Abstract
Objective
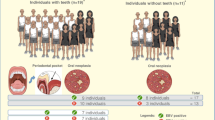
To detect the infection frequencies of different genotypes of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in subgingival samples from chronic periodontitis (CP) patients, and to discuss the correlation between infection with EBV and clinical parameters.
Methods
Nested-PCR assay was used to detect EBV-1 and EBV-2 in subgingival samples from 65 CP patients, 65 gingivitis patients and 24 periodontally healthy individuals. The amplicons were further identified by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (RFLP) with endonucleases Afa I and Stu I. Clinical parameters mainly included bleeding on probing (BOP), probing depth (PD), attachment loss (AL) in six sites of the dentition.
Results
In CP patients, gingivitis and periodontally healthy individuals, the infection frequencies were 47.7%, 24.6% and 16.7% for EBV-1, and 15.4%, 7.7% and 0% for EBV-2, respectively. In 2 out of the 65 CP patients co-infection of EBV-1 and EBV-2 was found. The positive rate of EBV-1 in chronic periodontitis patients was higher than that in gingivitis patients (P=0.01) and periodontally healthy individuals (P=0.01). But no significant difference was shown in EBV-1 frequency between gingivitis patients and healthy individuals (P>0.05) or in EBV-2 frequency among the three groups (P>0.05). In CP patients, higher mean BOP value was found in EBV-1 or EBV-2 positive patients than that in EBV negative ones (P<0.01), but with no statistical difference in the mean PD or AL value between EBV positive and negative patients (P>0.05). After initial periodontal treatment, 12 out of the 21 EBV-1 positive CP patients did not show detectable EBV-1 in subgingival samples.
Conclusion
nPCR plus RFLP analysis is a sensitive, specific and stable method to detect EBV-1 and EBV-2 in subgingival samples. Subgingival infection with EBV-1 is closely associated with chronic periodontitis. Infection of EBV in subgingival samples was correlated with BOP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, R., Morrison, L.A., Knipe, D.M., 1996. Persistence of Viruse. In: Fields, B.N., Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M. (Eds.), Field’s Virology, 3rd Ed. Lippinocott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, USA, p.219–250.
Armitage, G.C., 1999. Development of a classification system for periodontal disease and conditions. Ann. Periodontol., 4(1):1–6. [doi:10.1902/annals.1999.4.1.1]
Buck, M., Cross, S., Krauer, K., Kienzle, N., Sculley, T.B., 1999. A-type and B-type Epstein-Barr virus differ in their ability to spontaneously enter the lytic cycle. J. Gen. Virol., 80(Pt 2):441–445.
Cohen, J.I., 2000. Epstein-Barr virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med., 343(7):481–492. [doi:10.1056/NEJM200008173430707]
Contreras, A., Slots, J., 1996. Mammalian viruses in human periodontitis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 11(6):381–386.
Contreras, A., Slots, J., 2000. Herpesviruses in human periodontal disease. J. Periodontal. Res., 35(1):3–16. [doi:10.1034/j.1600-0765.2000.035001003.x]
Contreras, A., Zadeh, H.H., Nowzari, H., Slots, J., 1999a. Herpesvirus infection of inflammatory cells in human periodontitis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 14(4):206–212. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-302X.1999.140402.x]
Contreras, A., Umeda, M., Chen, C., Bakker, I., Morrison, J.L., Slots, J., 1999b. Relationship between herpesviruses and adult periodontitis and periodontopathic bacteria. J. Peridontol., 70(5):478–484. [doi:10.1902/jop.1999.70.5.478]
Contreras, A., Nowzari, H., Slots, J., 2000. Herpesviruses in periodontal pocket and gingival tissue specimens. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 15(1):15–18. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-302x.2000.150103.x]
Contreras, A., Mardirossian, A., Slots, J., 2001. Herpesviruses in HIV-periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol., 28(1):96–102. [doi:10.1034/j.1600-051x.2001.280115.x]
Idesawa, M., Sugano, N., Ikeda, K., Oshikawa, M., Takane, M., Seki, K., Ito, K., 2004. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in saliva by real-time PCR. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 19(4):230–232. [doi:10.1111/j.1399-302X.2004.00144.x]
Kamma, J.J., Slots, J., 2003. Herpesviral-bacterial interactions in aggressive periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol., 30(5): 420–426. [doi:10.1034/j.1600-051X.2003.20002.x]
Khanna, R., Burrows, S.R., Moss, D.J., 1995. Immune regulation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases. Microbiol. Rev., 59(3):387–405.
Konstantinidis, A., Sakellari, D., Papa, A., Antoniadis, A., 2005. Real-time polymerase chain reaction quantification of Epstein-Barr virus in chronic periodontitis patients. J. Periodontal Res., 40(4):294–298. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00796.x]
Kubar, A., Saygun, I., Ozdemir, A., Yapar, M., Slots, J., 2005. Real-time polymerase chain reaction quantification of human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in periodontal pockets and the adjacent gingiva of periodontitis lesions. J. Periodontal. Res., 40(2):97–104. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00770.x]
Li, Y., Zhang, J.C., Zhang, Y.H., 2004. The association between infection of Epstein-Barr virus and chronic periodontitis. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 39(2):146–148 (in Chinese).
Moss, D.J., Burrows, S.R., Silin, S.L., Misko, I., Khanna, R., 2001. The immunology of Epstein-Barr virus infection. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci., 356(1408):475–488.
Parra, B., Slots, J., 1996. Detection of human viruses in periodontal pockets using polymerase chain reaction. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 11(5):289–293.
Saygun, I., Yapar, M., Ozdemir, A., Kubar, A., Slots, J., 2004a. Human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus type 1 in periodontal abscesses. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 19(2):83–87. [doi:10.1046/j.0902-0055.2002.00118.x]
Saygun, I., Kubar, A., Ozdemir, A., Yapar, M., Slots, J., 2004b. Herpesviral-bacterial interrelationships in aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontal. Res., 39(4):207–212. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2004.00728.x]
Slots, J., 2002. Interactions between Herpesviruses and Bacteria in Human Periodontal Disease. In: Brogden, K.A., Guthmiller, J.M. (Eds.), Polymicrobial Diseases. ASM Press, Washington DC, USA, p.317–331.
Slots, J., 2004. Herpesviruses, the missing link between gingivitis and periodontitis? J. Int. Acad. Periodontol., 6(4):113–119.
Slots, J., Contreras, A., 2000. Herpesviruses: a unifying causative factor in periodontitis? Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 15(5):277–280. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-302x.2000.150501.x]
Slots, J., Sugar, C., Kamma, J.J., 2002. Cytomegalovirus periodontal presence is associated with subgingival Dialister pneumosintes and alveolar bone loss. Oral Microbiol. Immunol., 17(6):369–374. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-302X.2002.170606.x]
Slots, J., Kamma, J.J., Sugar, C., 2003. The herpesvirus-Porphyromonas gingivalis-periodontitis axis. J. Periodont. Res., 38(3):318–323.
Socransky, S.S., Haffajee, A.D., 2002. Dental biofilms: difficult therapeutic targets. Periodontol. 2000, 28(1):12–15. [doi:10.1034/j.1600-0757.2002.280102.x]
Sugano, N., Ikeda, K., Oshikawa, M., Idesawa, M., Tanaka, H., Sato, S., Ito, K., 2004. Relationship between Porphyromonas gingivalis, Epstein-Barr virus infection and reactivation in periodontitis. J. Oral Sci., 46(4):203–206. [doi:10.2334/josnusd.46.203]
Zappa, U., Reinking-Zappa, M., Graf, H., Espeland, M., 1991. Cell populations and episodic periodontal attachment loss in humans. J. Clin. Periodontol., 18(7):508–515. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.1991.tb00082.x]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors equally contributed to this work
Project (No. N021107286) was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Ym., Yan, J., Chen, Ll. et al. Infection frequency of Epstein-Barr virus in subgingival samples from patients with different periodontal status and its correlation with clinical parameters. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 7, 876–883 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0876
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0876