Abstract
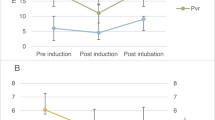
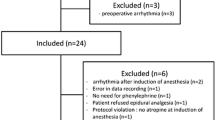
Objective: To investigate the dynamics of vascular volume and the plasma dilution of lactated Ringer’s solution in patients during the induction of general and epidural anesthesia. Methods: The hemodilution of i.v. infusion of 1000 ml of lactated Ringer’s solution over 60 min was studied in patients undergoing general (n=31) and epidural (n=22) anesthesia. Heart rate, arterial blood pressure and hemoglobin (Hb) concentration were measured every 5 min during the study. Surgery was not started until the study period had been completed. Results: General anesthesia caused the greater decrease of mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) (mean 15% versus 9%; P<0.01) and thereby followed by a more pronounced plasma dilution, blood volume expansion (VE) and blood volume expansion efficiency (VEE). A strong linear correlation between hemodilution and the reduction in MAP (r=−0.50; P<0.01) was found. At the end of infusion, patients undergoing general anesthesia retained 47% (SD 19%) of the infused fluid in the circulation, while epidural anesthesia retained 29% (SD 13%) (P<0.001). Correspondingly, a fewer urine output (mean 89 ml versus 156 ml; P<0.05) and extravascular expansion (454 ml versus 551 ml; P<0.05) were found during general anesthesia. Conclusion: We concluded that the induction of general anesthesia caused more hemodilution, volume expansion and volume expansion efficiency than epidural anesthesia, which was triggered only by the lower MAP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arndt, J.O., Höck, A.S., Stanton-Hicks, M., Stühmeier, K.D., 1985. Peridural anesthesia and the distribution of blood in supine humans. Anesthesiology, 63:616–623.
Brauer, K.I., Prough, D.S., Traber, L.D., 1999. Antecedent hemorrhage increases plasma volume expansion (PVE) in response to 0.9% saline infusion in sheep. Anesth. Analg., 88:S135. [doi:10.1097/00000539-199902001-00135]
Brown, D.L., 2000. Spinal, Epidural, and Gaudal Anesthesia. In: Miller, R.D. (Ed.), Anesthesia, 5th Ed. Churchill Livingstone, New York, p.1491–1515.
Drobin, D., Hahn, R.G., 1996. Time course of increased hemodilution in hypotension induced by extradural anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth., 77:223–226.
Ewaldsson, C.A., Hahn, R.G., 2005. Kinetics and extravascular retention of acetated Ringer’s solution during isoflurane and propofol anesthesia for thyroid surgery. Anesthesiology, 103(3):460–469. [doi:10.1097/00000542-200509000-00006]
Hahn, R.G., 1992. Haemoglobin dilution from epidural-induced hypotention with and without fluid loading. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 36:241–244.
Hahn, R.G., 1993a. Blood volume at the onset of hypotension in TURP performed during epidural anaesthesia. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol., 10:219–225.
Hahn, R.G., 1993b. Increased haemodilution in hypotension induced by epidural anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 37:357–360.
Kaye, A.D., Grogono, A.W., 2000. Fluid and Electrolyte Physiology. In: Miller, R.D. (Ed.), Anesthesia, 5th Ed. Churchill Livingstone, New York, p.1586–1603.
Kempen, P.M., Tick, C., 1990. Hemodilution, regional block and Cesarean section. Regional Anesthesia, 15(1S):9.
Lanne, T., Lundvall, J., 1989. Very rapid net transcapillary fluid absorption from skeletal muscle and skin in man during pronounced hypovolaemia circulatory stress. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica, 136:1–6.
Li, Y.H., Zhu, S.M., Hahn, R.G., 2006. The kinetics of Ringer’s solution in young and elderly patients during induction of general and epidural anesthesia. Anesth. Analg., in press.
Mark, J.B., Steele, S.M., 1989. Cardiovascular effects of spinal anesthesia. International Anesthesiology Clinics, 27:31–53.
Olsson, J., Svensén, C.H., Hahn, R.G., 2004. The volume kinetics of acetated Ringer’s solution during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth. Analg., 99(6):1854–1860. [doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000134809.07605.3C]
Retzlaff, J.A., Tauxe, W.N., Kiely, J.M., 1969. Erythrocyte volume, plasma volume, and lean body mass in adult men and women. Blood, 33:649–667.
Svensén, C., Hahn, R.G., 1997. Volume kinetics of ringer solution, Dextran 70, and hypertonic saline in male volunteers. Anesthesiology, 87:204–212. [doi:10.1097/00000542-199708000-00006]
Tølløfsrud, S., Tonnessen, T., Skraastad, O., 1998. Hypertonic saline and dextran in normovolaemic and hypovolaemic healthy volunteers increases interstitial and intravascular fluid volumes. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 42:145–153.
Tølløfsrud, S., Elgjo, G.I., Prough, D.S., 2001. The dynamics of vascular volume and fluid shifts of lactated Ringer’s solution and hypertonic-saline-dextran solutions infused in normovolemic sheep. Anesth. Analg., 93:823–831. [doi:10.1097/00000539-200110000-00005]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 20051899) supported by Office of Education of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yh., Lou, Xf. & Bao, Fp. Dynamics of vascular volume and hemodilution of lactated Ringer’s solution in patients during induction of general and epidural anesthesia. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 7, 738–744 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0738