Abstract
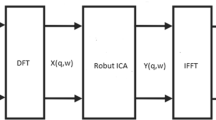
Former frequency-domain blind devolution algorithms need to consider a large number of frequency bins and recover the sources in different orders and with different amplitudes in each frequency bin, so they suffer from permutation and amplitude indeterminacy troubles. Based on sliding discrete Fourier transform, the presented deconvolution algorithm can directly recover time-domain sources from frequency-domain convolutive model using single frequency bin. It only needs to execute blind separation of instantaneous mixture once there are no permutation and amplitude indeterminacy troubles. Compared with former algorithms, the algorithm greatly reduces the computation cost as only one frequency bin is considered. Its good and robust performance is demonstrated by simulations when the signal-to-noise-ratio is high.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardoso, J.F., Souloumiac, A., 1993. Blind beamforming for non-Gaussian signals. IEE Proc-F, 140:362–370.
Depena, A., Serviere, C., Castedo, L., 2003. Inversion of the sliding Fourier transform using only two frequency bins and its application to source separation. Signal Processing, 83(2):453–457. [doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(02)00424-3].
Jacobsen, E., Lyons, R., 2003. The sliding DFT. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 20(2):74–80. [doi: 10.1109/MSP.2003.1184347].
Kurtia, S., Saruwatari, H., 2000. Evaluation of Blind Separation Method Using Directivity Patter under Reverberant Conditions. ICASSP 2000. Istanbul, Turkey, p.3140–3143.
Mitianoudis, N., Davies, M.E., 2003. Audio source separation convolutive mixtures. IEEE Trans. on Speech and Audio Processing, 11(5):489–497. [doi: 10.1109/TSA.2003.815820]
Parra, L., Spence, C., 2000. Convolutive blind source separation of non-stationary sources. IEEE Trans. on Speech and Audio Processing, 8(3):320–327. [doi: 10.1109/89.841214]
Peled, R., Braun, S., Zacksenhouse, M., 2005. A blind deconvolution separation of multiple sources, with application to bearing diagnostics. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing, 19(6):1181–1195. [doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.08.019]
Smaragdis, P., 1998. Blind separation of convolved mixtures in the frequency domain. Neurocomputing, 22:21–34. [doi: 10.1016/S0925-2312(98)00047-2]
Sun, X., Scott, C.D., 2001. A Natural Gradient Convolutive Blind Source Separation Algorithm for Speech Mixtures. ICA 2001. San Diego, California, USA, p.59–63.
Throckmorton, C.S., Tantum, S.L., Tan, Y.Y., Collins, L.M., 2007. Independent component analysis for UX0 detection in highly cluttered environments. J. Appl. Geophys., 61:304–317. [doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2006.05.007]
Unger, H., Zeevi, Y.Y., 2006. Blind separation of spatio-temporal synfire sources and visualization of neural cliques. Neurocomputing, 69:1475–1484. [doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.024]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 2005EB040486) supported by the National Torch Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Gb., Li, Jw. & Li, Cx. A novel blind deconvolution algorithm using single frequency bin. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 8, 1271–1276 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.A1271
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.A1271