Abstract
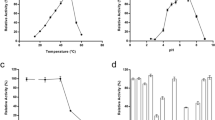
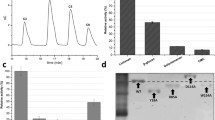
Mulberry longicorn beetle, Apriona germari, has been reported to produce two endo-β-1,4-glucanases or AgEGases (accession Nos. Q6SS52 and Q5XQD1). AgEGase sequence contains catalytic motif (amino acid residues 37–48), which is the characteristic of family Glycohydrolase 45 and is identified as the substrate binding site. The application of bioinformatics approaches includes sequence analysis, structural modeling and inhibitor docking to relate the structure and function of AgEGases. We have dissected the sequence and structure of AgEGase catalytic motif and compared it with crystal structure of Humicola insolens endoglucanases V. The results show an involvement of sulfur containing amino acid residues in the active site of the enzyme. Cys residues and position of disulfide bonds are highly conserved between the two structures of endoglucanases of A. germari. Surface calculation of AgEGase structure in the absence of Cys residues reveals greater accessibility of the catalytic site to the substrate involving Asp42, a highly conserved residue. For the inhibition study, tannin-based structure was docked into the catalytic site of AgEGase using ArgusLab 4.0 and it resulted in a stable complex formation. It is suggested that the inhibition could occur through formation of a stable transition state analog-enzyme complex with the tannin-based inhibitor, as observed with other insect cellulases in our laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beguin, P., Aubert, J.P., 1994. The biological degradation of cellulose. Microbiol. Rev., 13(1):25–58.
Bell, T.A., Eichells, J.I., Smarr, W.G.Jr, 1965. Pectinase and cellulase enzyme inhibition from sericea and certain other plants. Botanical Gazette, 126(1):40–45. [doi:10.1086/336293]
Betts, W.B., Dart, R.K., Ball, A.S., Pedler, S.R., 1992. Biosynthesis and Structure of Lignocellulose. In: Betts, W.B. (Ed.), Biodegradation of Natural and Synthetic Materials. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Bhat, K.M., 2000. Cellulases and related enzymes in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv., 18(5):355–383. [doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(00)00041-0]
Coughlan, M.P., Ljungdhal, L.C., 1988. Comparative Biochemistry of Fungal and Bacterial Cellulolytic Enzyme Systems. In: Aubert, J.P., Beguin, P., Millet, J. (Eds.), Biochemistry and Genetics of Cellulose Degardation. Academic Press, London. p.11–30.
Davies, G.J., Dodson, G.G., Hubbard, R.E., Tolley, S.P., Dauter, Z., Wilson, K.S., Hjort, C., Mikkelsen, J.M., Rasmussen, G., Schuelein, M., 1993. Structure and function of endoglucanase V. Nature, 365(6444):362–364. [doi:10.1038/365362a0]
Henrissat, B., 1991. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J., 280:309–316.
Henrissat, B., Bairoch, A., 1993. New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J., 293:781–788.
Lee, S.J., Kim, S.R., Yoon, H.J., Kim, I., Lee, K.S., Je, Y.H., Lee, S.M., Seo, S.J., Dae Sohn, H., Jin, B.R., 2004. cDNA cloning, expression, and enzymatic activity of a cellulase from the mulberry longicorn beetle, Apriona germari. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol., 139(1): 107–116. [doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.06.015]
Lee, S.J., Kim, S.R., Yoon, H.J., Kim, I., Lee, K.S., Je, Y.H., Lee, S.M., Seo, S.J., Dae Sohn, H., Jin, B.R., 2005. A novel cellulase gene from the mulberry longicorn beetle, Apriona germari: gene structure, expression, and enzymatic activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol., 140(4):551–560. [doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.12.003]
Li, Y., Guo, R., Yini, Q., Dingi, M., Zhang, S., Xui, G., Zahoi, F., 2005. Purification and characterization of two endo glucanases from Mollusca Ampullaria crossean. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 37(10):702–708. [doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00099.x]
Marsden, W.L., Gray, P.P., 1986. Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in lignocellulosic materials. CRC Crit. Rev. Biotech., 3:235–276.
Sami, A.J., Shakoori, A.R., 2006. Heterogeneity in cellulases of some of the local agricultural insects pest. Pak. J. Zool., 38(4):337–340.
Sami, A.J., Akhter, M.W., Malik, N.N., Naz, B.A., 1988. Production of free and substrate bound cellulases of Cellulomonas flavigena. Enzyme Microbial Technol., 10(10):626–631. [doi:10.1016/0141-0229(88)90110-X]
Sami, A.J., Rehman, F.U., Alam, M., Haider, R., 2005. A Repoprt on Multiplicity of Cellulases in Pests and Its Comparison with Multiple Forms of Bacterial Cellulases. In: Biocatalysis: Enzymes Mechanism and Bioprocess. Biochemical Society Focussed Meeting Manchester, 21–22 Nov, Poster No. 14.
Sami, A.J., Haider, K.M., Rehman, F.U., 2006. Determination of Structure-Function Relationship in Apriona germari Endoglucanases Using Bioinformatics Approaches. Biochem. Soc. Meeting Biosci., 23–27 July Glasgow Abstract No. 558.
Schindler, M., Assaf, Y., Sharon, N., Chipmann, D.M., 1977. Mechanism of lysozyme catalysis: role of ground-state strain in sub-site D in hen egg white and human lysozyme. Biochemistry, 16(3):423–431. [doi:10.1021/bi00622a013]
Strynadka, N.C.J., James, M.N.G., 1991. Lysozyme revisted: crystallographic evidence for distortion on an N-acetyl muramic acid residue bound in site D. J. Mol. Biol., 220(2):401. [doi:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90021-W]
Thompson, M., 2004. ArgusLab 4.0 Poster Presentation: Molecular Docking Using ArgusLab: An Efficient Shape-Based Search Algorithm and the Ascore Scoring Function. Fall 2004 ACS Meeting, Philadelphia.
Watanabe, H., Tokuda, G., 2001. Animal cellulases. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 58(9):1167–1178. [doi:10.1007/PL00000931]f
Watanabe, H., Sugimura, M., 2003. Evidence of the presence of bilaterian animals. Proc. Biol. Sci., 270(3):69–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sami, A.J., Haider, M.K. Identification of novel catalytic features of endo-β-1,4-glucanase produced by mulberry longicorn beetle Apriona germari . J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 8, 765–770 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0765
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0765