;2-5]
Masic, B., Wood-Gush, D.G.M., Duncan, I.J.H., McCorquodale, C., Savory, C.J., 1974. A comparison of feeding behavior of young broiler and layer males. British Poultry Science, 15:281–286.
Oomura, Y., Ooyama, H., Yamamoto, T., Naka, F., 1967. Reciprocal relationship of the lateral and ventromedial hypothalamus in the regulation of food intake. Physiology and Behavior, 2(2):97–115. [doi:10.1016/0031-9384(67)90020-0]
Saito, E.S., Kaiya, H., Tachibana, T., Tomonaga, S., Denbow, D.M., Kangawa, K., Furuse, M., 2005. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regulatory Peptides, 125(1–3):201–208. [doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2004.09.003]
Savory, C.J., 1974. A comparison of the feeding behaviour of young broiler and layer males. British Poultry Science, 15(15):499–505.
Schwartz, M.W., Woods, S.C., Porte, D.Jr, Seeley, R.J., Baskin, D.G., 2000. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature, 404(6778):661–671.
Stanley, B.G., Leibowitz, S.F., 1984. Neuropeptide Y: stimulation of feeding and drinking by injection into the paraventricular nucleus. Life Science, 35(26):2635–2642. [doi:10.1016/0024-3205(84)90032-8]
Tachibana, T., Saito, S., Tomonaga, S., Takagi, T., Saito, E.S., Nakanishi, T., Koutoku, T., Tsukada, A., Ohkubo, T., Boswell, T., Furuse, M., 2004. Effect of central administration of prolactin-releasing peptide on feeding in chicks. Physiology and Behavior, 80(5):713–719. [doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2003.12.005]
Tatemoto, K., Carlquist, M., Mutt, V., 1982. Neuropeptide Y—a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic. Nature, 296(5858):659–660. [doi:10.1038/296659a0]
Wang, X., Day, J.R., Zhou, Y., Beard, J.L., Vasilatos-Younken, R., 2000. Evidence of a role for neuropeptide Y and monoamines in mediating the appetite-suppressive effect of GH. Journal of Endocrinology, 166(3):621–630. [doi:10.1677/joe.0.1660621]
Wang, X., Day, J.R., Vasilatos-Younken, R., 2001. The distribution of neuropeptide Y gene expression in the chicken Brain. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 174(1–2):129–136. [doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(00)00436-6]
Zhou, W., Murakami, M., Hasegawa, S., Yoshizawa, F., Sugahara, K., 2005. Neuropeptide Y content in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus responds to fasting and refeeding in broiler chickens. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology—Part A Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 141(2):146–152. [doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2005.04.015]
Zhou, W., Aoyama, M., Yoshizawa, F., Sugahara, K., 2006. Developmental increases in hypothalamic neuropeptide Y content with the embryonic age of meat-and layer-type chicks. Brain Research, 1072(1):26–29. [doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.029]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. Y306220), and the Scientific Research Startup Fund of Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Gq., Hu, Xf., Sugahara, K. et al. Type-dependent differential expression of neuropeptide Y in chicken hypothalamus (Gallus domesticus). J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 8, 839–844 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0839
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0839